Best Practices to Write Title and Meta Description Tags for SEO
The title tag and meta description are basic but core elements of SEO. And because Google tends to use meta tag content to generate snippets, they can have a direct impact on a searcher’s decision to click through to your website.
But if you think that search engines will display whatever you write in your page’s metadata word for word in the SERPs, you’ve got another thing coming. Search engines can pull any text from your web pages because they might think it’s more relevant and display that text in the snippet instead. However, there are certain rules that will help you make the most of your tags when it comes to promoting your website.
Similar to a business card, title tags and meta descriptions store data on the content of your pages, and when the time’s right, share that information with both search engines and people. And if you want to please both of them, you simply can’t ignore title and description tags. Let’s take a look at why metadata is important in SEO and how to use it correctly.
-
The title tag is the primary title displayed on SERPs and browser tabs. It should accurately summarize the page’s content and include your target keyword.
-
The meta description provides a concise summary of the page’s content, appearing below the title tag in SERPs. It doesn’t directly impact rankings but can significantly influence click-through rates (CTRs).
-
For the best possible results, keep titles under 55-60 characters, place the main keyword at the beginning, avoid keyword stuffing, and include your brand name. Plus, ensure the main title is easily identifiable on the webpage and maintain consistency in language between title tags and page text.
-
When writing meta descriptions, keep them under 155 characters, write concisely in 1-3 sentences, use an active voice, add a call to action, include keywords but avoid keyword stuffing, and add product information.
-
To check title and description tags on your website, you can use dedicated tools like SE Ranking’s Website Audit and On-Page SEO Checker.
-
To add title and meta description tags on your site, you can directly edit the section of your HTML files or use a plugin like Yoast SEO for WordPress.
-
While Google generally uses the HTML title and meta description, it may rewrite them if they don’t accurately represent the page’s content or if the HTML tags are poorly written.
What are title tags and meta descriptions?
SEO title and meta description are HTML header tags designed to provide a quick overview of a page’s content for search engines and users.
What is a title tag?
The title tag is an HTML element that summarizes the main idea of a web page and is displayed in the SERPs as well as in browser tabs. It is also often referred to as the meta title or SEO title. Title tag usually serves as a concise summary of the page’s content and helps both users and search engines understand what the page is about.
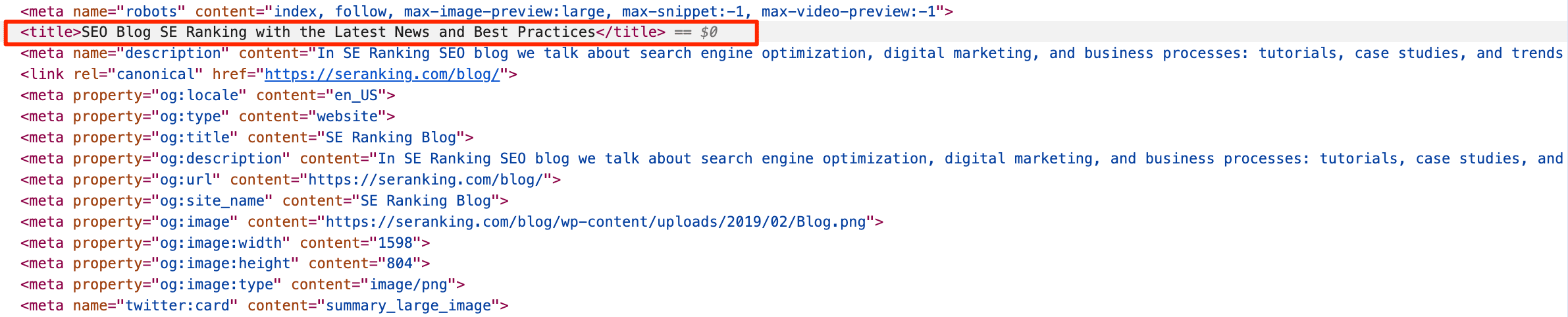
It is wrapped into the <title> tags and always goes inside the <head> element of a page’s HTML code.
Here is how it looks in the code:
<title>Your SEO title</title>
What is a meta description tag?
A meta description is an HTML tag that provides a summary of a web page’s content, appearing below the title tag in SERPs. While it does not directly impact search engine rankings, a well-written meta description can significantly influence click-through rates (CTR) by offering a compelling preview of what users can expect from the page.
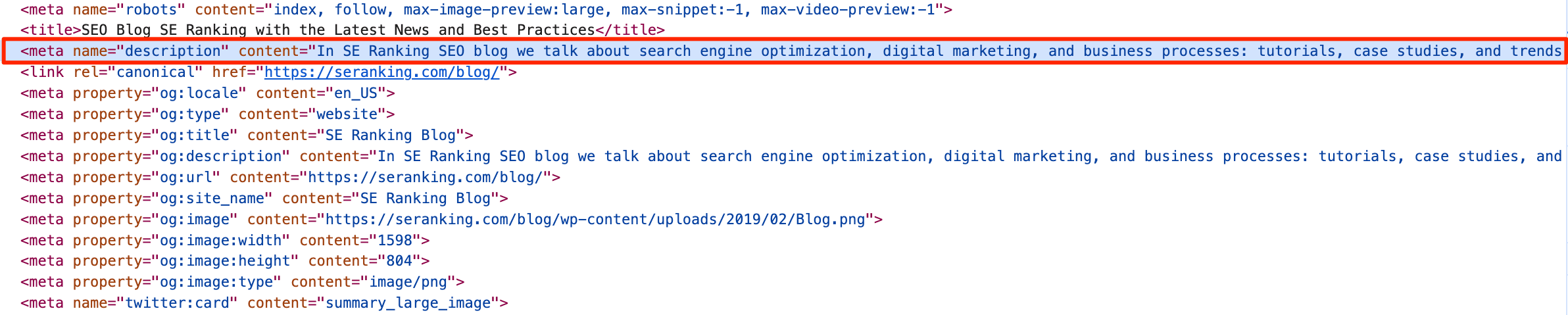
It always goes inside the <head> element of a page’s HTML code and starts with <meta name=”description” tag.
Here is what your meta tag description looks like in the HTML code:
<meta name=”description” content=”Your description.”/>
Why the title tag doesn’t fall under the “meta” category while the description tag does?
While the title tag is not technically a “meta” tag, it is commonly referred to as a “meta title” within SEO community to emphasize its metadata-related function. This term helps clarify that it pertains to the metadata about the page, even though it is not an actual <meta> tag.
In other words, the term “meta title” helps avoid confusion by clearly differentiating the title tag from other page elements (e.g., <h1> title), despite it not being a <meta> tag itself.
On the other hand, the meta description is an explicit meta tag, included in the HTML with the <meta> keyword. It provides a brief summary of the page’s content, typically used as the snippet in SERPs.
Why title and description tags are important for SEO
Both titles and meta descriptions are highly important from the SEO perspective.
Let’s go through each attribute in more detail.
The impact of title tags on SEO
The title tag lets search engine robots know what your page is about and helps them understand how relevant it is to the user’s search query. So, a title tag is an important on-page SEO element and you should optimize it for your focus keyword. It can help you improve your rankings for the keyword you use in your title (and for the keyword cluster around this search term as well).
If you don’t yet track your website rankings regularly, make sure to set up automatic position tracking with the help of the Keyword Rank Checker.
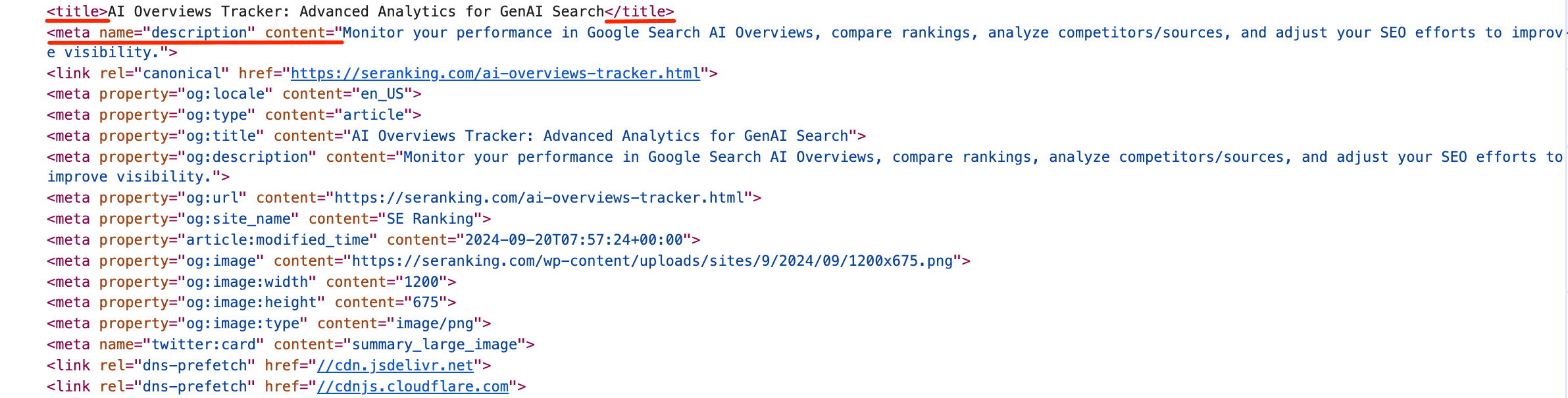
Moreover, as Google states, “one of the primary ways people determine which search results might be relevant to their query is by reviewing the titles of listed web pages.” So searchers can see the HTML title tag right in the SERP as the title of the snippet.
