Defining semantic SEO and how to optimize for semantic search
The search has changed dramatically over the past decade, with semantic web technology emerging as a key feature. Users now expect search engines to grasp natural language better than ever before. And yes, Google has achieved some remarkable accomplishments in language processing.
When search engines were less advanced, it rarely took one click to find precise answers to queries. Today, Google delivers extremely accurate results by interpreting the intent behind the user’s entire query and providing targeted, helpful answers quickly. This often includes instant responses in the form of AI Overviews or featured snippets.
-
Semantic SEO is about topics, not keywords.
Semantic SEO means optimizing your content for entire topics and user intent instead of just stuffing keywords into your text. It considers how concepts relate to each other and what users are actually trying to find.
-
Entities are essential for semantic SEO.
Entities (e.g., individuals, places, organizations, concepts, etc.) helps search engines understand semantic relationships. For example, semantic search can distinguish “apple” the fruit from “Apple” the company by analyzing context and related entities. Google’s Knowledge Graph and embeddings map these entities, improving semantic SEO comprehension.
-
Semantic SEO is even more critical in the era of AI search.
LLMs expand queries into multiple related questions and synthesize comprehensive answers using semantic understanding. Pages optimized for semantic structure, relevance, depth, and clarity are more likely to be cited by AI systems.
-
Implementing semantic SEO requires a multistep approach.
Effective semantic SEO combines semantic keyword research, structured content creation, and metadata optimization. Using pillar pages, content hubs, and topic clusters helps organize content logically and builds topical authority. Adding internal links, FAQ sections, and semantic markup further adds context and creates semantic relations between articles.
-
Start with semantic keyword research.
Identify semantic keywords, long-tail phrases, and LSI terms using tools like SE Ranking or Google search suggestions. Group them by topic, intent, and search volume to plan your content efficiently. Organizing them into pillar clusters, content hubs, or topic maps ensures your pages are contextually connected and optimized for semantic SEO.
-
Next, optimize page metadata for semantic relevance.
Clear, descriptive metadata increases semantic relevance and the likelihood that LLMs cite your content. For example, research shows that pages with high semantic alignment in meta descriptions can receive up to 4.7 AI citations versus 4.1 for low-alignment pages.
-
Produce in-depth, well-structured semantic content.
Answer user questions thoroughly, use semantic HTML, and structure sections with question-based headings. Plus, our research data shows that pages with integrated FAQ blocks in your main content average 4.9 AI citations versus 4.4 for pages without. So, make sure to include comprehensive FAQs and related subtopics where it is relevant throughout your content to AI visibility.
-
Build a logical internal linking structure for semantic SEO.
Use descriptive, topic-focused anchor texts to link related pages and reinforce semantic relationships. For example, linking a main “sneakers” page to a “kids sneakers” page helps search engines understand the connection between topics and can improve the visibility of the subpage for related queries.
-
Use structured data to boost semantic SEO.
Structured data turns your content into “machine-readable” information, which allows search engines to identify relationships between entities more easily (like marking events with dates and locations, and so on). This helps your pages appear in rich results and improves contextual relevance for AI and traditional search engines.
What is semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the process of optimizing your content for a topic rather than a single keyword or phrase. It looks into user intent, user experience, and the relationships between related entities and concepts. This approach helps search engines deliver more meaningful results and enhances the overall user experience in search.
Semantic SEO and entities
Since search engines are not human and don’t have an emotional connection to concepts and ideas like us, Google had to take, a mathematical approach to “explain the world” to them. This resulted in Google’s User-context-based search engine patent.
This system is designed to identify informational context by analyzing words, phrases, and their combinations. It divides information into distinct topics (domains) and identifies unique words or phrases that help classify the content. It creates a vocabulary list, where each word has a “context vector” based on its appearance rate in each domain.
When a topic belongs to a unique domain, Google can use its knowledge base to understand the topic’s meaning. It looks for related terms from that domain to determine the page’s topical context.
Also, note the importance of entities in this context, which are individuals, places, organizations, concepts, or any distinct object or idea that holds meaning.
