The complete SEO anatomy of HTML h1 to h6 heading tags
HTML heading tags, more commonly known as <h1>, <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, and <h6> tags, make it easier for people and search engines alike to get a quick understanding of what a page is about. On top of that, they can also influence how high your pages are ranked on the SERPs.
And because their importance in search engine optimization and user experience is so significant, it’s vital to know exactly what they are, why they’re important, plus how to use them properly for increased benefits.
So, if you have any confusion about the topic, this post aims to answer the most common questions surrounding HTML heading tags.
Heading tags or Header tags?
Let’s start off with the terminology to avoid confusion as to what h tags should be called.
- Heading tag is the most commonly used and appropriate term for h tags; this is what Google uses in its guidelines.
- Header tags is sometimes used as a synonym for heading tags, and Bing uses it in its guidelines. However, this term can create сonfusion as its singular form has another meaning: the <header> tag.
Header tag means the <header> that marks the upper section of an HTML page and is not visible to users. It’s needed to build a page’s layout.
What are heading tags
Heading tags define a page’s main heading (<h1>) as well as the sub-headings (<h2>-<h6>) of various content sections.
From the perspective of both people and search engines, these tags are used as summarizing text that gives readers and crawlers the gist of the content by concisely conveying its main message.
The World Wide Web Consortium defines six levels of section headings in HTML, with <h1> being the most important one and <h6> being of least importance:

At SE Ranking, we publish our content using WordPress. But regardless of whether you create content in Google Docs, WordPress, or another service, the heading options are always available:
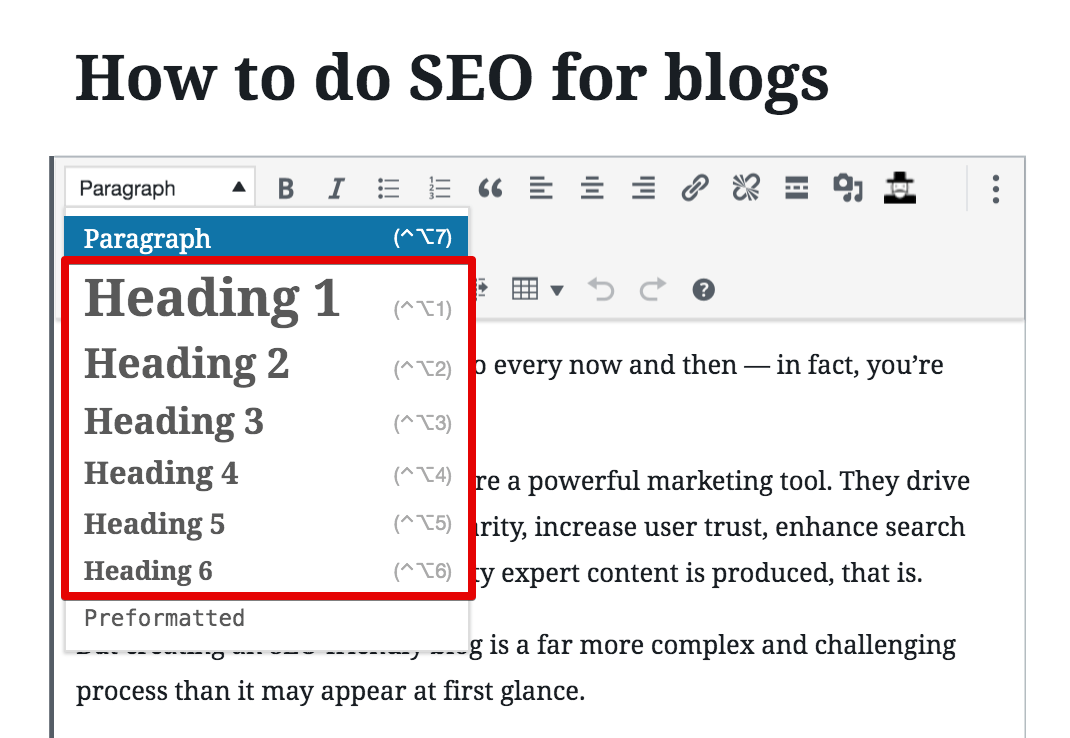
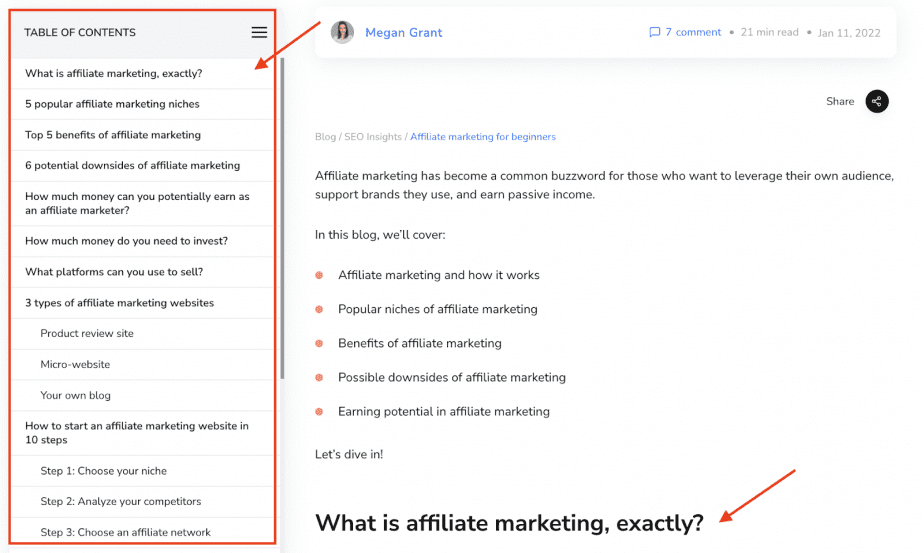
Now, if we take a closer look at one of my previously published posts, you’ll see that I’ve pointed out its first two HTML headings in the screenshot below:
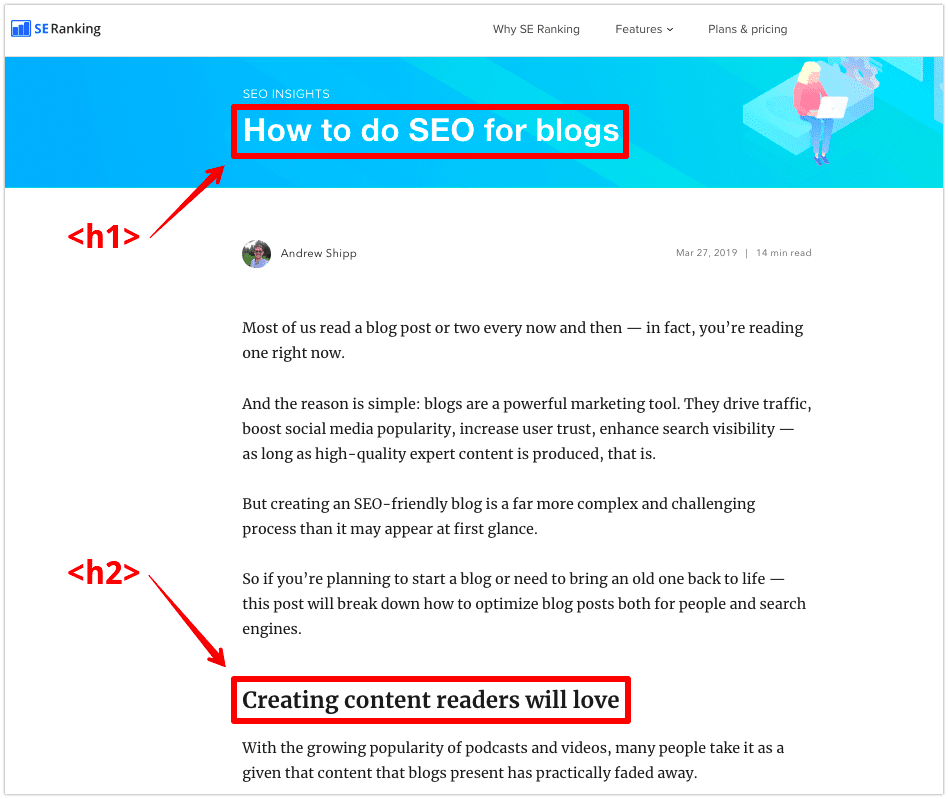
Sure, you might think that I simply increased the font, emboldened the text or changed its color. Although that may be the case, it’s a little bit more complicated than that.
When we take a look at the page’s source code, we can see that these H tags are actually marked with the <h1> and <h2> tags respectively:
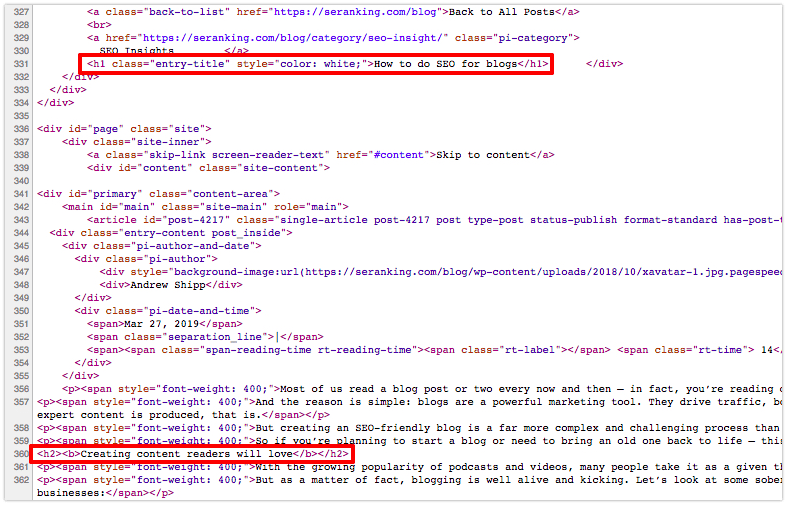
Here you can also see the basic rule behind the work of HTML tags: Heading tags come in pairs, so a closing tag with an additional slash before “h” is required.
<h2>This is heading</h2>.
There you have it! Now that we’ve covered what HTML heading tags are, let’s focus on the ‘why’.
What is an H1 tag
It’s the main heading that sums up the essence of the content in one phrase. Search engines crawl pages and use h1 as a strong indicator of what a page is about. Meanwhile, the tag is also a part of its main text content.