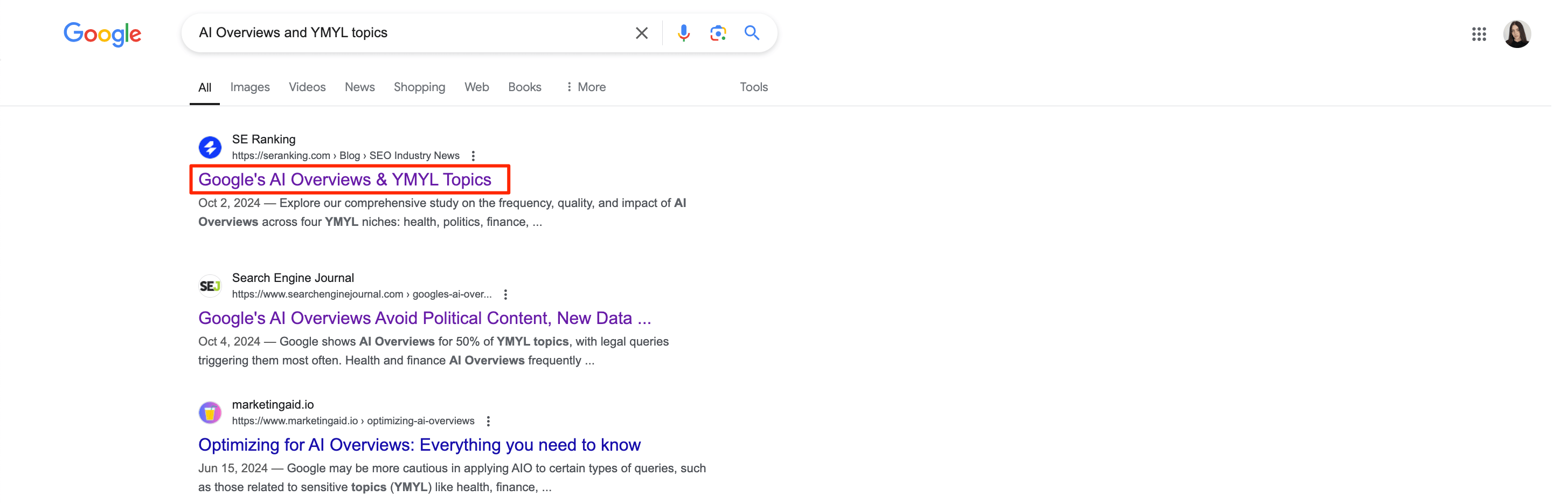
Another place where you can find the title is the text you see in your browser tabs. Even if you have multiple tabs open, you’ll still be able to see the beginning of the title tag. You can see the full title by hovering over a tab.
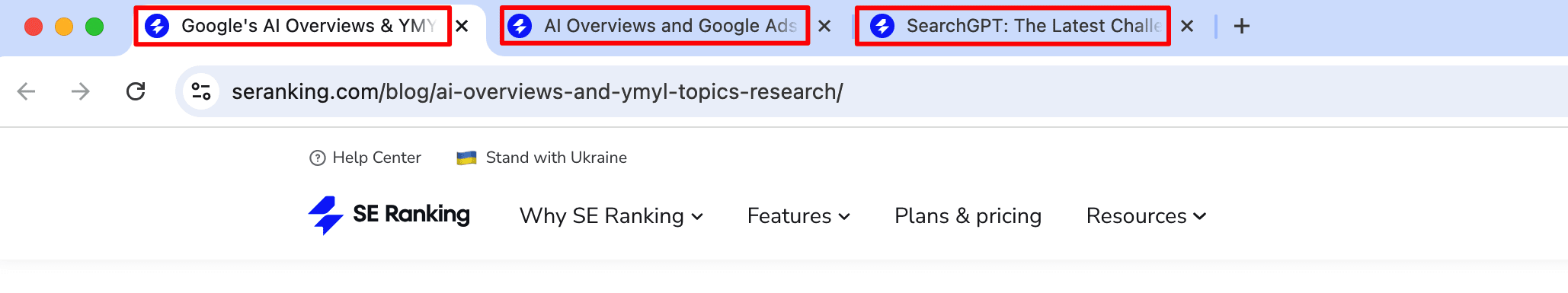
The third and final place where the title tag can be found is on social media when you publish a post and link out to the original web page. The title you indicate in the article will be pulled into the social media post by default. But if you want to display another title on social media, you can change it via the Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress.
As you can see, the title tag appears as the title of a web page in search engines and on social media, and as searchers, we tend to look at it before clicking through in order to understand whether or not the page answers our search query and intent.
Meanwhile, the title tag is an important indicator for search engines that tells them what your page is about and what its relevance is.
For this reason, it’s crucial that you know how to write title tags for SEO, as in know how to optimize your page for search engines, and drive the maximum amount of organic traffic to it.
The impact of meta descriptions on SEO
More than a decade ago, Google said that they can use the meta description tag to generate a description of a page that will be featured in the snippet, but they certainly don’t use it to rank pages. Not much has changed since then.
But since the description can increase the click-through rate of the SERP snippet, it does have an indirect effect on page rankings.
The descriptive text you find in snippets right under the title is the meta description tag:
Google tends to take the text for the snippet description from the HTML meta description tag itself, but if the latter turns out to be uninformative, just as the case is with the title tag, the search engine can also use content from your page to generate a snippet.
To prevent Google from pulling text from your page to generate a description, use the data-nosnippet HTML attribute. You can also limit the length of the snippet using the max-snippet:[number] tag. You can learn more about these tags from Google’s official guide.
How to check title and meta description tags on your website
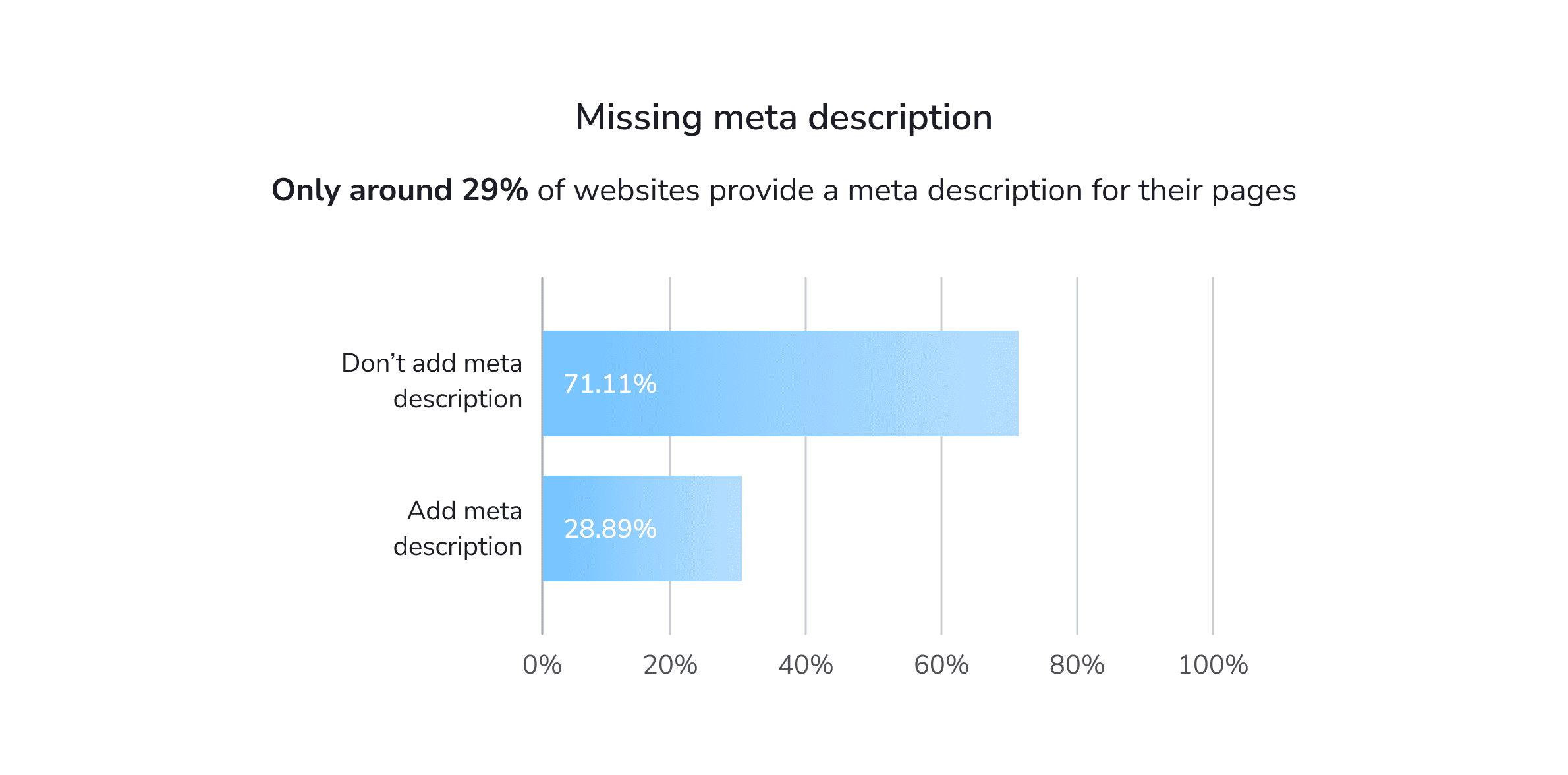
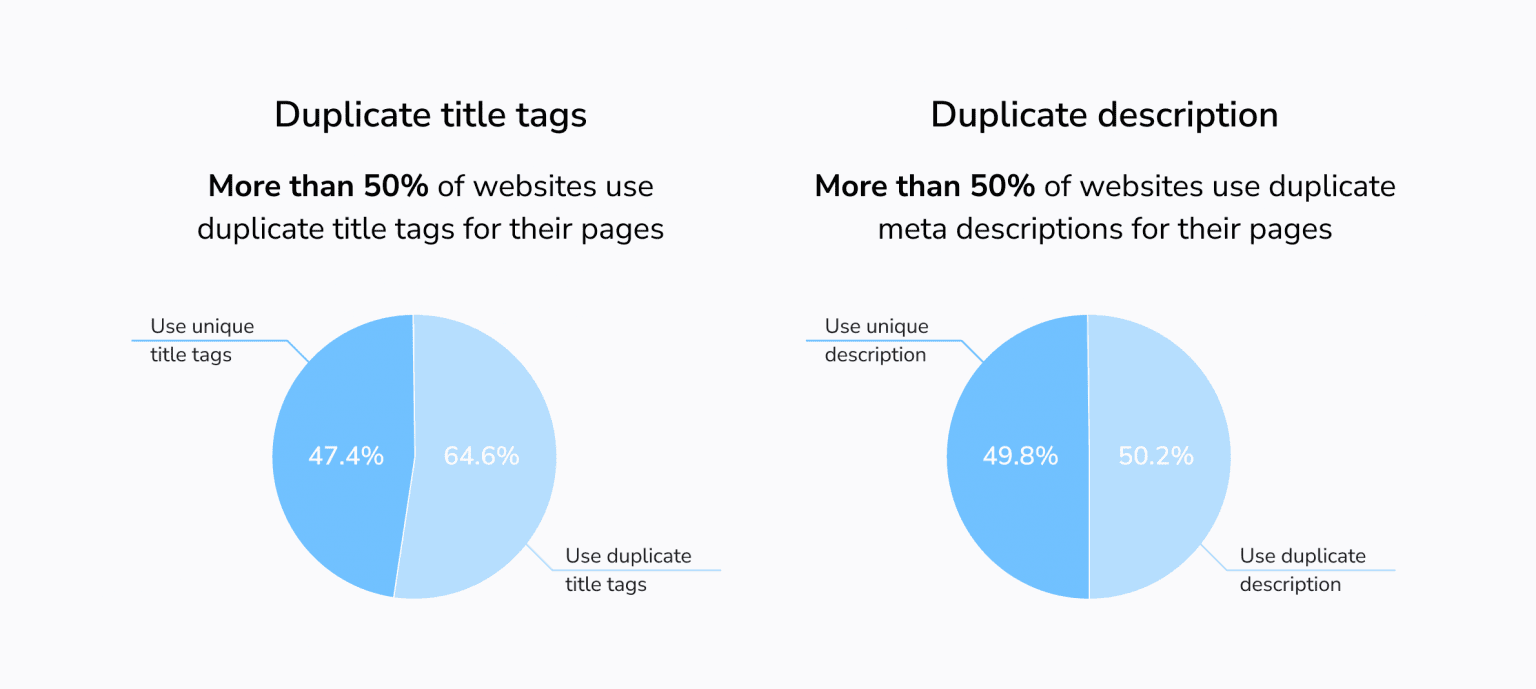
To begin with, many websites have issues with meta tags. Some time ago, we analyzed 40,000 sites to find out which issues are hindering their promotion efforts and here’s what we found. 71.11% of the analyzed websites had an empty or missing meta description tag, slightly more than 50% had duplicate descriptions, and 64.6% had duplicate titles.