Search engines use entities to better understand the relationships between different concepts and the contexts they appear in. Entities allow search engines to transcend literal keyword matching and grasp the intent behind a search query. For example, if a user enters a request containing “apple,” search engines can figure out whether they mean the fruit or the company by looking at the context and other related entities in the query.
This is possible thanks to embeddings, which help computers understand both the meaning of words (semantic) and how they are used in sentences (syntax). Embeddings transform words or phrases into numbers (vectors) by placing similar words closer together in a virtual space. For instance, in this vector space, words like “king” and “queen” appear near each other because they are strongly related. Instead of searching through all the data, these vector databases compare numerical representations (vectors) to find the closest match.
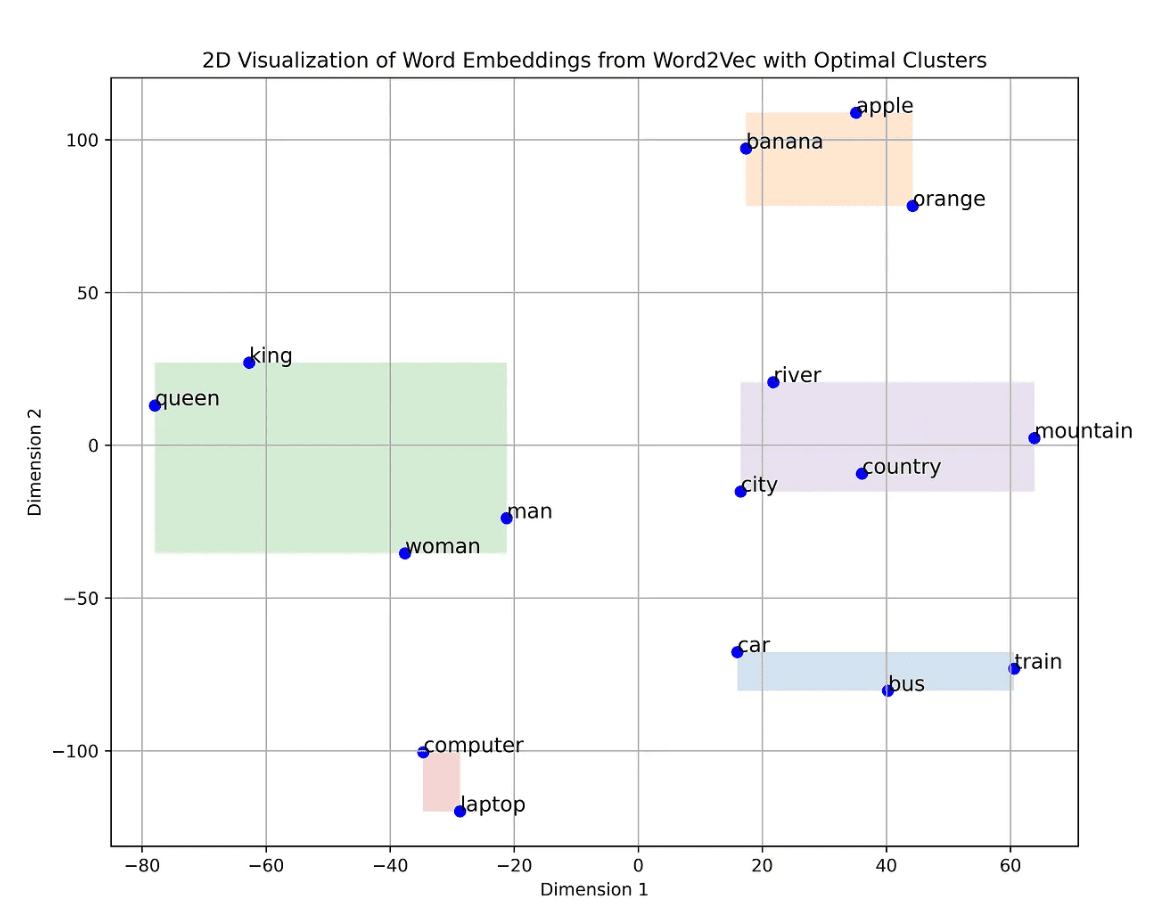
Google organizes entities and their interrelationships using a framework called the Knowledge Graph. This can be thought of as a vast network of interconnected domains on the subject matter. Here’s what it looks like:
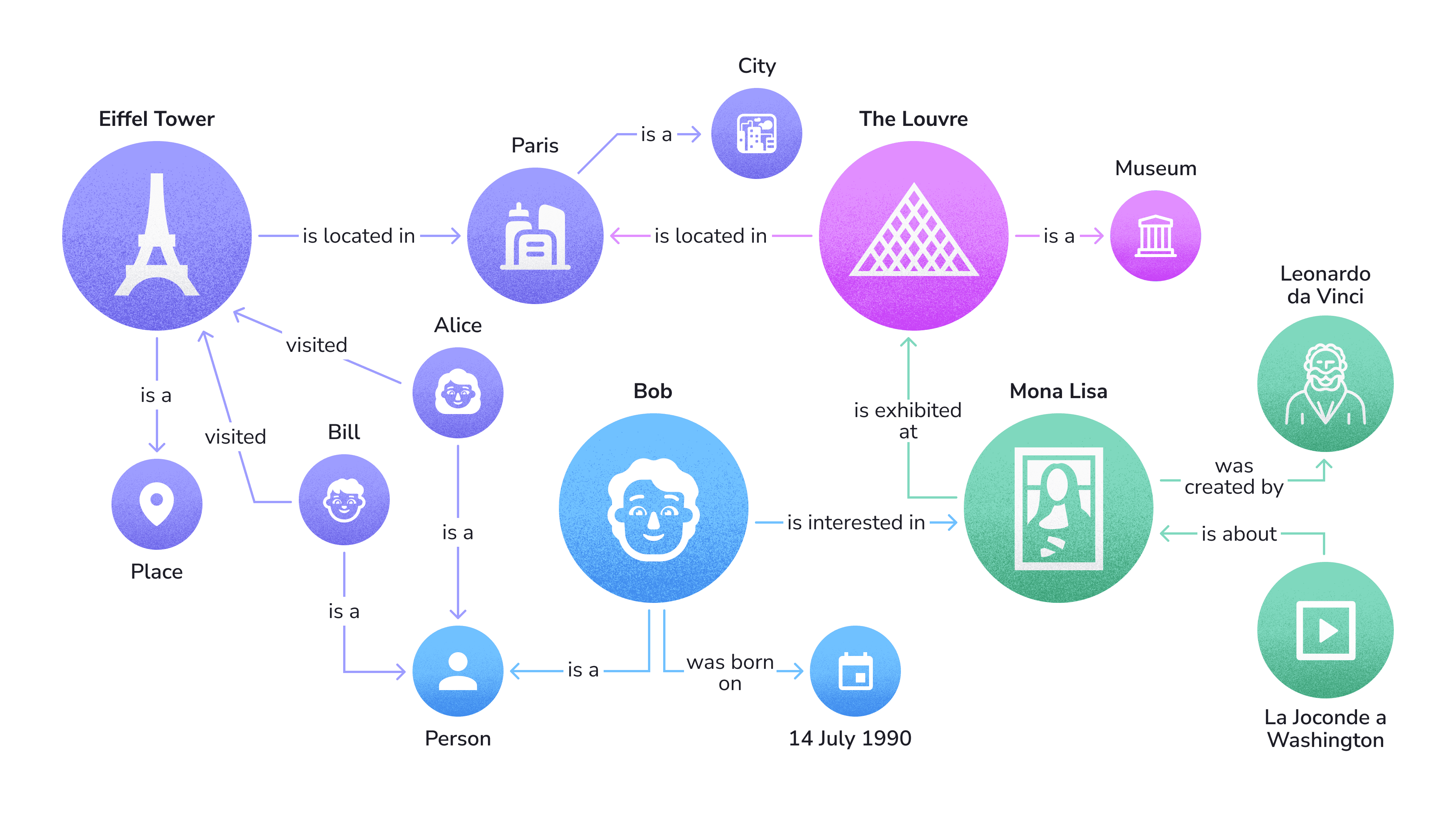

The main goal of semantic SEO is to build context on and around your page so its embedding aligns closely with the embeddings of users’ related queries in a vector space. This helps the mathematical model identify your page as relevant to the user’s query.
Why is semantic SEO important?
Semantic SEO isn’t a new idea. Even back in the days of “classic” search engines, it wasn’t just about stuffing a page with keywords. Search engines were already trying to understand intent (what a user actually meant, not just what they typed).
Now, with AI search, semantic SEO has become not just helpful but essential. Generative AI doesn’t simply match keywords to pages; it interprets meaning, evaluates relevance, and looks for content that genuinely answers a question.
A big reason for this comes from the process of query fan-out. Instead of treating a search as a single, isolated question, AI expands it into multiple related queries and synthesizes the answer based on the data found on several sources.
Still, as people use more conversational, natural language in search, it becomes impossible to predict and optimize for every possible way a user might phrase a question. What is possible, however, is understanding user intent (what they’re really trying to achieve) and creating content that meets that intent relying on entities rather than direct keywords.
For example, when someone searches “how to lose weight safely,” AI might combine insights from related areas like diet, exercise, and lifestyle to provide a clear, actionable answer.
So, your content needs to be a trusted source across a web of related questions, not just one isolated query. Semantic SEO, once a “nice-to-have,” is now the foundation for visibility in both classic and AI search.
Semantic SEO best practices
In old-school SEO, you could perform a site audit, choose a keyphrase, use it in your title/description, headers, and throughout the text, and then cross your fingers and hope to rank for it. However, if you’re a webmaster in today’s evolving search landscape, you’re going to come across some big challenges.
Fili Wiese, a technical SEO consultant at SearchBrothers and ex-Google engineer, suggests taking a more comprehensive approach.

Divide your work into three following stages to use semantic SEO properly: keyword research, content creation, and optimization.
Perform semantic keyword research
In the first semantic SEO stage, focus on choosing a topic based on user intent. Compile a list of relevant keywords.
Here is our recommended action plan for this stage:
- Create a keyword list. Compile a list of related keyphrases and LSI keywords that are semantically related to your target keyphrase.
- Perform semantic analysis. Use tools to analyze keyword relationships, uncover hidden connections, and align your content with user intent.
- Identify long-tail keywords. Identify long-tail keywords that address your topic and have a clear intent.
- Systematize your keyword list. Organize your keyword list by combining similar queries into groups. This process is called keyword clustering, or grouping.
Use Google to create a keyword list
While you shouldn’t rely on Google alone for keyword ideas, it’s a great place to start.
Begin by thinking about the keywords you want to rank for. For example, if you run a yoga studio in LA, you probably want to rank for commercial keywords like “yoga school” or “yoga studio LA”, but you’ll also want your blog to rank for informational queries like “downward-facing dog” or “meditation techniques.” Here’s how to uncover the most popular queries.
- Google suggestions
As you type a keyword into Google, several suggestions will appear. These are a mix of trending semantic keywords and suggested search terms influenced by search patterns.
Don’t forget to include long-tail keywords in your list. These queries tend to be more specific, often taking the form of questions or full sentences.
- People Also Ask (PAA)
The “People also ask” section in Google can become a valuable source of related topics that Google associates with your target query. Each question listed is a potential topic your audience is interested in, and exploring these can help expand your content ideas.