H1 is a common element of a web page’s layout and your website users expect to see it at the top of the pages they visit. It is a quick thing that helps users decide whether a page is relevant. Depending on what they see, users will either keep reading and potentially convert or quit the page. Thus, your task is to create high-converting headlines by following copywriting best practices and understanding how headlines function.
And this is where I want to introduce you to the concept of user intent.
User intent, or search intent, is an essential concept in SEO. You should build each page with its H1 based on such intents. In a nutshell, the user intent is the reason why searchers come to your page and what information they seek to find there. This means two things for your H1: The HTML tag needs to match the user intent and be relevant to your page’s main content.
The user intent can generally be separated into commercial and informational intent. For instance, a page about your company’s services would have commercial intent, and an H1 like “Online marketing services” will match it.
Meanwhile, phrases like “What is” and “How to” in your H1 indicate informational content. In this case, the first one requires the content to provide a definition and additional information about the concept. In the second case, users expect a guide with a set of steps or tips on how to solve a particular issue.
H1 vs Title tag
The H1 tag is an HTML element for the first-level heading within the body text of a web page. It’s visible to both website users and search bots, and is needed not only to provide information about the page’s content, but also to give it structure and improve the layout.
The title tag is also an HTML element that is not visible on the page itself (but is visible if you check the HTML code or hover over the page tab). It’s displayed on the SERPs to help users find the right result for their search query. This piece of HTML is mainly needed for search engines.
To recap, the title tag’s goal is to entice people to click-through to the page from the SERPs, while the <h1> tag acts as the main headline for the page when readers land on it. So, both tags are needed to help users and search bots understand what a web page is about, and how it’s relevant to a search query.
Here is the rule of thumb for creating these tags: Use focus keywords in different variations that properly describe your article’s central topic or the page’s content.
Now let’s see an example:
H1: Google’s featured snippets: The biggest slice of the SERP pie?
Title: Featured Snippets: Types, Benefits, and Ways to Optimize for Them
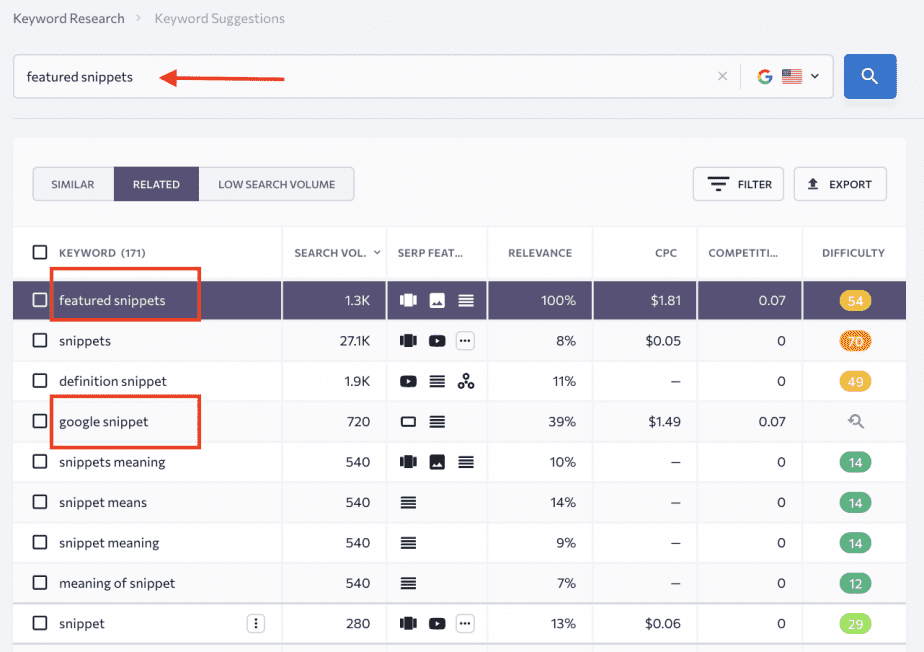
To make this task easier, you can use our Keyword Generator. Go to the Keyword Research module, enter a seed keyword (the most general and short phrase that properly describes your page), and choose your country of interest.
Here, check under the Similar and Related tabs to find the two most relevant keywords with the highest search volume (choose those with lower difficulty scores among keywords with a high search volume). But do not take one-word search terms because they usually have a vague search intent.