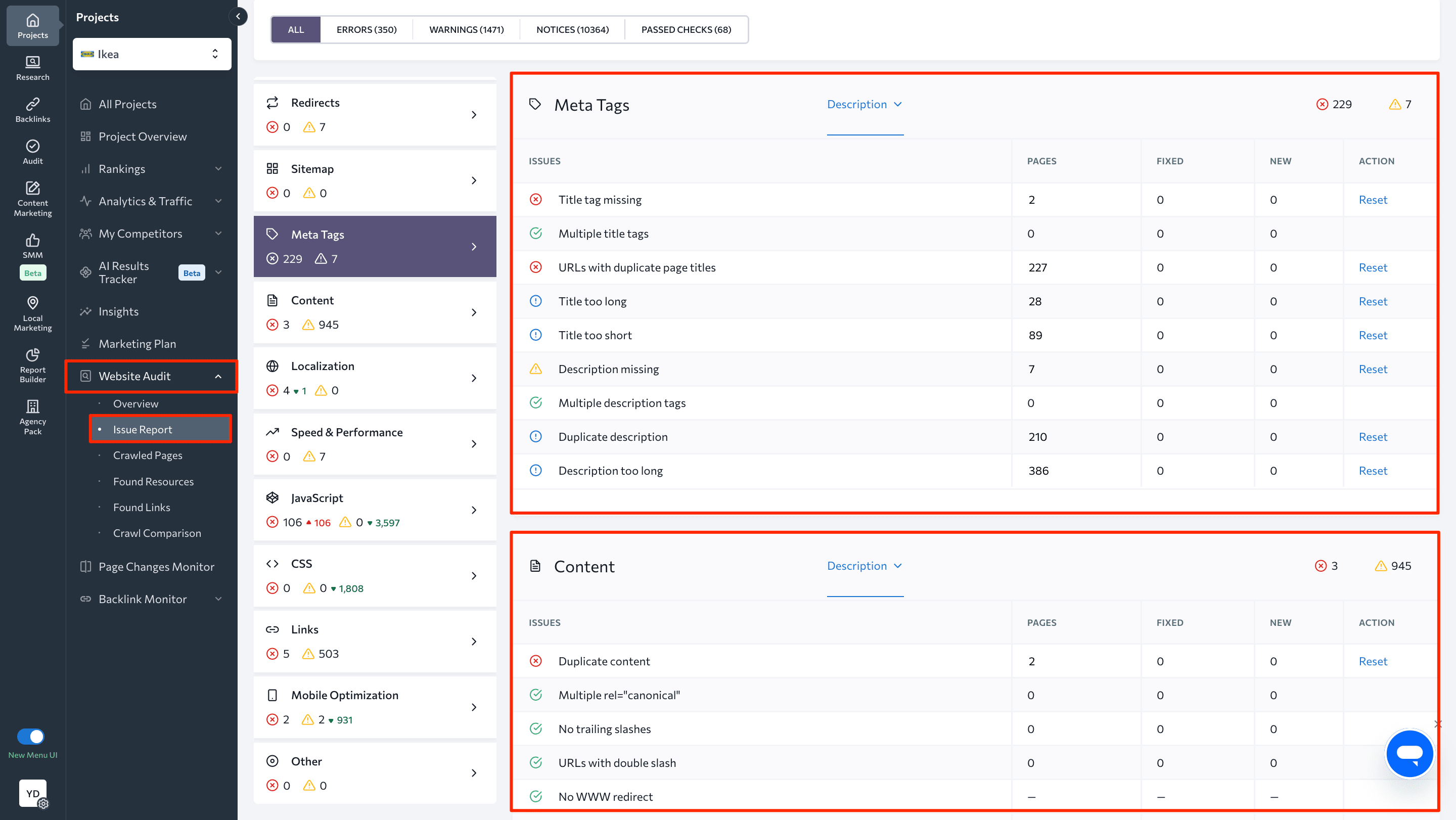
So, if you’re not sure that your website’s meta tags are in order, check all of your pages using SE Ranking’s Website Audit Tool.
In just a few minutes, the tool will scan all your site’s pages—including subdomains—and will check your meta tags in the process.
Under Issue Report, you will see a long list of technical SEO checks broken down into categories. What you want to look at here are the Meta Tags and Content sections. They’ll point out pages that don’t have meta tags, have duplicate titles and descriptions, or have tags that are too short and too long. Next to each issue, you’ll find a list of all web pages where the given issue was found.
Before doing website audit, you can manually set the optimal length for your page title and description tags. Go to Settings, choose Report Setup, and specify relevant parameters.
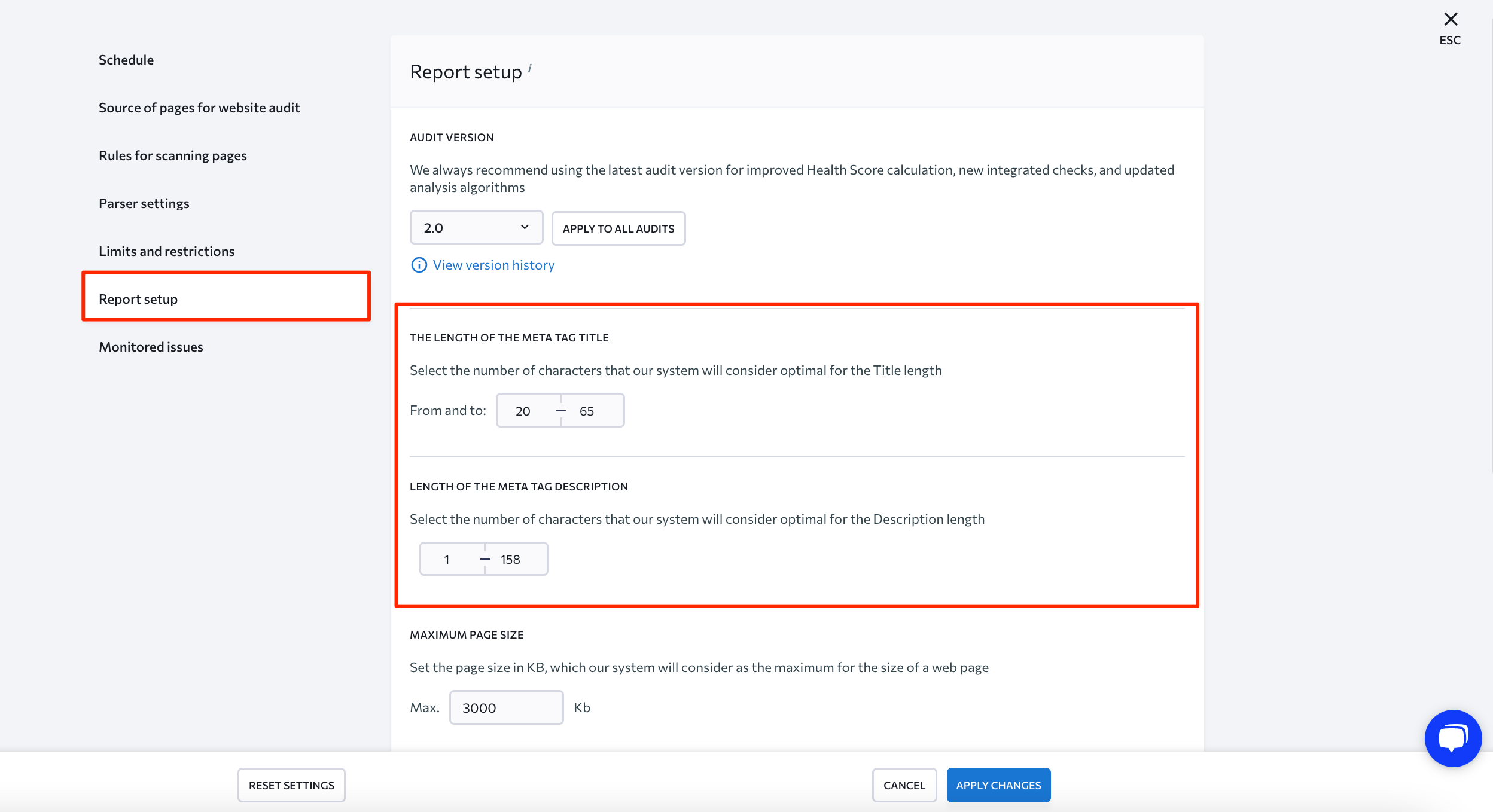
Moreover, you’re at liberty to schedule automatic checks to get regular reports sent right to your inbox. That way, you’ll be able to stay on top of your site’s meta tags, among other things.