- Related searches
You can also scroll to the bottom of the SERP to find “Related searches,” which often uncover additional keyword ideas you might not have thought of.
- Synonyms and LSI keywords
Although these keyword types are often confused with one another, keep in mind that not all related search terms are synonyms.
For example, “yoga asana” and “yoga pose” are synonyms. The search term “yoga class”, however, is only related to the previous phrases and does not have the same meaning.
You can find synonyms and LSI phrases either by using an autocomplete feature or looking at the bottom of the SERP.
You can keep exploring to gather all the queries Google has to offer. Looking at these keywords might even spark some ideas for related queries of your own.
To support a strong semantic SEO strategy, it helps to understand how search interest evolves over time. Our Google Trends for SEO guide shows how to use trend data to identify timely topics, seasonality, and related search queries that support broader semantic relevance.
While using Google is a time-tested way of collecting semantic search data, you can also use semantic SEO software to speed things up and get better results.
Search for keywords with SE Ranking
SE Ranking’s Keyword Planner has a huge database that goes beyond search engine suggestions. It hosts over 4 billion unique search queries, which means you can generate thousands of keyword ideas in one click.
Each keyword has plenty of metrics, including its Google search volume, which is the number of monthly searches it gets. The yoga topic, for example, has 550K monthly searches.
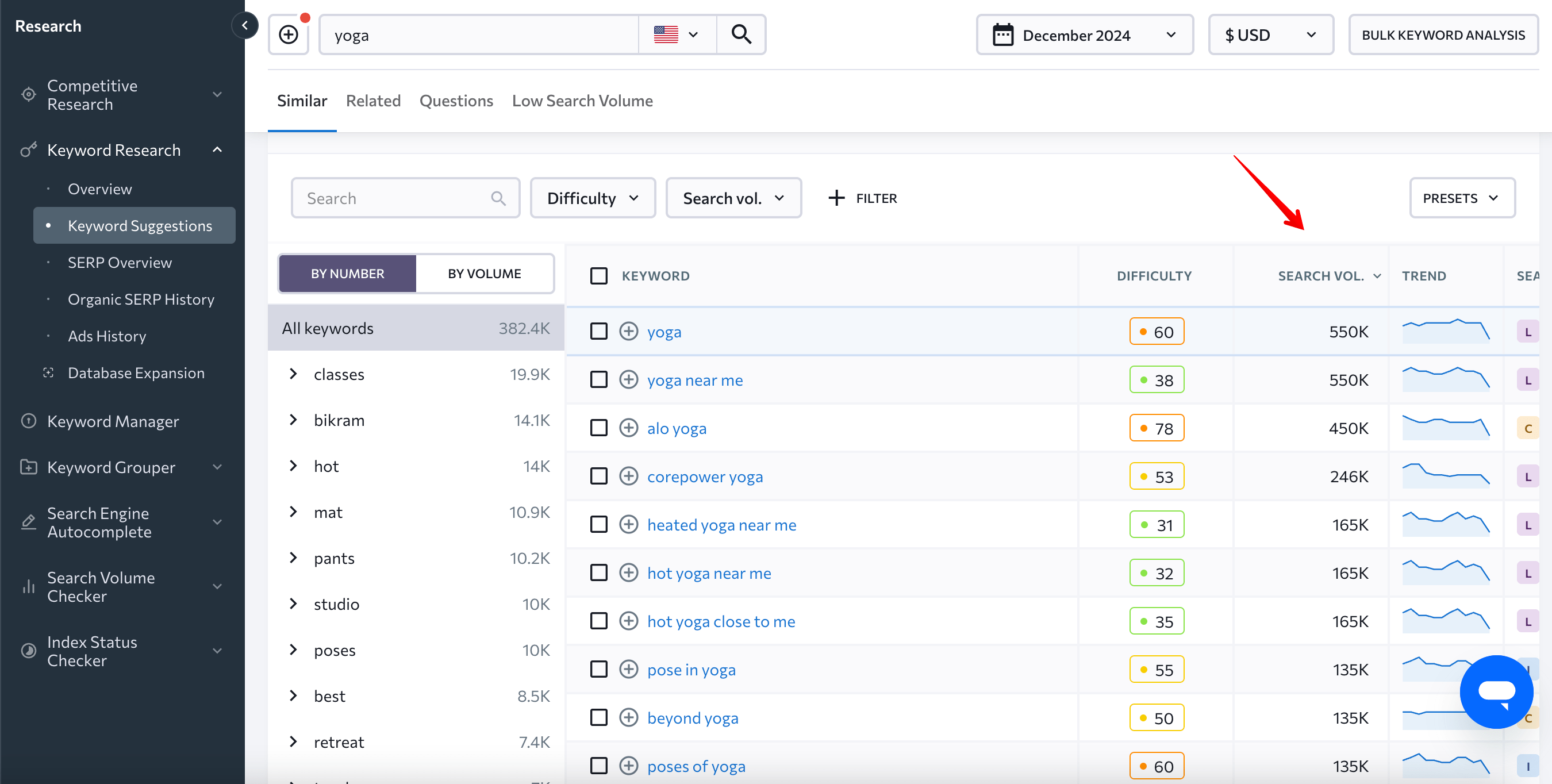
You can use filters to leave out keywords that you don’t intend to rank for. For example, it’s possible to filter out keywords with super high search volumes. These keywords are generally too vague and overly competitive.
For more ideas, go to SE Ranking’s Related, Questions and Low Search volume tabs. While the Similar keywords tab only features search terms with variations of the seed keyword, the Related keywords tab presents a wide range of semantically related queries.
SE Ranking also lets you perform competitor research to draw keyword ideas. You don’t even need to choose which competitor to analyze—the Competitor Research tool will identify your top SEO rivals and come up with a list of keywords that you’re not ranking for but your competitors are. This helps you discover some of the more obscure but useful topics related to your business niche.