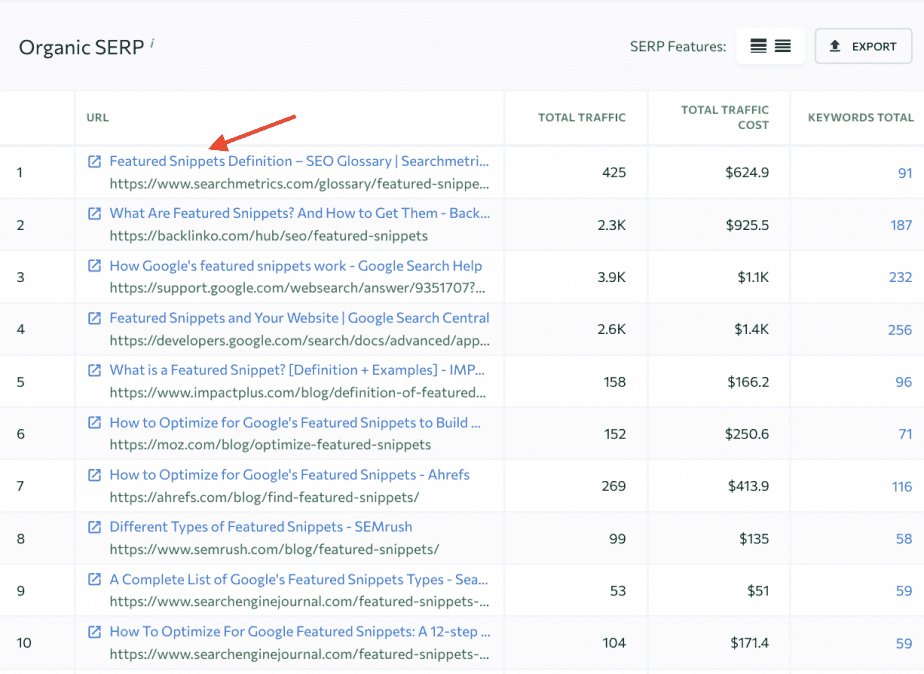
The two keywords in the screenshot below seem to be a good choice for our blog article about Featured Snippets.
Meanwhile, in this module, you can also check the top-10 organic results for these search queries to get an idea of what h1 HTML tags they have. Tip: Take a quick look at their Titles first.
Why do you need to use headings?
Heading tags provide web pages with two huge benefits: readability and hierarchy. They carry out two primary tasks, namely ensuring a positive user experience when visiting a web page and helping search bots better understand your content.
In fact, the reasons why you should be using headings can be broken down into two main categories. Let’s take a closer look at each one.

Heading tags enhance user experience
Heading tags improve your content’s readability and make it easier for people to digest. With 43% of people saying they skim through content to see if it contains the info they’re looking for, it’s essential to provide them with signposts. So proper headings enable people to quickly glance over content to figure out whether it’s what they need to find.
Alternatively, headings can help readers keep track of where they are in case they are interrupted. This can result in people staying on your page for longer periods of time.
Now, this is where having orderly, honest, well-phrased heading tags can clearly communicate the content’s structure to readers and, hopefully, entice them to keep reading or even take action.
So, just ask yourself this: Would anybody read your content if you just publish a post that looks like a solid wall of text?

Of course not. They would bounce from your page like a rubber ball.
Finally, the structure of HTML headings is also crucial for helping visually impaired people read digital content. Now, since H tags are written out in HTML, screen reader assistive technology can interpret the structure of any web page and read it out loud to disabled users. Plus, screen readers provide shortcuts that allow users to easily move between headings, facilitating navigation.
Heading tags help search engines understand your page
Well-written heading tags make it easier for search engines to understand a page’s main topic and structure. Bing confirmed it does, and while Google isn’t as transparent, it officially states that headings are important in order for users to be able to navigate the page. Meanwhile, during a Google Webmaster Hangout session, John Mueller confirmed that Google does use H tags to better understand the structure of the text on a page and it’s among the ranking factors that Google uses.
H tags help crawlers understand what category the page fits into and which queries it may be able to answer. That way it helps Google determine the relevance and semantic structure of a web page. All in all, headings are part of the page content and, as we know, content is the cornerstone for SEO.
That is, having a clear and proper page structure can help Google understand when it’s relevant to display a page in response to a searcher’s query, plus it makes the page eligible for featured snippets.
Featured snippets, or zero position results, are quick answers displayed by Google to user search queries. Since you need to already be ranking on page one to become a candidate for a Google snippet, HTML headings can be very helpful here. The display of featured snippets relies on Google’s ability to determine what page best answers a question and what exactly is a specific part of the text about. And structuring your content is what helps Google with this task.
For example, “best screen recorders 2022” is a type of question that is best put in a list-style blog post. Such pages are usually structured with one <h1> tag followed by a list of items wrapped in an <h2> tag. Or you can have an <h2> tag follow the <h1> tag, and only then have a list of items marked with the <h3> tag.
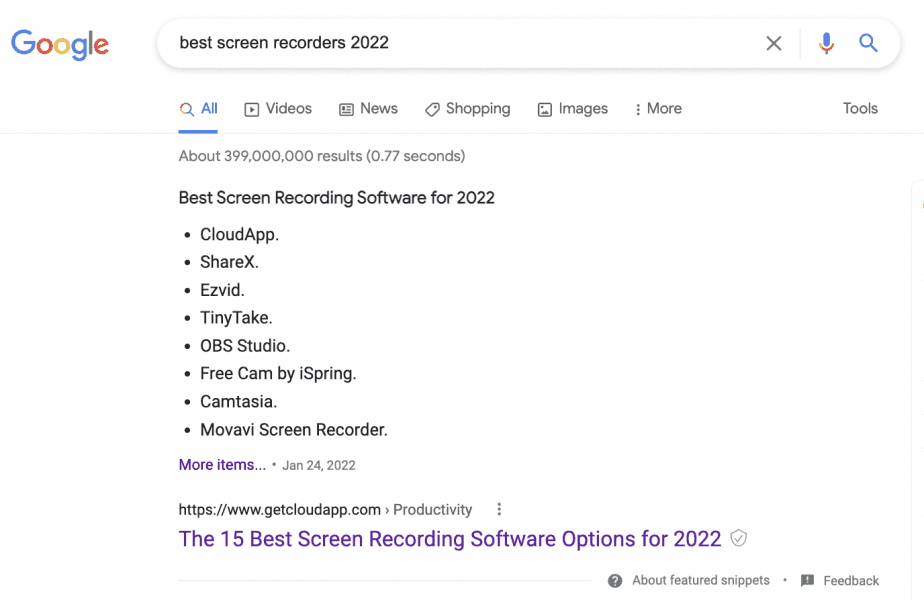
And you can see on the page itself that the heading “Best Screen Recording Software for 2022” is indeed wrapped into the <h2>, and the list of screen recording software solutions is <h3>.