Meanwhile, with our On-Page SEO Analyzer, you can also determine how your page is optimized compared to your main competitors and get a list of on-page SEO steps to take to outrank them in SERPs.
Enter a URL, focus keywords, choose a location, and press Run audit. After it’s finished, you will see possible issues with your SEO title and description and learn how to optimize them for your keywords.
So, sign up for a free 14-day trial today and start getting all of your website’s meta tags in order.
And if you have a specific page in mind, use our free Title and Meta Description Checker to ensure its meta tags are optimized for the target keyword and fall within the acceptable length for accurate display on SERPs.
10 best practices for writing the title tag
Now, let’s explore practical tips on how to write title tags that capture attention and drive clicks.
1. Each page must have a unique title tag
If several of your website’s pages have the same title tag, both search engines and searchers will be confused. Think about it: if you write the same title tag for several of your web pages that cover different topics—they could be around the same topic, but answer different questions—searchers won’t be able to tell them apart and decide which one is relevant to their specific search intent.
In such cases, Google will probably display a different title in the SERP by pulling a piece of text from your content that it thinks is more relevant to the searcher’s query. But the text that the search giant, or any other search engine, pulls may not be attractive enough to get people to click through to your web page.
2. The title must accurately describe what the page is about
If you have a web page that talks about a restaurant that delivers food across New York, don’t write something like “How to bake a cake at home” in the title tag. The title should concisely and accurately reveal the main topic of the page. Remember that search engines are all about providing searchers with content that is relevant to their search intent. As a rule of thumb, write for people because they are the ones who pay most attention to the title to see if it offers a solution to their problem.
3. Keep your title tags under 60 characters
Lengthy titles are truncated by search engines to about 50-60 characters, which adds up to 600 pixels—the width of the title in the SERP. This is why it’s better to take this limit into account when creating the title tag. Otherwise, searchers may see an incomplete title.
Moreover, be especially mindful of character limits when optimizing for mobile devices. Keep both title tags and meta descriptions relatively short to ensure they are fully visible on smaller screens.
4. Put the main keyword at the beginning of the title tag
While you need to make sure your title is readable and click-worthy, there’s a rule that many SEOs have agreed on: The closer the keyword is to the beginning of the title tag, the more weight it has with search engines.
Here are some examples of such titles:
- Cropped Blue Jeans for Women: Skinny, Flared & More [“cropped blue jeans”]
- CBD Oil: All the Rage, But Is It Safe & Effective? – WebMD [“cbd oil”]
- Freelance Writing: How to Start and Build a Successful Career [“freelance writing”]
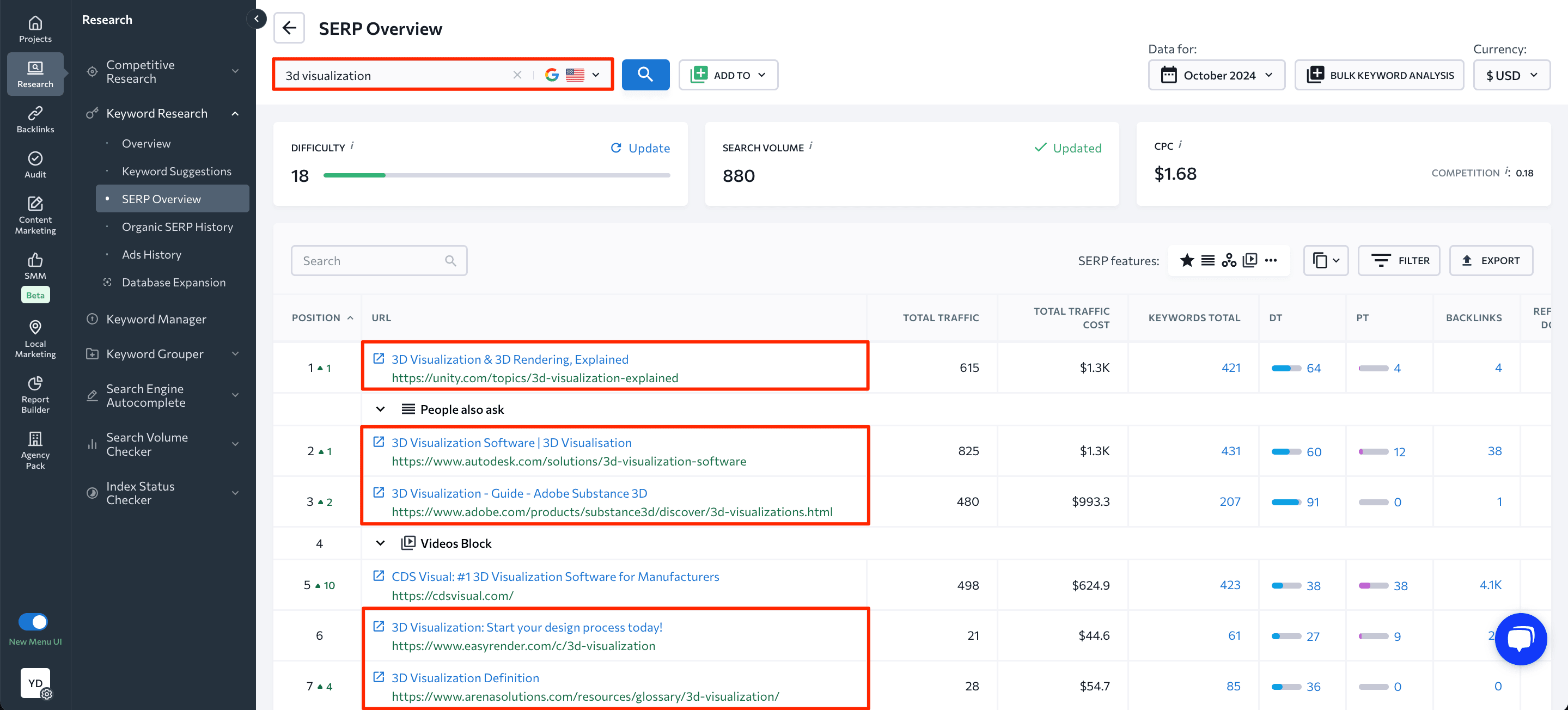
And when you check out the top 10 results in highly competitive niches, you’ll probably see this rule applied to the majority of websites there.
For instance, here you can see that 5 websites that are ranking among the top 7 search engine results for “3d visualization” use the keyword at the beginning of title tags.
To maximize your title’s SEO potential, use delimiters like hyphens, colons, or pipes to separate your primary and secondary keywords. This technique is especially effective when the keywords share few or no common words.
Here are some examples:
- Best CBD Oil | Shop Cannabidiol Oil [“best cbd oil”, “cannabidiol oil”]
- Carpet Cleaning Services | Boston Cleaners | Rugs, Couches [“carpet cleaning services”, “boston cleaners”]
By the way, if you are not sure what keywords to focus on and use in your title, you’ll need to perform keyword research beforehand. Using SE Ranking’s Keyword Search Tool, you can enter a seed keyword, choose the needed location, and the tool will generate a list of keywords you can choose from (remember the rule: relevancy, high search volume, low difficulty).
5. Avoid keyword stuffing in title tags
Including a few descriptive terms in the <title> element can be useful, but repeating the same (or pretty similar) words and phrases over and over will not be beneficial from an SEO perspective. For instance, a title featuring keywords like “Widgets, widget tools, widget products, widget apps” doesn’t add value for the user. This type of keyword stuffing can make your content seem spammy to both Google and potential visitors.
Moreover, if you target the same keywords for different pages on your website, you can even get affected by keyword cannibalization and lose ranking positions for all of them.
Here’s what to do instead: Focus on crafting concise, descriptive, and compelling titles that accurately represent the content of the page. Use your primary keyword naturally within the title, ideally closer to the beginning, and complement it with a secondary keyword or related phrase. Aim to provide context and encourage clicks by incorporating value-driven elements, such as benefits, numbers, or action-oriented language.
For example, a good title could be: “Top 10 Widget Tools to Streamline Your Workflow.” This approach not only improves user experience but also aligns with SEO best practices, helping search engines better understand the page’s relevance.
6. If your price or quality is a competitive advantage, add it to the SEO title
If you’re creating a title for a page with a commercial intent, such as Gifts under $20 or Free deliveries across Los Angeles, it’s wise to add this information to the page’s SEO title to stand out among SERP competitors and get more people to click on your advantageous offer.