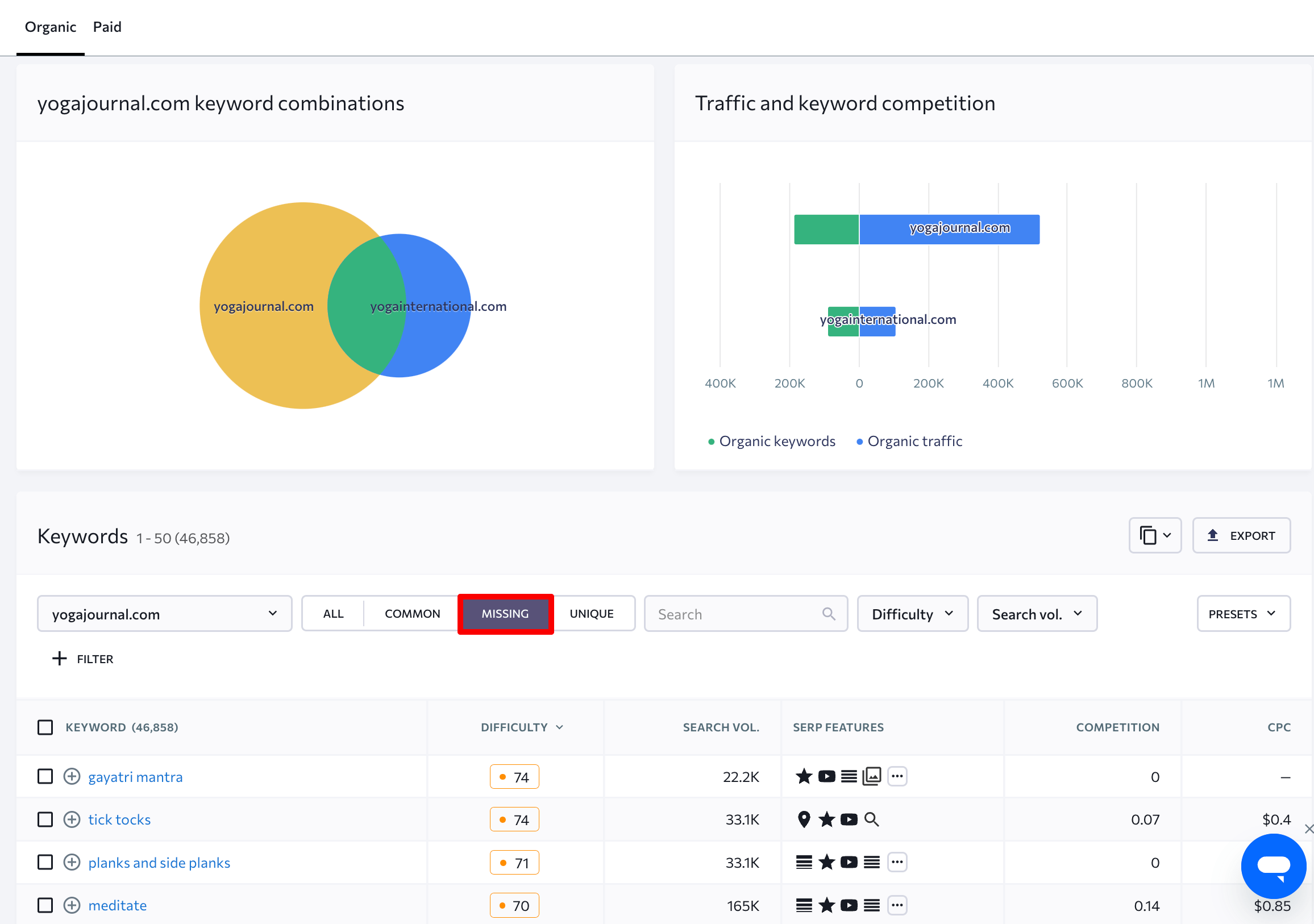
Pro tip: Find topics to get more visibility in AI.
If you also want to see what topics AI engines are looking for under the hood when composing answers to your focus queries, start tracking them in AI search tools like AI Mode, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and others using our AI Results Tracker.
Once you have ranking data, you can see the URLs that these AI engines used as sources when composing answers to your target query. Then, look at the titles and H1s of those pages. The topics they cover are potential candidates for your own content.
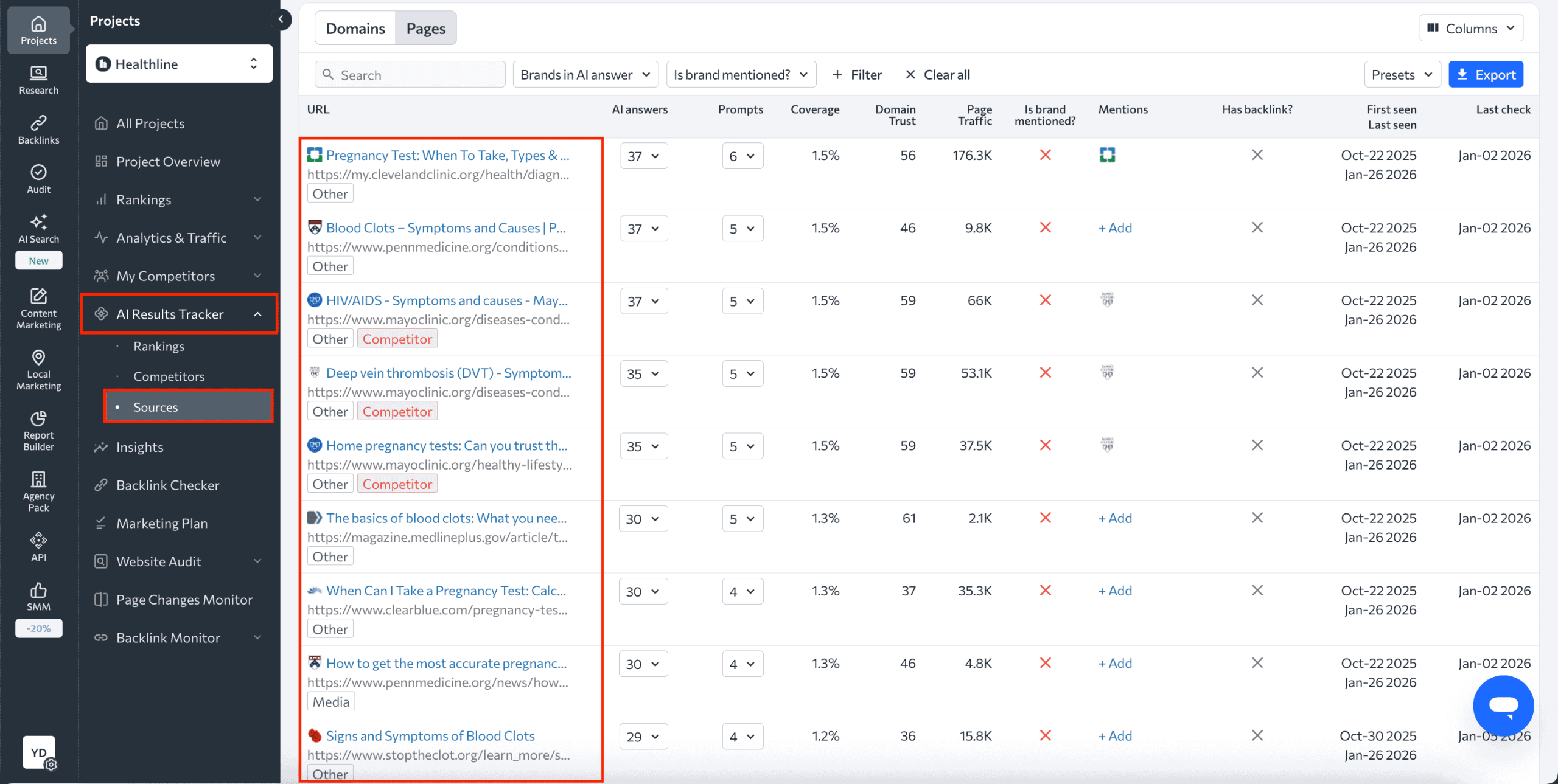
By creating content around these ideas, you increase the chances that AI systems will reference your pages when answering similar queries.
Cluster all of your keywords
Once you’ve gathered your keywords from all possible sources and compiled them into a spreadsheet, remove any duplicates. Now you can move on to keyword clustering.
Observe your list closely and think of ways to categorize keywords into different groups.
Let’s say, for example, that you have a long list of keywords about “yoga asanas”.
Here are some ways to group them:
- By their semantics: “yoga poses”, “yoga postures”, “asanas list”, etc.
- By user intent: “how to do yoga asanas”, “what are the beginner yoga poses”, etc.
- By search volume: high-volume keywords versus low-volume keywords, etc.
Grouping keywords by search volume helps you in structuring your website. Think of high-volume keywords as categories, and low-volume keywords as potential article topics or service/product pages.
Semantic search engine optimization entails creating content clusters based on topics rather than keywords. Use the pillar cluster model, content hub, and topic maps to group content according to semantic SEO principles.
To apply the pillar cluster model, group keywords by topic for each page. This method organizes topics by grouping more specific subtopics under a broader main topic. This allows you to group keywords around a central theme while breaking them into multiple distinct pages. Topic clusters help search engine bots understand the context, relationship, and hierarchy of each page within a structured content framework.