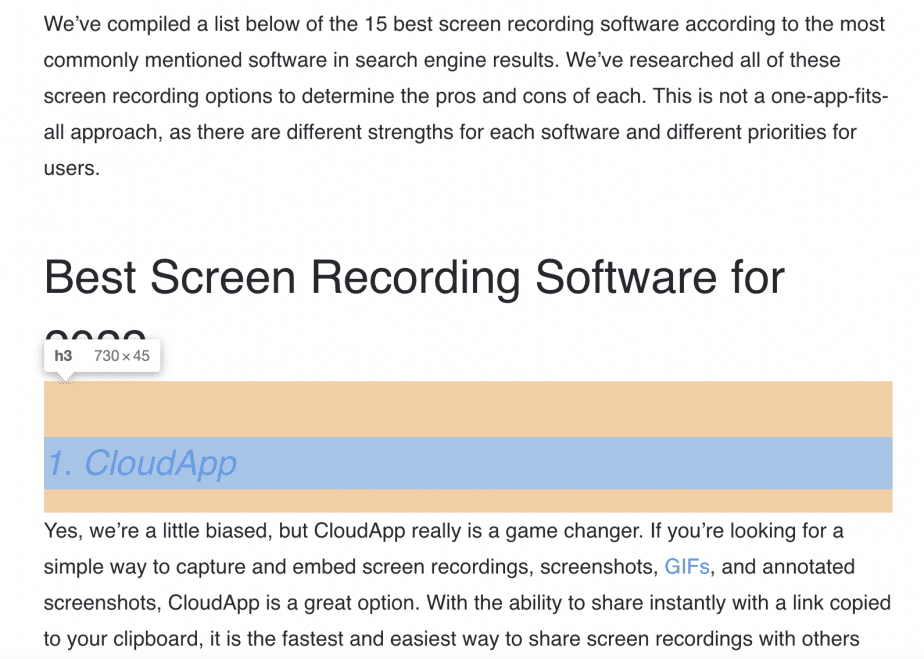
So not only do heading tags impact SEO, but the use of HTML H tags also helps produce quality content with good readability. And keep in mind that the better the text is from the user’s perspective, the better it is for SEO.
And isn’t that the end goal?
Best practices for using heading tags
Knowing the ‘what’ and the ‘why’ of heading tags, let’s now look at the ‘how’.
So far we’ve determined that search engines are all about making it easy for people to look for and find the right content online. This means that in order to stand a chance of having high SEO rankings, you can’t afford not to optimize your HTML H tags.
Here are some SEO best practices for creating effective HTML headings in your content.
Focus on the <h1> tag
Right off the bat, I want to say that even though you can get ranked organically without using H tags, doing so is a huge wasted opportunity that will result in you having an incomplete SEO profile.
Now, since the <h1> tag is meant to clearly describe the content that’s present on a page, it must:
- Focus on the same user intent as the main content
- Be written concisely, naturally, and organically
- Be placed at the top of the page
- Differ from the meta title tag and be unique across the site
- Include a focus keyword
- Not use inline styles
- Be used once per page
As for the H1 length, Google doesn’t give recommendations, but simply says to “avoid very long headings.” Here I would suggest keeping it under 60-70 characters as this is the limit for meta title tags which have a similar purpose as the H1 HTML tag. And the fact that Google did an experiment with replacing title tags with H1s only backs up this suggestion.
Now you may be wondering: Can I have two or more H1 tags?
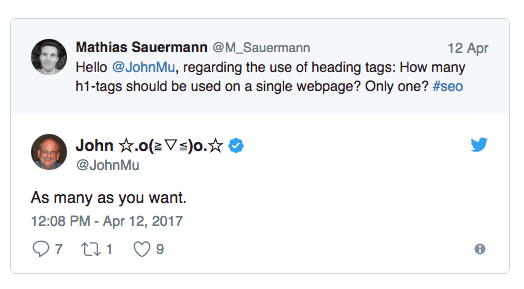
While having more than one <h1> tag is not officially a problem, there are two ways Google can go about this scenario. The search giant will either give:
- More weight to the first <h1> tag (Bing confirmed it does);
- Equal weight to every <h1> tag on a page, resulting in their overall diminished value.
Taking into account the fact that HTML5 allows pages to have more than one <h1> heading tag, but internet browsers decided not to adopt this recommendation and, therefore, support was dropped—I’d advise you stick to using a single <h1> tag for SEO purposes.
Additionally, it must be noted that it is very common to see content creators just repeat the title tag where the <h1> tag should be, which is a big wasted opportunity. So, make sure you have both of them in place and that they’re different.