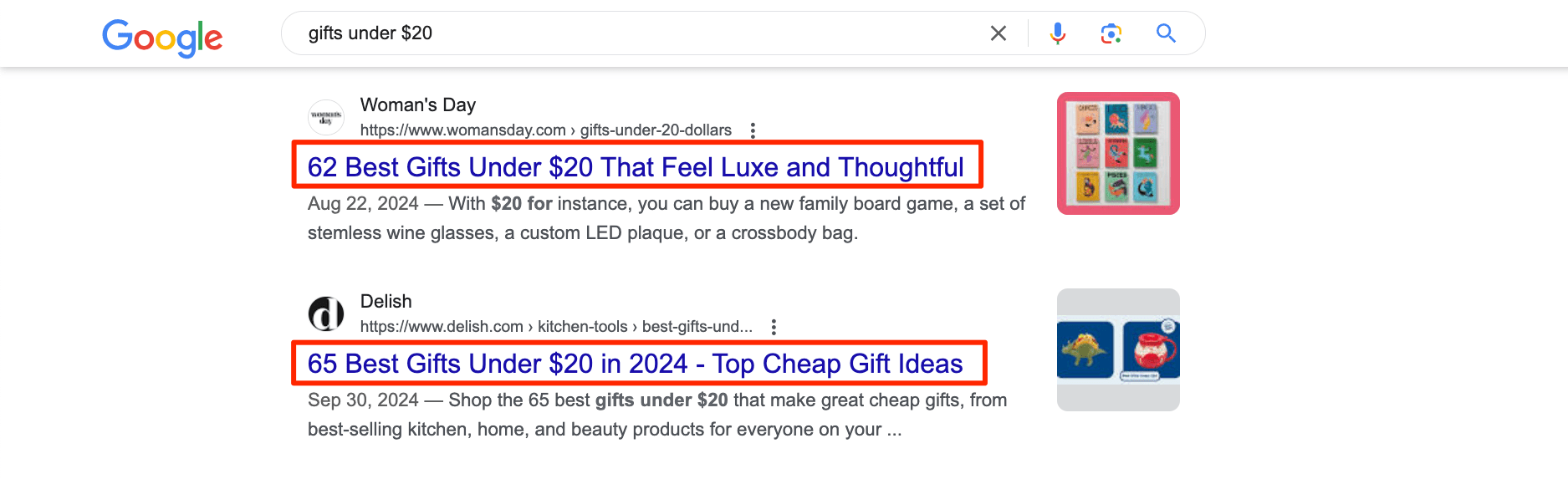
Here is another example of a good title tag:
House Cleaning Service Boston, MA. Free Estimate | The Maids
It includes the focus keyword at the beginning (“house cleaning service boston”) and their benefit—”free estimate”. So, this is good for both users and for improving your CTR, which directly translates to more website visitors and potentially conversions.
Still, be sure to exclude flight price details from <title> elements. In fact, Google’s algorithms generally avoid showing pricing in title links for flight pages due to the fast-changing nature of airfare, which can fluctuate every few minutes. This means the price listed in the title could easily become outdated and won’t align with the actual price on the landing page.
7. Add your brand name to the title tag
The <title> element on your homepage is an ideal spot to add some descriptive information about your site.
However, if you apply the same text to the <title> of every page, it can come across as repetitive, especially when multiple pages appear in SERPs.
To keep things unique, position your brand name either at the beginning or end of each page’s <title> element, separated by a hyphen, colon, or pipe. For example:
<title>TravelExplorer: Plan Your Next Getaway Today</title>
Generally, placing the brand name at the beginning works best for the homepage or key pages like About Us or Sign Up. For other pages, it’s often more effective to place the brand name at the end, ensuring that the page’s primary topic stands out more prominently in SERPs.
But don’t add your brand term as a rule. In most cases, your website will already be visible in the search for your brand name.
Keep in mind that in some cases, Google may automatically add the brand name to the page’s title, provided that the title itself consists of only 2-5 words and there’s enough room left to add the name of the site or company.
It’s also worth checking if the promoted brand is being searched for in other countries, like China or Bulgaria, for example. If you see that such search queries have a high search volume, include the transliterated brand name in the title too.
8. Ensure the main title is easily identifiable
When generating title links, Google takes into account multiple sources, such as the primary visual title, heading elements, and other large text on the page. If several headings share the same visual significance, it can lead to confusion. To improve clarity, make sure your main title is easily distinguishable from other text on the page, standing out as the most prominent element. This can be achieved by using a larger font size or ensuring that the title is the first visible <h1> element on the page.
Generally, Google does not object to having the same text for the title and H1; however, from an SEO perspective, it’s preferable to keep them closely related in meaning but slightly different. The title tag should prioritize encouraging clicks, while the H1 should focus on engaging visitors once they arrive on the page.
9. Maintain consistency in language between title tags and page text
For instance, if a page is written in Hindi, the <title> element should also be in Hindi, rather than in English or transliterated into Latin characters. Google aims to display a title link that aligns with the primary language and writing system of a page. If Google finds that a <title> element does not correspond with the writing system or language of the page’s main content, it may select alternative text for the title link in SERPs.
10. If you’re working with huge websites, create title templates
If you’re running or managing an online store, you can automatically add the name of products and their distinct characteristics like color and model to the page’s SEO title. But it’s important to point out here that Google recommends writing informative and descriptive titles and avoiding using terms that don’t add any real value.
10 best practices for writing the meta description tag
Now, let’s move on to the best practices on how to write quality meta descriptions. Apart from tips provided by Google, we will also offer other practices widely known within the SEO community.
1. Each page must have a unique meta description tag
By doing so, you get the opportunity to put forward the text you want to be displayed in the snippet description and influence the snippet’s click-through rate. Otherwise, search engines will take a piece of the page’s content that they think is more relevant to the search query and use it in the snippet instead.
2. Keep your meta description length under 155 characters
Google will truncate the meta description tag if it goes over 155 characters in most cases, so there’s no point in creating extensively long description tags that searchers won’t even get to fully read.
3. Concisely describe what the page is about in 1-3 sentences
The information provided in the SEO description tag should supplement what was said in the title tag. The main purpose of the description tag is to advertise your content and convince users to click the link in the SERP and go to your website. This is where you can get creative with your CTAs and write attention-grabbing copy. Just keep in mind that the SEO meta description should be concise and clear so that everyone can understand what information they will get by going to your page.
4. Write with your reader’s goals and challenges in mind
When writing meta descriptions, it’s crucial to consider your reader’s needs and pain points. By understanding their goals and challenges, you can create compelling copy that resonates and encourages clicks.
Start by clearly stating what your product or service offers. Be concise and specific, highlighting the core value proposition. For instance, instead of saying “We sell shoes,” you might say “Stylish, comfortable sneakers for everyday wear.” This provides a clear understanding of the product’s purpose.
Next, emphasize the unique benefits or competitive advantages that set you apart. What makes your offering different from others on the market? Are there specific features, qualities, or solutions that address your reader’s needs in a superior way? By showcasing your unique selling points, you can pique interest and entice potential customers to learn more.
5. Put primary keywords into the description tag (but don’t go overboard)
As with the title, it’s good practice to add keywords to the meta tag but try not to use the same ones. It would be best if you could use long-tail variations of your focus keyword in your SEO descriptions.
Moreover, if your page meta description tags contain keywords that answer the searcher’s intent and query, they may be highlighted in the SERPs. When this happens, searcher attention automatically gets pulled toward the highlighted keywords, letting them know that they’ve found what they were looking for.
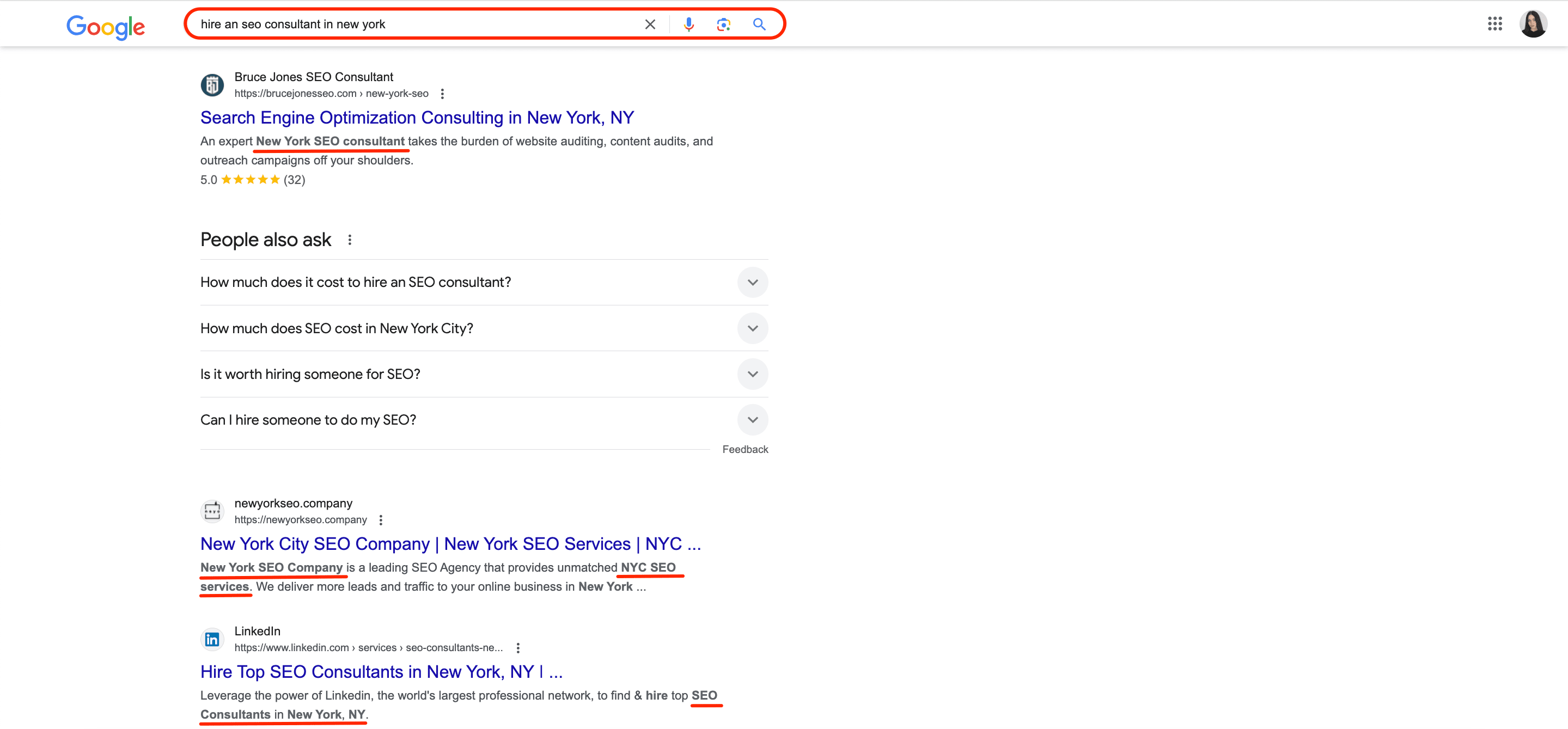
SE Ranking’s Keyword Grouper tool lets you know what keywords Google will highlight for any search query you’re interested in. This gives you data that you can use to your advantage when writing SEO meta description tags.