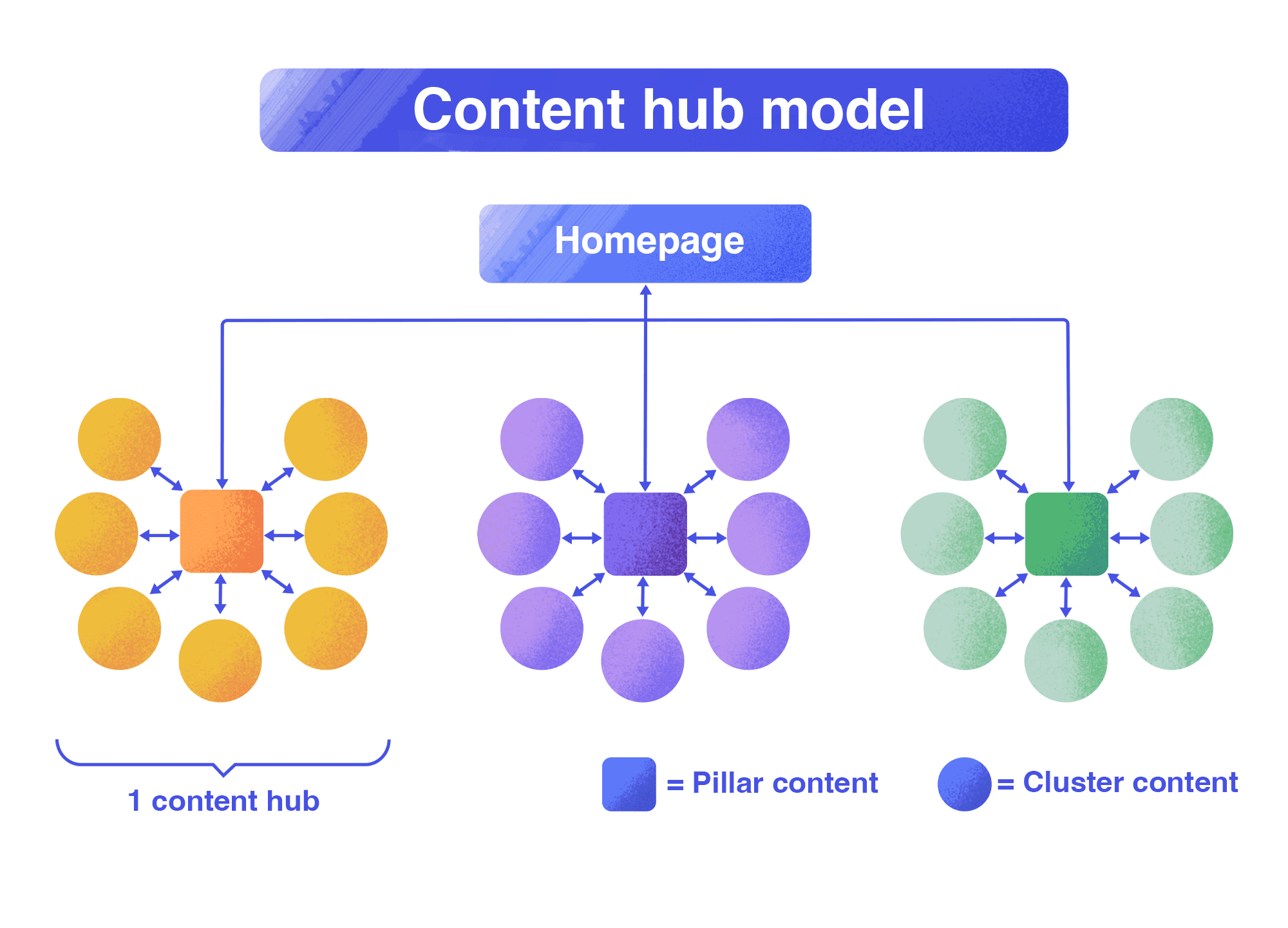
Once you have grouped keywords by their main themes and supporting subtopics, you can use the content hub method to organize them on your website. Content hubs are centralized collections of all your content on a specific subject, designed to serve as a comprehensive resource. The hub comprises the pillar page, which covers the broadest aspects of the main topic, and supporting pages that explore specific subtopics in detail. These pages are connected with hyperlinks.
Another method for clustering your keywords and structuring your content is topic mapping. This is similar to the knowledge graph, where pages are grouped and linked based on associations, which represent relationships between topics. Unlike the pillar and content hub methods, there is no distinction between the primary and supporting content. This approach is designed to connect topics in a semantically meaningful way.
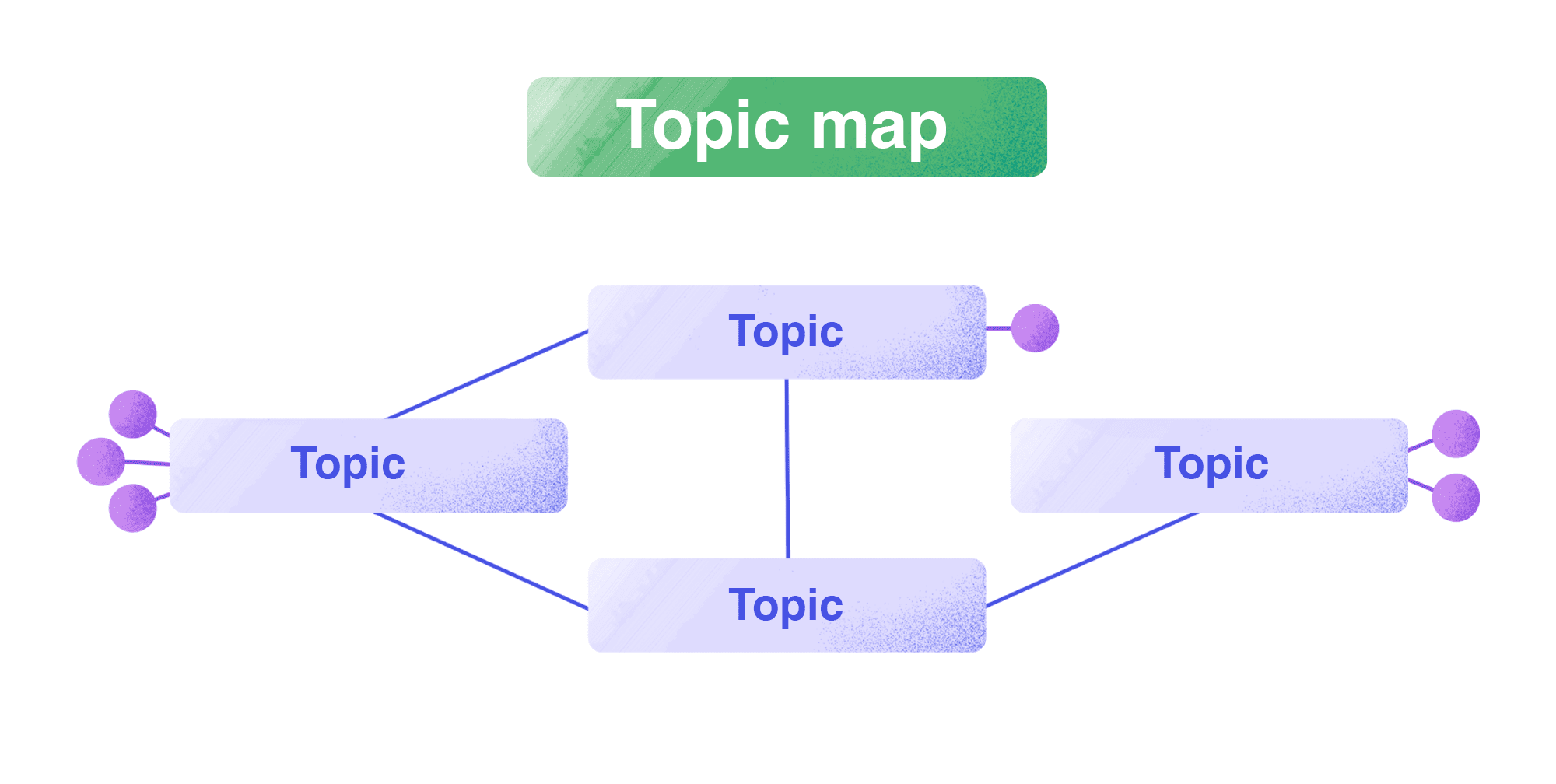
Note that all of these cluster methods are unique, but each can organize your content effectively while avoiding keyword cannibalization.