Proper use of <h2>-<h6> tags
The use of <h2>-<h6> heading tags purely depends on the content’s complexity.
Your h2-h6 headings need to serve as an outline for a web page. Similar to writing an outline for a paper, put your main points into h2 tags and subpoints of the content into h3 tags and so on. And it’s not a surprise that if a page has a table of contents, it should be made up of the page’s headings (starting from H2).
It’s common to use <h2> and <h3> tags, while <h4> is rarely used, not to mention <h5> and <h6> tags.
Anyway, here are the best practices on the proper use of <h2>-<h6> heading tags:
- Use as many <h2> tags as you need to mark the different content sections of a page. It’s common to have an <h2> tag every 200-500 words to let the text breathe.
- Keep them relevant to the topic and make sure they sound natural
- Don’t spill all the beans in the heading tags, but use them to spark reader interest, so they are curious enough to read the next content section.
- Maintain heading hierarchy and don’t skip levels
- Optimize all HTML headings for featured snippets almost as if they are a collection of FAQs
I want to emphasize that <h2>-<h6> tags are great for helping organize long-form content, such as case studies or “how-tos.” To make the topic of web pages extra clear for people and search engines alike, use search terms in your headings to increase your chances of coming up in search. However, including keywords in them isn’t an absolute must—and here’s why.
Ever since Google rolled out the Hummingbird search algorithm update, crawlers have been able to grasp a text’s overall semantic meaning as well as the user intent.
As a result, the relevancy of a page for internet surfers now isn’t only measured by the direct keywords used (keyword stuffing was never a good thing). Google also considers synonyms, contextual definitions, and the use of language to understand the content.
All in all, we can say that a page’s SERP ranking now heavily relies on a combination of the content’s relevance, quality, structure, and user experience. And HTML headings help both groups—users and search engines.
Verifying your headings
Let’s assume you’ve gone through all of the H tags you have on your site and optimized them (usually, it takes a lot of time to do it manually). So, how can you check to make sure all of the work you put into it wasn’t in vain?
Inspecting an HTML Element
When using browsers like Google Chrome or Safari, right-click on an element, and choose “Inspect” and “Inspect Element” respectively.
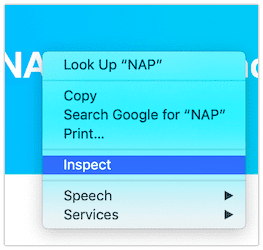
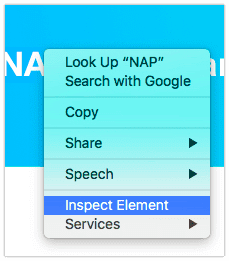
Inspecting an element in Google Chrome (left) and Safari (right)
This will open up a panel that will allow you to view both HTML and CSS info for the selected element. Just look to see if it has an <h*> tag anywhere around it.
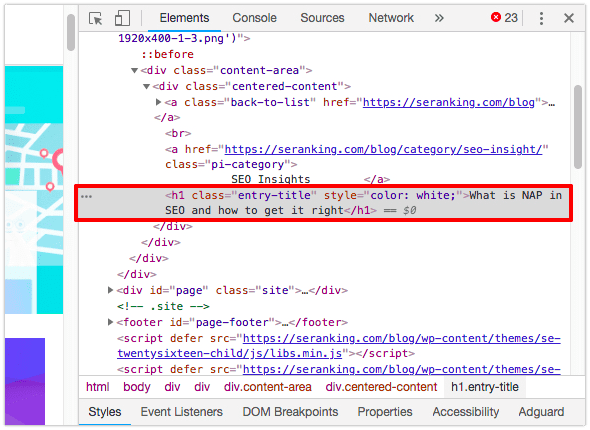
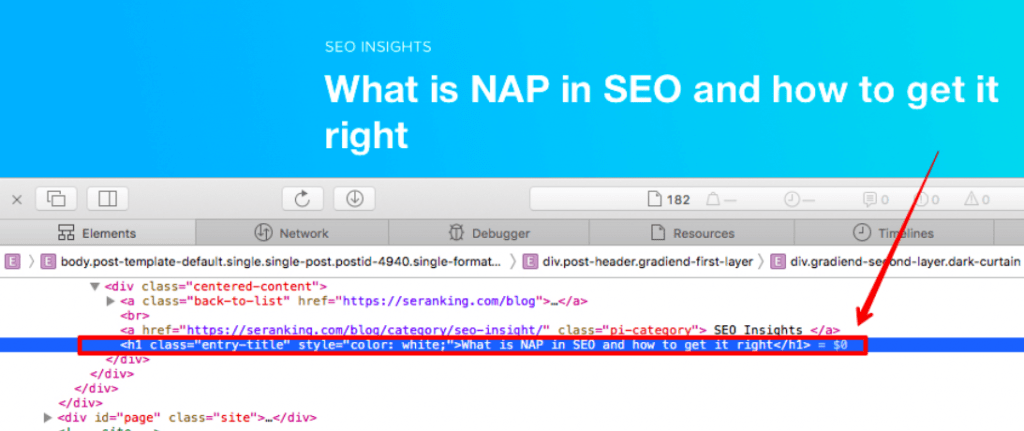
Analyzing the Source Code
When using the Google Chrome and Safari browsers, right-click an HTML page and select “View Page Source” or “Show Page Source” respectively.