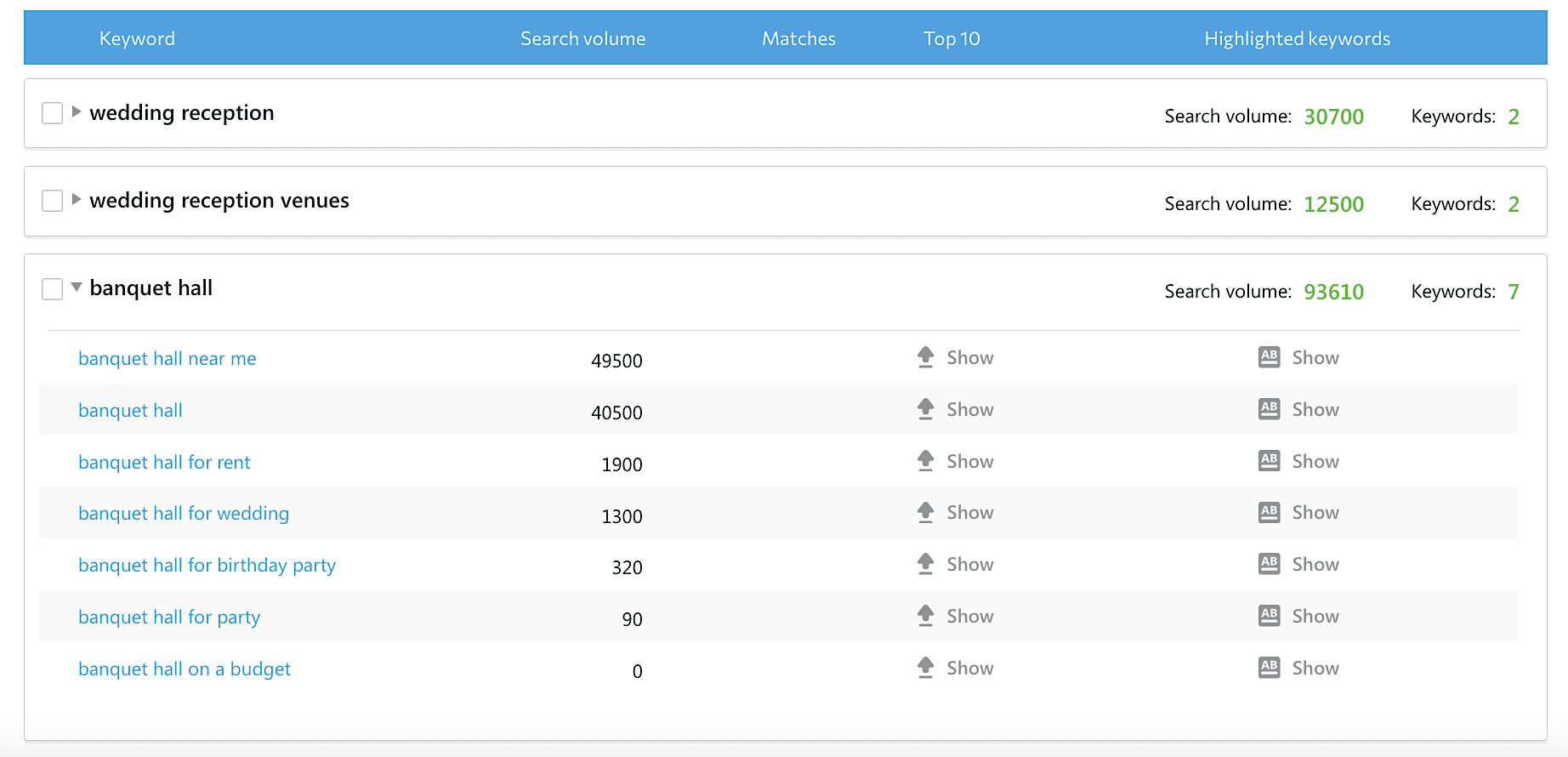
6. Add product information and other useful data to the description
You can include important product information, such as manufacturer, characteristics, and specifications to the description. This way, you will basically give people all the data they need to make a purchase decision in your favor.
For example, here is a meta description optimized for a product page:
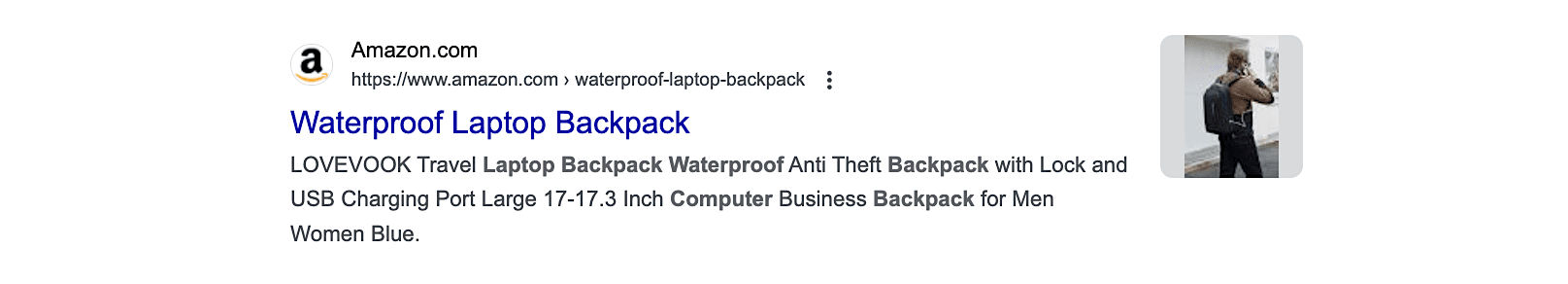
This product description highlights the backpack’s key features: waterproof construction, laptop compatibility, blue color, USB charging port, lock, and unisex design. Potential buyers seeking a backpack with these specific attributes will be more drawn to this listing compared to a generic one that lacks such details.
On top of that, if your website offers emergency services, like towing and locksmith services, you can specify the business phone number and price right in the description tag. That way, searchers can immediately get the information they need and reach out to you.
You can also specify where you provide your services to show more relevant information that corresponds to the searcher’s query, and as a result, increase the clickability of the snippet—provided that the region where you provide your services is relevant for the searcher.
7. Write meta description tags in an active voice
Active voice tends to be clearer and more straightforward than passive voice. It makes your message easier to understand, which is essential in the limited space of a meta description. When users can quickly grasp what your page offers, they’re more likely to click through.
Plus, using active voice creates a sense of immediacy and action. It invites users to engage with your content rather than simply passively absorbing information. Phrases like “Discover the best recipes” are more compelling than “The best recipes can be discovered,” making users feel like they have something to gain.
For example, the SEO description below lacks the clarity and impact of active voice. It makes the information feel distant and less engaging.
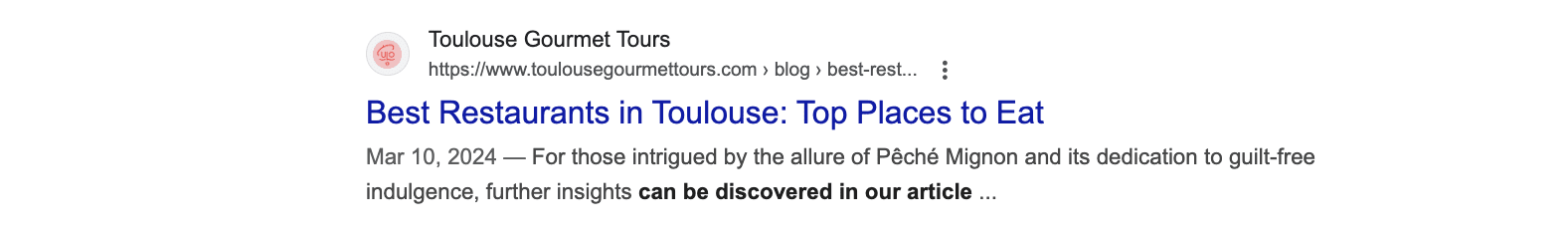
A better option would be: “Discover the secrets behind Pêché Mignon’s delicious, guilt-free treats in our article.”
Or, it could be something like this: “If you’re curious about Pêché Mignon’s approach to guilt-free indulgence, check out our article.”
8. Add a call to action
A call to action (CTA) instructs your reader to take a specific action, such as buying something, calling your company, signing up for service, etc. It usually starts with a verb, explaining what users need to do next.
Here’s an example of meta description without CTA:
“Wide range of gardening tools for beginners and experienced gardeners. Everything your gardening project needs in a single store with free delivery.”
And this is what it looks like with one:
“Discover our extensive collection of gardening tools, perfect for all skill levels. Browse now to start your gardening journey and get free delivery!”
Anyway, when creating CTAs, make sure to align them with the intent users have behind search. For transactional searches, use persuasive CTAs that encourage immediate action, such as “Buy now,” “Order today,” or “Add to cart.” Whereas for informational ones, make sure your CTAs are informative and helpful, such as “Learn more,” “Read our guide,” or “Download our ebook.”
9. Use emojis wisely
Emojis can be a great way of bringing emotion and some fun into your snippets but under certain conditions.
Google displays only those emojis in the SERPs that it finds relevant to the search query, blocking those that deceive searchers and look spammy.
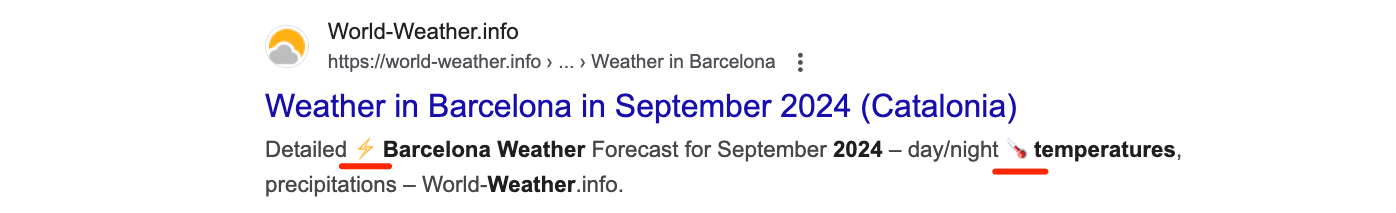
Keep in mind that in most cases emojis won’t be blocked if they are used in the meta description tag, not in the title tag. Here you can find emojis to use in your metadata.