That’s it for traditional keyword research and clustering. You can brainstorm ideas using search engines or streamline the process with SE Ranking. Then you can add new topics to your content plan and group pages by theme.
Optimize page meta data for semantic relevance
URLs, titles, and meta descriptions do more than help users. They signal relevance to search engines and LLMs.
Specifically, AI systems calculate the cosine similarity between a user’s query and your page’s URL, title, or meta description to decide how relevant your page is for a given topic.
So, the more your meta data clearly reflects the content and intent of your page, the more likely AI search engines are to reference your page as a source when generating answers.
- URLs
Avoid generic or overly narrow URLs. Instead, aim for descriptive URLs that cover the topic as a whole. These types of URLs naturally receive more citations in AI search.
For more insights on creating SEO-friendly URLs, see this article.
- Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions used to be mainly about boosting CTRs. And in classic SEO, that’s still true. But in the era of AI search, they play a bigger role.
They act as ranking signals for AI citations. Data shows that higher semantic alignment in meta descriptions directly correlates with higher citation counts. Pages with low-relevance descriptions (0.00–0.48 similarity) average only 4.1 citations, while higher alignment steadily improves visibility (up to 4.7).
Check out this guide for best practices on meta descriptions.
So, make sure to create meta descriptions that accurately describe the topic of the page. Clear, comprehensive descriptions help AI models understand your content and increase the likelihood your page is cited.
Produce in-depth, well-structured content
Now that you’ve gathered all your keywords and optimized metadata, let’s explore how to write content with semantic search optimization in mind.
Use semantic markup
Semantic markup is just as critical to achieving higher rankings as performing careful keyword research.
Semantic markup, also known as semantic HTML, is a set of elements that clearly outlines the structure of your content and gives it meaning.
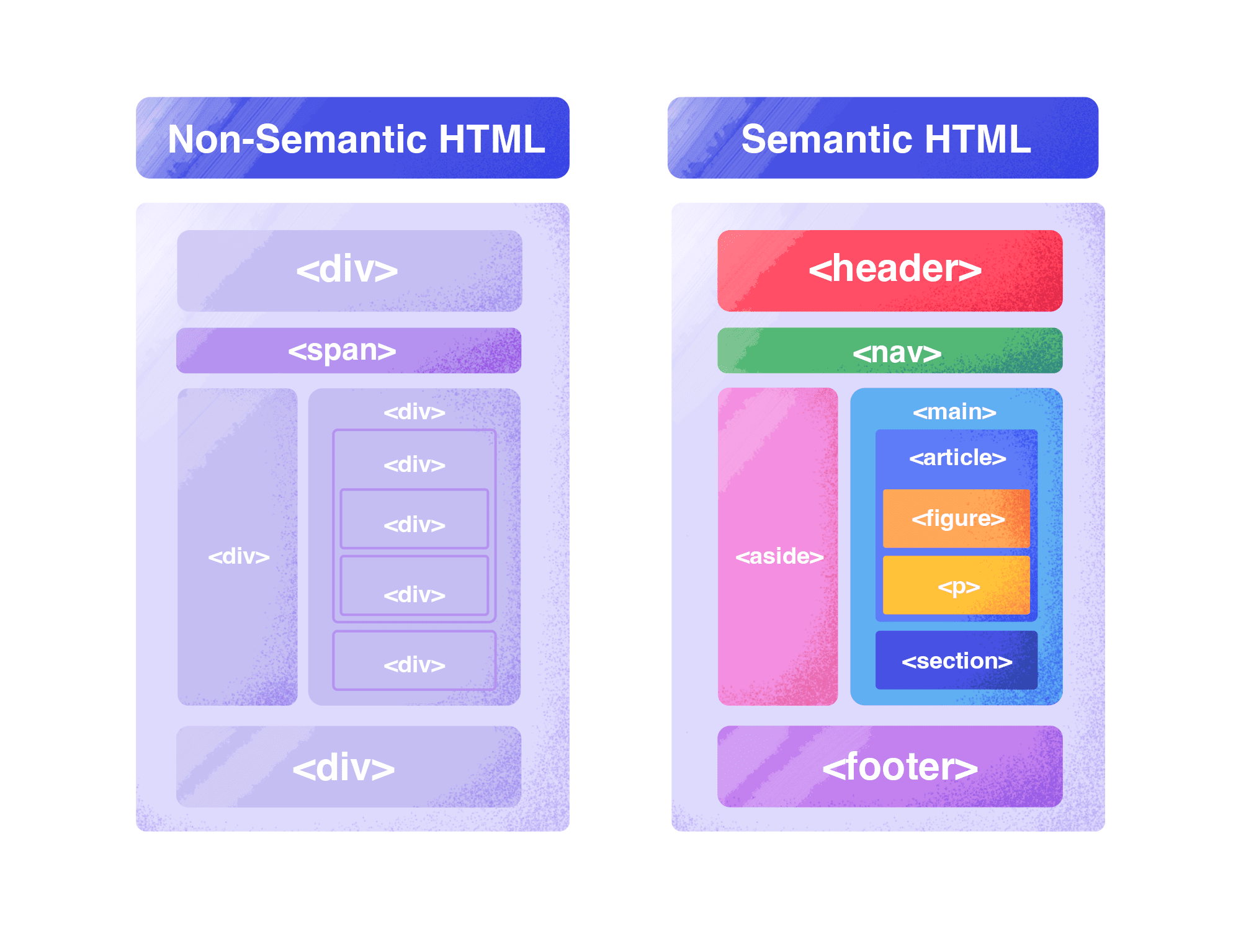
For example, an <h1> tag indicates that the embedded phrase is the title of your article. This is both presentational and semantic markup because it shows users and search engines where the title is.
Here are some examples of semantic HTML tags:
- <h1> through <h6>
- <blockquote>
- <form>
- <table>
- etc.
Semantic elements can help some parts of your content, like lists, appear as featured snippets.
Structure content with questions
Still, when using <h1> tags for page structure, consider how you phrase them to improve AI visibility. Instead of generic statements, frame your blog post sections as direct questions whenever it’s relevant to the content.
Why this works: Our research shows that pages that use question-based titles or H1 headings tend to perform slightly better in AI Mode. Data shows such URLs average 4.6 AI Mode citations, compared to 4.5 citations for those with non-question headings. This likely happens because clearly phrased questions help AI Mode identify intent and extract concise answers more efficiently.
For detailed guidance on structuring HTML headings effectively, see this guide on HTML heading tags.
Key tip: Always align your H1 with the main question your content answers. Subheadings (H2, H3, etc.) can then support specific aspects of that answer.
Use FAQ blocks effectively
Next, adding FAQ sections or Q&A blocks directly within your main content can significantly improve AI visibility.
Why it matters: Our data confirms that pages featuring FAQ blocks in the main content average 4.9 AI Mode citations, compared to 4.4 citations for pages without them. This shows that AI Mode rewards content that directly answers user questions rather than content optimized only for metadata or keywords.
Note: Simply adding FAQ schema markup without visible answers does not impact AI Mode citations. The model looks for actual text content that clearly answers questions.