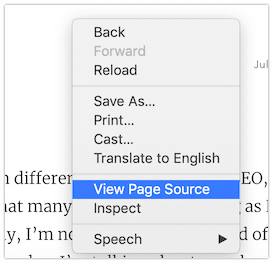
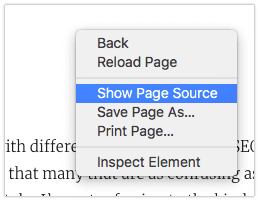
In the window or panel that opens up, use CTRL+F and ⌘ Cmd+F respectively to enter the H tag you’re looking for. If it’s not there, you know the drill: back to the drawing board.
Checking headings in WordPress
With most of the websites that exist today using WordPress, chances are you’re employing it too for all your publishing needs.
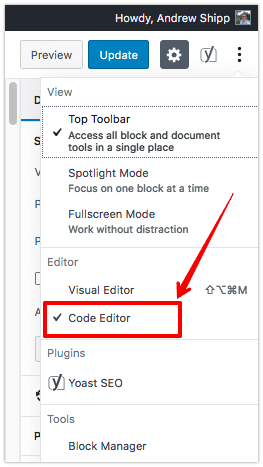
So, in order to make sure your H tags are all in place as intended, all you have to do is click the three-dotted menu in the top right-hand corner, and switch from the Visual Editor to the Code Editor to view the page’s HTML code, as shown below:
Check your H1 and other headings with automated solutions by SE Ranking
Retro-checking your site’s headings manually seems like an impossible, never-ending task, especially if your website’s been around for a while and it has dozens or even hundreds of pages. Luckily, there are a number of tools out there that can perform this task automatically.
At SE Ranking, we have developed two tools that specialize in scanning your entire website, as well as doing an on-page SEO analysis of a specific web page.
Let’s take a look at what each one of them can do to help you optimize your HTML H tags.
Website Audit
To get comprehensive website audit reports and quickly check the headings, use SE Ranking’s Website Audit. The tool will give you a list of your pages along with their h1 and h2 tags and will automatically point out issues with your HTML headings. You’ll also get instructions on how to fix them. By the way, you’re welcome to take advantage of the free trial to try out all of its features.
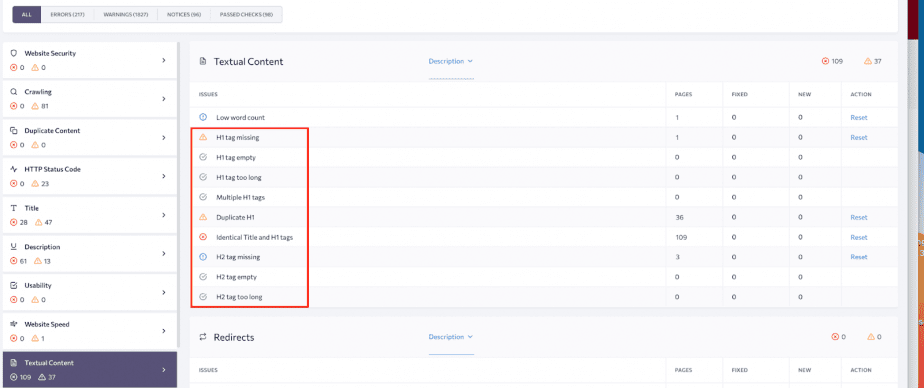
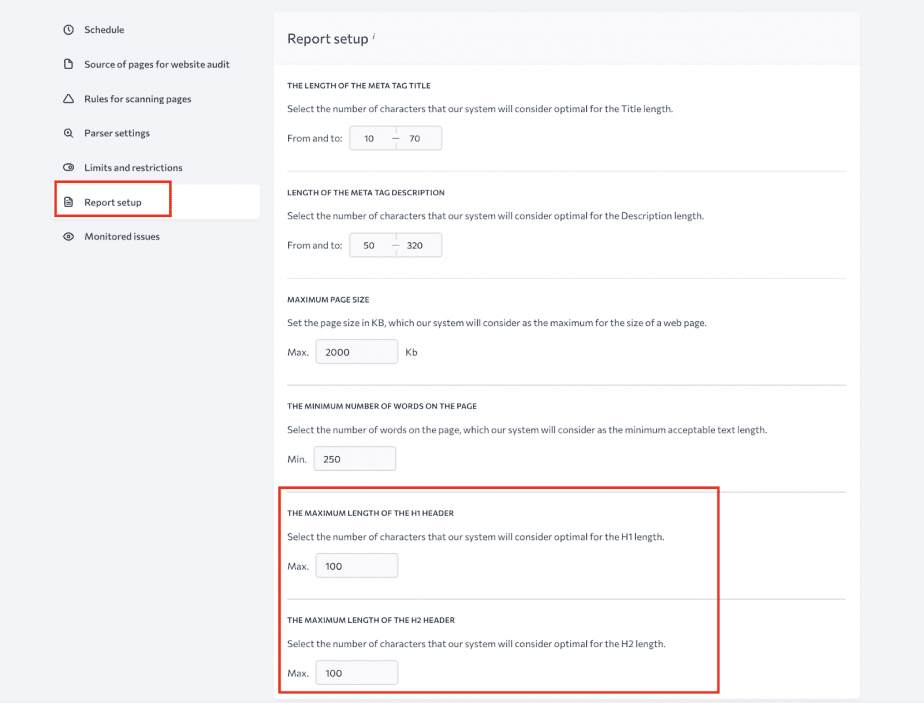
While the default limit set on the length of the <h1> and <h2> tags is 100 characters, the tool allows customization so that you can easily change it if you’re getting good results with longer or shorter headings. That way, the audit won’t see it as an error if your tags go above or below the 100-character limit.