So, descriptions really can attract the attention of potential users in the SERPs, which is why you simply can’t afford to ignore them.
10. Create meta description templates
News sites, educational blogs, and smaller websites generally have no problem creating unique descriptions for their content. But for larger online marketplaces, hand-written descriptions can be a challenge.
If your site has a lot of pages and it’s rather difficult to manually enter descriptions for each one, create description templates. You can add templates to your site’s pages with the help of a coder or use plugins for popular CMSs.
For instance, with Yoast, you can create customizable templates for your SEO titles and meta descriptions using over 50 different variables. Once you’ve set up a template, the plugin will automatically generate SEO-friendly titles and descriptions for all of your posts and pages.
How to add title tag and meta description on your site
Many CMS don’t give you the option to add meta tags via the admin panel. For this reason, you have to install special plugins, such as mentioned above Yoast SEO for WordPress and Easy Frontend SEO for Joomla.
For example, if you have the Yoast SEO plugin installed and activated, go to the page, scroll down and find this section to add your title and description tags.
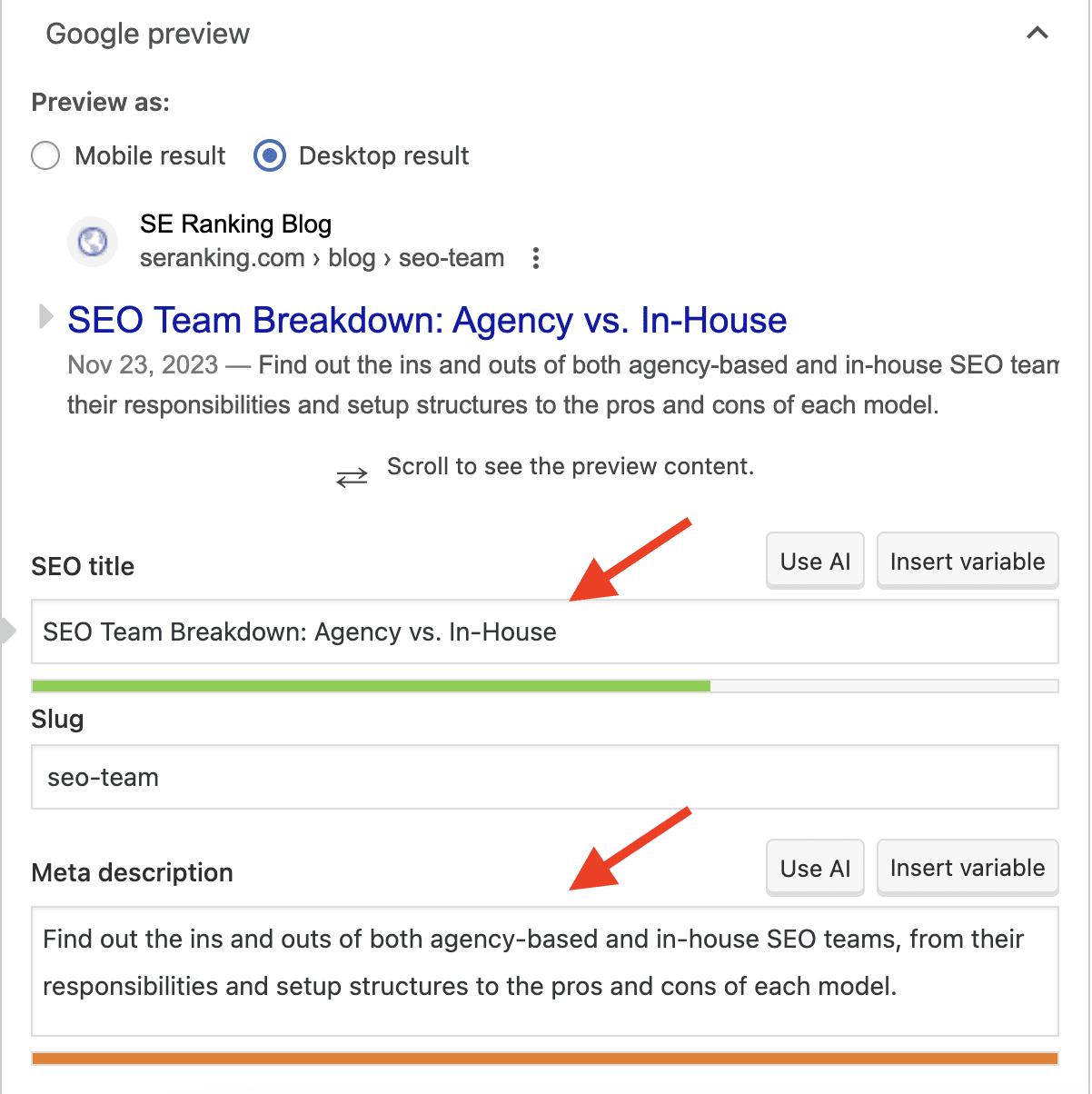
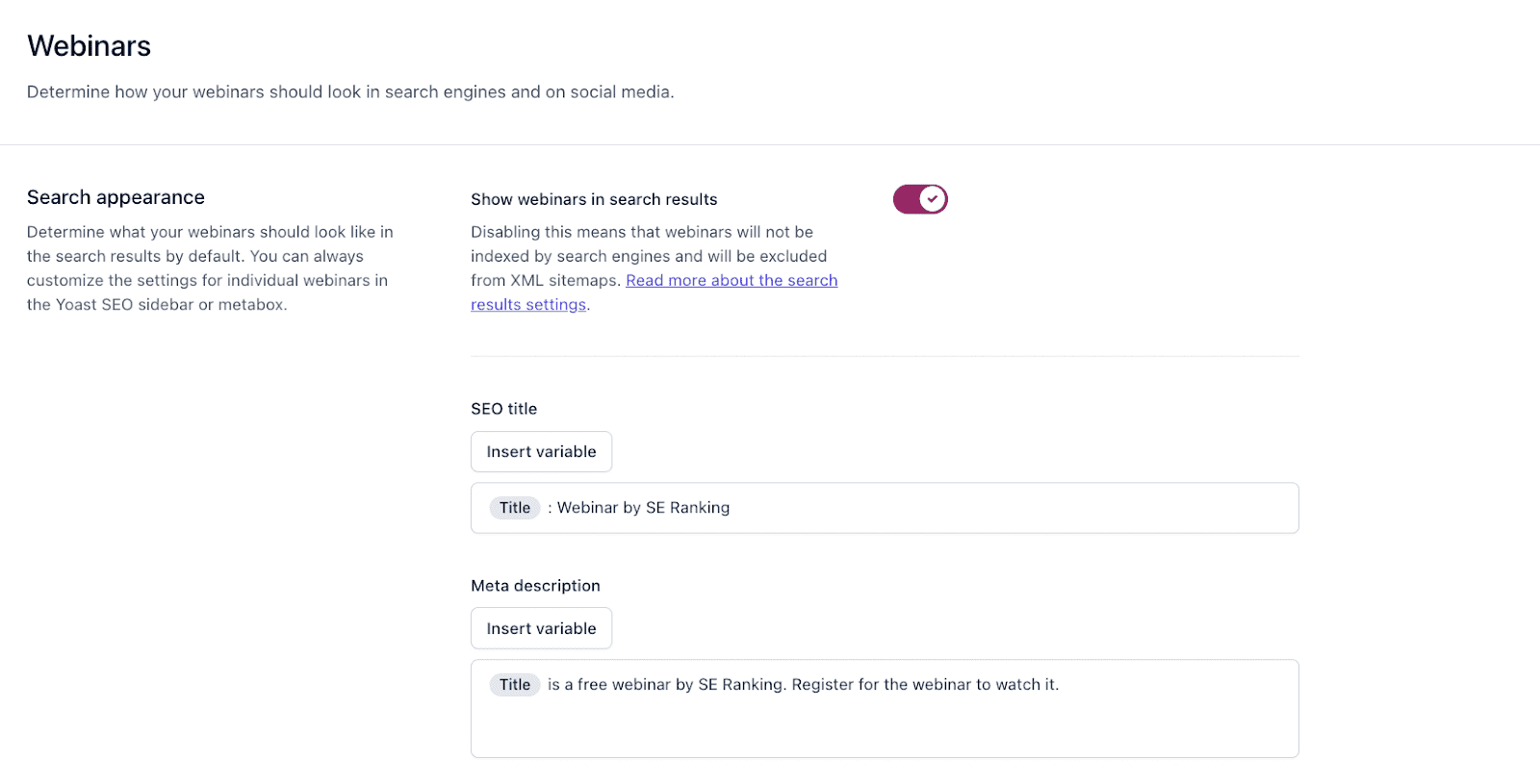
Yoast SEO also allows users to add title and description tags in bulk by creating templates based on a page type. For this, go to SEO from the left sidebar menu, and click on Search Appearance.
Here you can use variables to generate meta tags en masse. For example, in the screenshot below, you will have the same SEO title and description template for all WordPress author pages with a unique element: H1 of a page (Name here). So, with the templates, you won’t have to write unique meta tags for each page but you do get unique title and description tags as a result.
If your CMS doesn’t give you the possibility to add meta tags by default, or if for some reason you cannot install the required plugin, you can open the PHP file of the necessary page via an FTP client and add title and meta description tags to it.
Why Google can rewrite title tag and meta description
Sometimes, search engines may not use your HTML title in the snippet at all. In August 2021, SEO experts started actively discussing that Google had been replacing the title tag with H1 (but other elements can be used as well). This was the result of Google trying to improve the relevancy of the titles shown in the SERP.
For example, this page has the title tag “Tiktok’s societal impact: What are the pros and cons? | Vox.”