Actionable tips:
- Include headers like “Frequently Asked Questions” or “Common Questions” to signal to AI that these sections contain direct answers.
- Format each FAQ as a clear question followed by a concise, complete answer.
- Integrate FAQs throughout the article where relevant rather than clustering them at the end, to keep the content informative and contextually rich.
Make your content richer, not longer
Simply stuffing your content with keywords won’t cut it anymore. These days, the content around your keywords must meet user intent to rank high. Think about the topic, not just the keywords, and make sure you’re meeting your customers’ needs and not mindlessly inserting key phrases into your content.
Here’s what Lee Wallis, Head of Digital at Excite Media, Winner for SEO—Australian Web Awards 2021, suggests:

Whenever possible, try to prioritize evergreen content.
Use special tools to learn how to optimize your content
Specialized tools can enhance your semantic writing process and increase your chances of success against your competitors. Plenty of content tools are available to help with semantic SEO automation, saving you time and money by generating and optimizing text for search. We’ll go over how to use them, specifically SE Ranking’s Content Creation Tool.
Begin by analyzing SERP content. The tool observes top competitors to determine how many words, headings, paragraphs, and images (such as infographics) your article should have. It also provides relevant keywords and key phrases.
Second, structure your content around your competitors’ best practices. Content Editor pulls headings from your competitors’ pages so you can incorporate them into your article or use them as inspiration as you plan and outline your content structure.
Third, use AI tools to expedite content creation. You can generate topics, headings, and paragraphs in mere seconds with AI Writers.
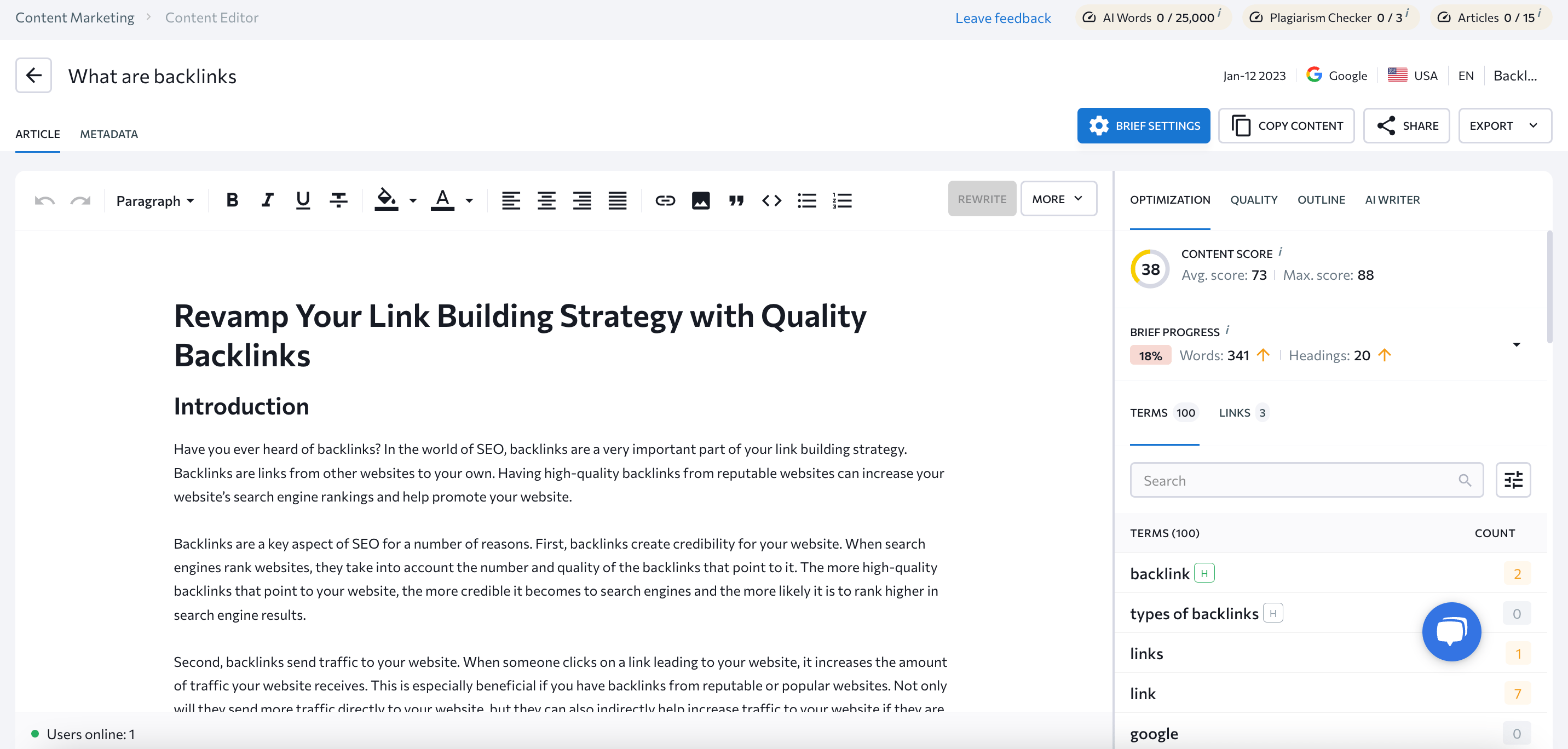
Next, respond to the tool’s content improvement recommendations, specifically on keyword usage, readability, grammar errors, and plagiarism. Use this instant feedback to refine and optimize your content as you progress.
From SEO optimization and keyword analysis to real-time content analysis and collaboration features, this tool improves your content’s quality, visibility, and search engine rankings.
Build a clear internal linking structure
Let’s move on to finetuning your semantic SEO writing with strategies around internal linking, including placing relevant anchor texts, and more.
Carefully constructing your internal link structure helps your content appear in the right place in search.
This structure contains three elements:
- Menu link structure
- Breadcrumb link structure
- Internal link structures in the body of the article
Linking pages together helps readers navigate your site while giving Google a clear idea of how to crawl and discover new pages on it. For example, a company that sells sneakers can have a basic “sneakers” page that appears higher in search results than a “kids sneakers” page for the query “sneakers for kids”. This seems illogical. However, if the main category links to the “kids sneakers” page, it can help Google prioritize the subcategory page for the given query.
In other words, with a smarter internal linking structure, the better your site will perform for both Google and users.
When setting up internal linking, make sure that your page contains topical anchor texts.
In the HTML code of a page, an anchor text looks like this:
<a href=”https://www.example.com”>Anchor Text</a>
Let’s say your page has a lot of links with anchor text about bikes. Google will use this information to determine the topic of the page your links point to. Here are some tips for working with anchors in semantic SEO:
- Use descriptive anchor text: It must reflect the meaning of the linked page to both users and search engines.
- Incorporate long-tail keywords: This keeps things natural.
Implement structured data
To help Google better understand your content, use structured data—a format for classifying page content. Structured data acts as a language that conveys the context behind your content to search engines. Google uses this information to make your content more attractive to users on SERPs.
Let’s look at the AccuWeather website. Google’s Knowledge Graph covers basic information about their company, including when it was founded, who the founder is, the headquarters, etc.