Learn how to audit a website properly in our new guide and get a checklist will all the basic steps.
On-Page SEO Checker
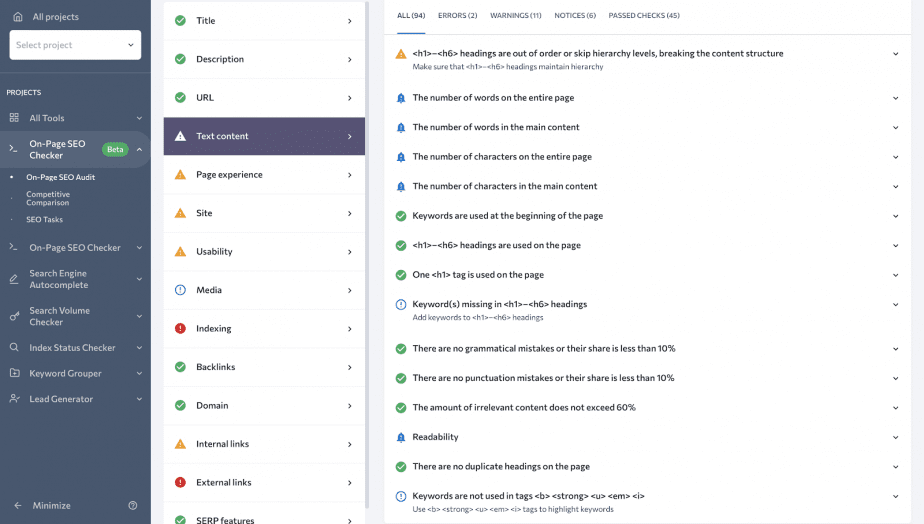
An alternative solution is to conduct an on-page SEO check of a specific web page and make a meaningful analysis of all its headings. You can do this with SE Ranking’s very own On-Page SEO Checker. As the name suggests, it can audit a specific web page against the target search query, and provide deep insights via a comprehensive SERP analysis. Also, this tool checks not only h1 and h2 tags as Website Audit does, but every H tag on your page as well.
Under the On-Page SEO Audit tab, you can see a separate section labeled Text content that is devoted to analyzing textual content, including HTML heading tags.
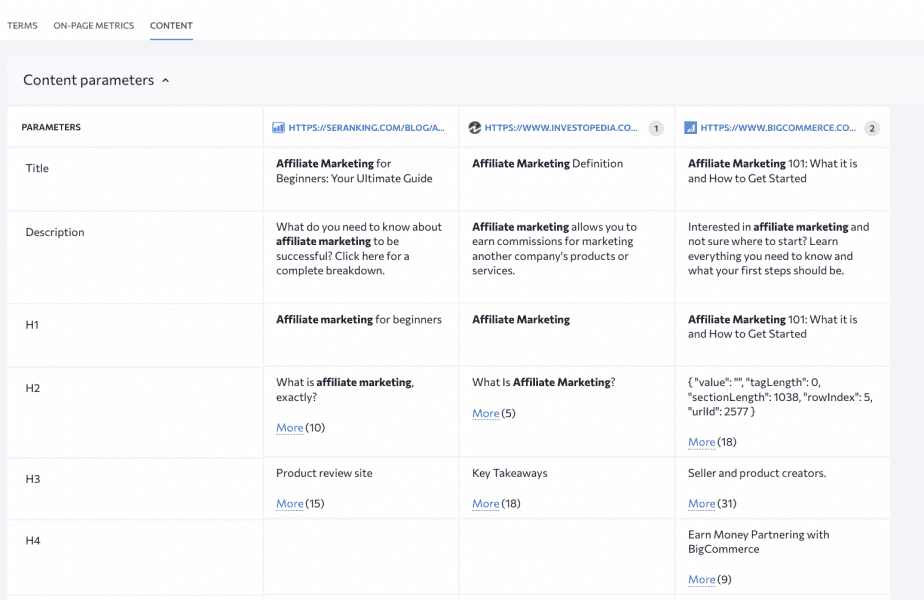
On top of that, go to Competitive Comparison and find the Content tab there. Here you can check all of the headings that your main SERP competitors have.
Apart from that, this tool also evaluates several other elements of on-page SEO including the description, URL, content, images, interlinking, page experience, and more, which can immensely aid in enhancing your on-page SEO endeavors.
Final thoughts
The proper use of HTML heading tags helps enhance the experience of your readers by improving your content’s readability and accessibility. Plus it can even have an impact on your SEO as these HTML elements provide search engines with important information.
So, make sure to add HTML heading tags to your content, but remember to follow best practices for maximum effect.
I hope this post will be a reference point to you for implementing heading tags and following SEO best practices. Do let me know if I missed anything, or if you had a different experience with H tags!