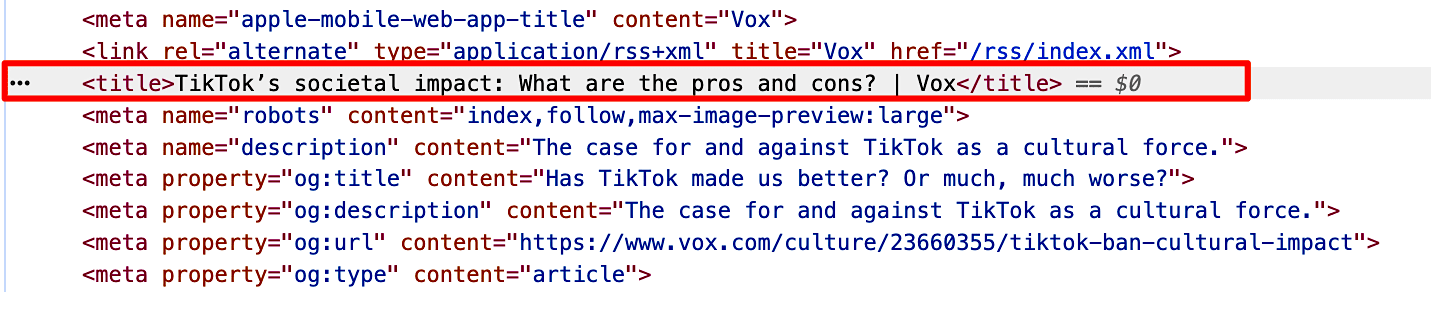
However, Google shows its H1 in the SERP.

According to Google, “When we know the user’s query, we can often find an alternative text from a page that better explains why that result is relevant. Using this alternative text as a title helps the user, and it also can help your site.”
Let’s look at several reason why this can happen:
- Your title does not answer the search query. For example, when internet surfers enter a search query with a low search volume, the search engine can decide to select another piece of text from the page that more closely matches the intent;
- Your HTML title tag is missing or search engine robots were unable to crawl your page and were forced to use the information provided by anchor texts from the backlinks that link out to your page;
- The meta tag title is spammed with keywords;
- Your HTML title tag is too long;
- Your title tags contain huge repetitive text parts or generally are the same across the website.
In these cases, Google automatically generates title links on its SERPs by analyzing both the content of a webpage and its external references across the internet. The purpose of these title links is to accurately represent and describe each search result.
To automatically determine the title links, Google utilizes several sources:
- Text within the <title> elements
- The main visual title displayed on the webpage
- Heading elements like <h1>
- Content in og:title meta tags
- Other significant and visually prominent content styled in various ways
- Any other text present on the page
- Anchor text used within the page
- Text in links that direct to the page
- Structured data associated with the website
However, Google said that still over 80% of pages shown in SERPs will retain their original HTML title tag.
Additionally, Google may choose to rewrite the meta description for various reasons, including:
- Lack of relevancy. If the meta description doesn’t accurately represent the content or is too vague, Google may select alternative text from the page that provides a clearer or more engaging summary.
- Optimization for user queries. Similar to title tags, if Google determines that a different piece of content on the page better answers the user’s search query, it may display that text instead of the provided meta description.
For example, here’s how the meta description of our page looks like for the “SE Ranking vs Semrush” query:
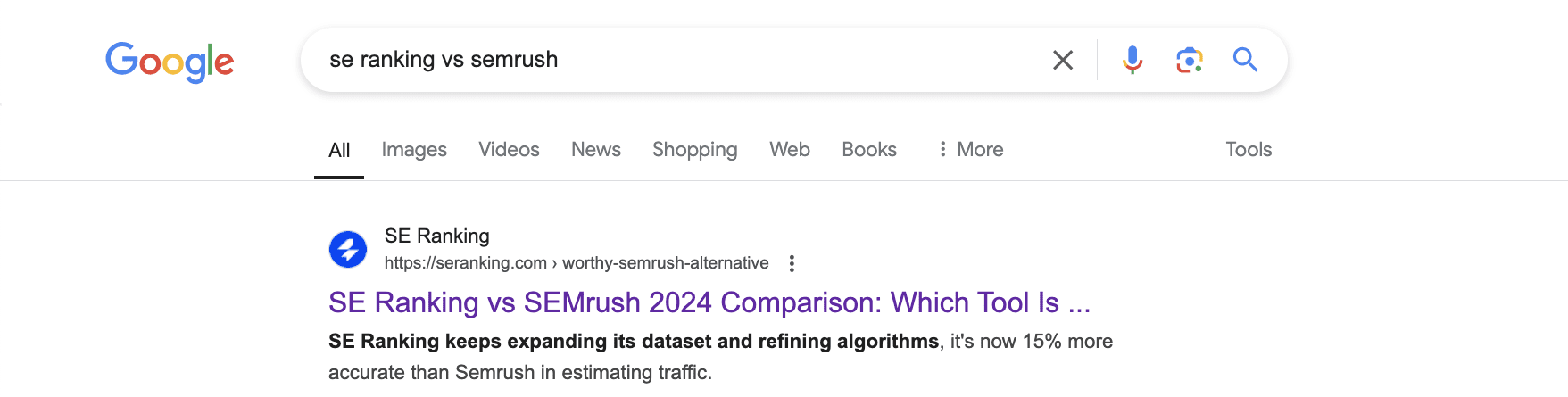
And here’s how the meta description of the same page looks like for the “SE Ranking and Semrush which tool is better” query:
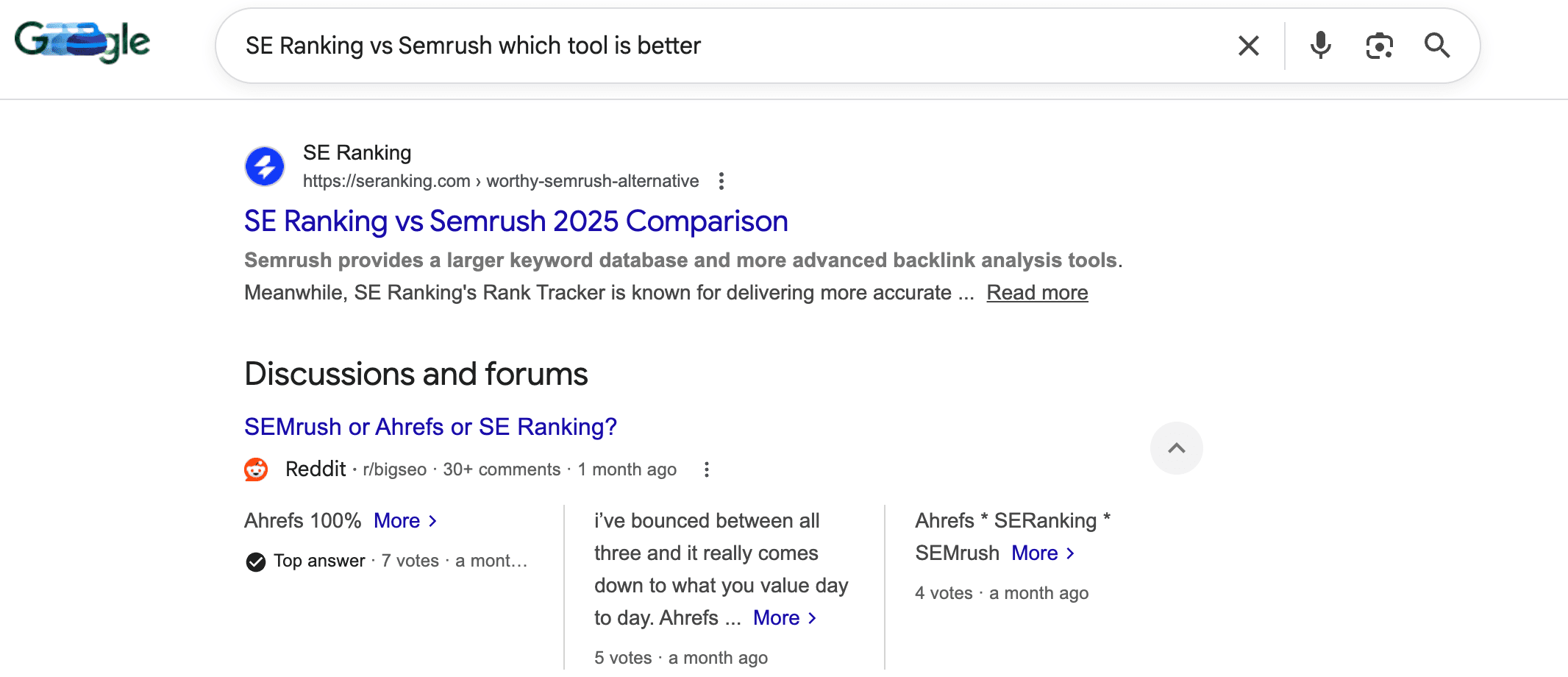
As you can see, Google dynamically adjusts the displayed meta description based on the specific search query to provide users with the most relevant information directly within SERP.
- Character limits. If the meta description exceeds the recommended length, Google might truncate it or replace it with more relevant content.
- Identical descriptions. If your meta description is identical to another page’s meta description, Google may rewrite it to differentiate the results and provide a unique summary for users.
Anyway, while you cannot entirely stop Google from potentially rewriting your meta descriptions, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of this happening. For this, you’ll need to follow all the best practices for writing meta description mentioned above in the article.
Closing thoughts
If you plan on taking your search engine optimization efforts seriously, you need to keep two big things related to meta tags in mind.
First, each page must have its own unique title and meta description tag. This is not an option, but a necessity! And second, write meta tags not for search robots, but for people who will potentially visit your website.
Think about it this way: you only have about 10 seconds to convince searchers to click through to your page and not on that of a competitor. That’s where your meta tags come into play as searchers only see your page title and description in the SERP and have to make a call judging by the text they see.
Now you know everything there is to know about meta tags and will be able to avoid making mistakes that prevent you from acquiring organic traffic for the search results. If you’ve had success using other advice and tips on setting up your metadata, share your experience in the comments section below.
And if you’re ready to move one step further, check out our complete guide on other HTML tags that matter for SEO.