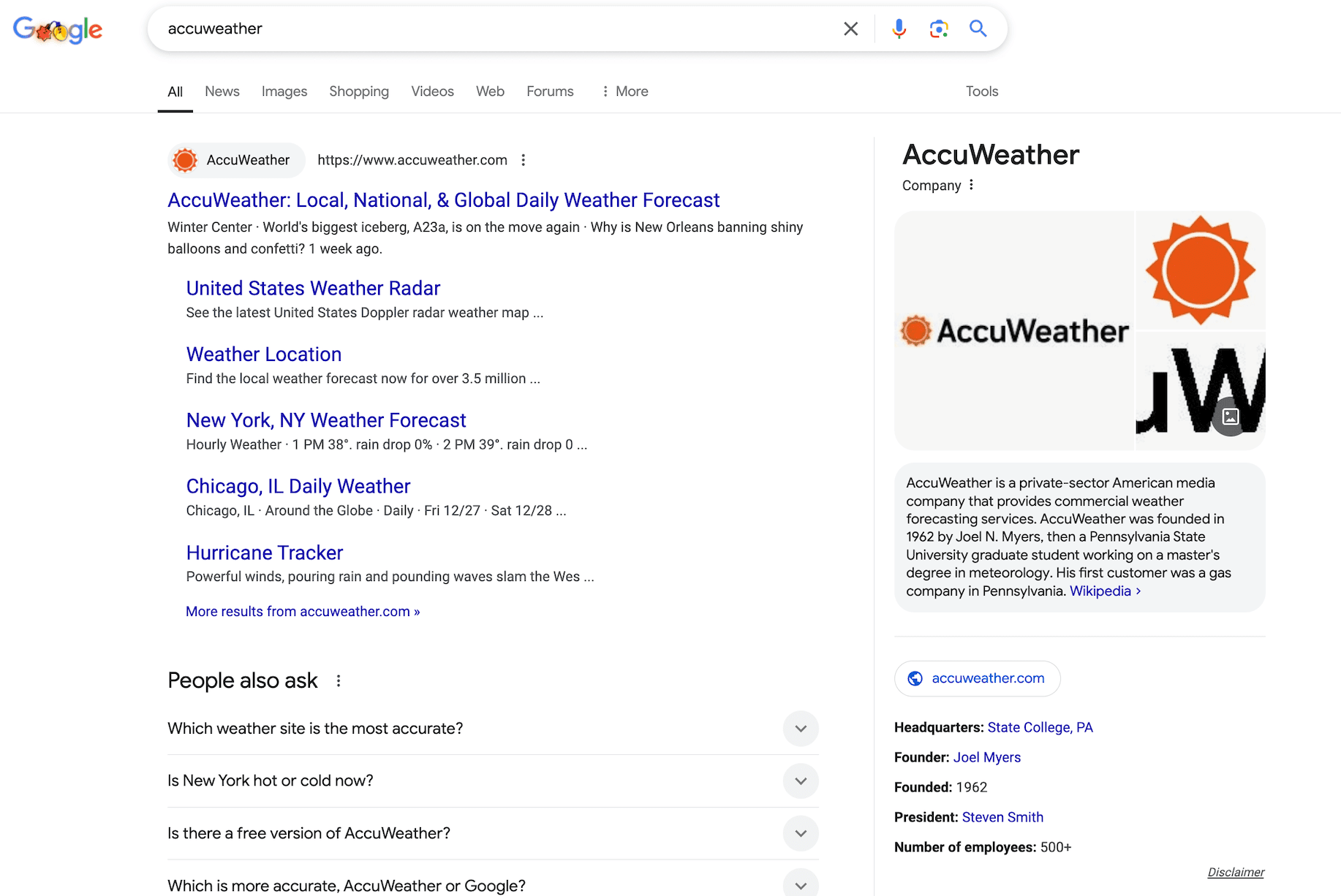
AccuWeather included structured data to help Google understand its page content.
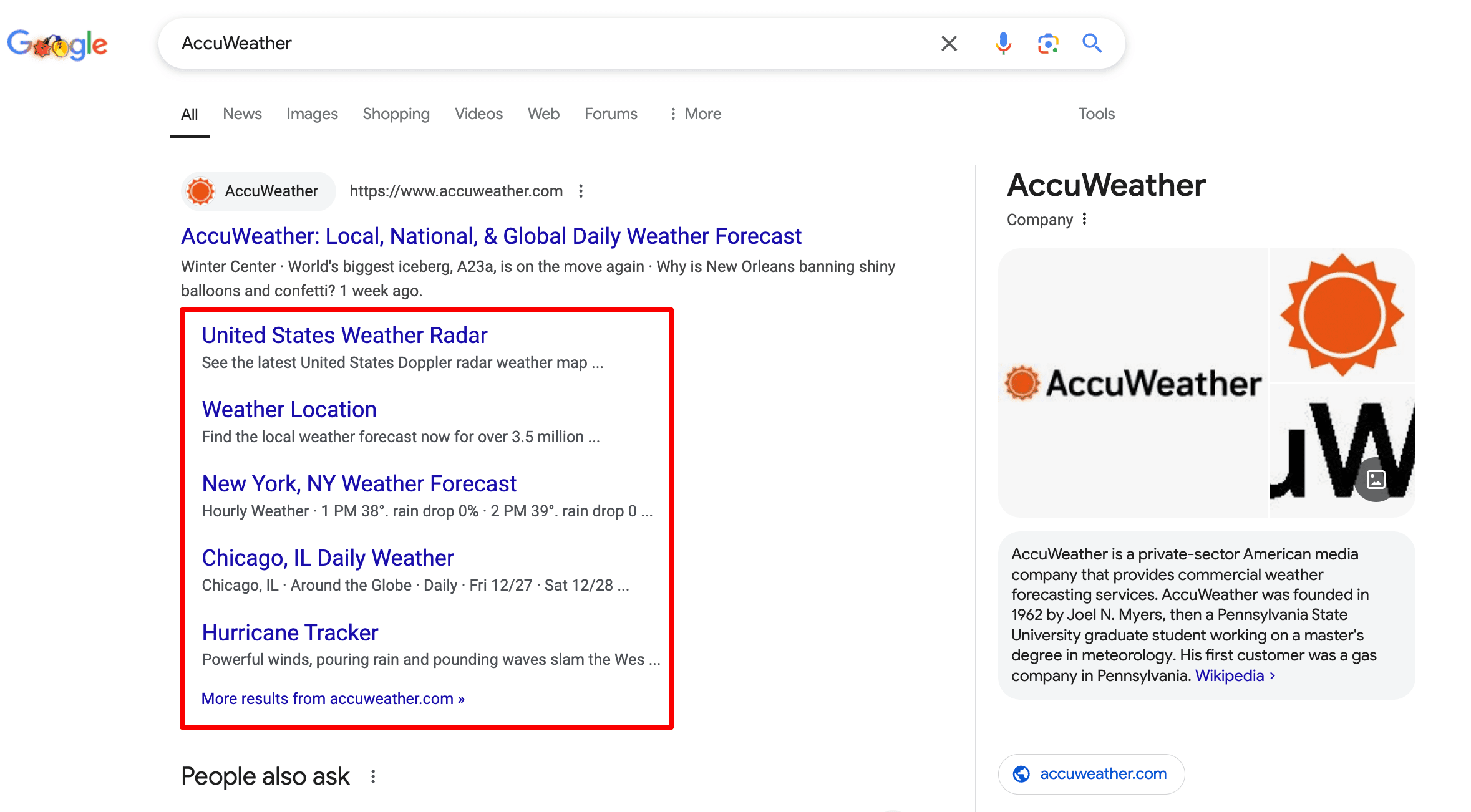
Users can see pressing news directly in search results because its structured data identifies individual elements of weather forecasts.
Conclusion
Ultimately, semantic SEO is about clarity, context, and helpfulness. Pages that do this well aren’t just optimized for search. They become trusted resources that AI and humans alike turn to for answers.
Following the steps in this semantic SEO guide, you should be able to think like a reader and a machine at the same time: provide concise answers, organize content logically, and connect related topics. When your content clearly explains a subject and anticipates follow-up questions, it naturally earns visibility in both traditional and AI search.