Google image SEO: How to optimize your images to boost their rankings
Content optimization is key to SEO success, but content is more than just words. Images play a crucial role as well, and ignoring their power can negatively impact the overall content performance.
In fact, research shows that images are featured on 37.81% of SERPs. Of course, this number significantly depends on the niche, user intent behind search, and many other factors. But the fact is that there is a huge potential behind image SEO. And businesses that ignore this trend risk falling behind.
In this guide, we’ll explore what image search optimization is, explain why optimizing images for search engines is important, and provide actionable image SEO tips to help you increase your chances of appearing in your target SERPs.
Key Takeaways
- Google image SEO is the practice of optimizing website images to enhance search engine visibility and ranking.
- The key steps of image optimization for search include creating original and useful images, maintaining high image quality and resolution, making filenames and alt text descriptive, adding captions, selecting appropriate format, and compressing image files.
- Stock images are acceptable for SEO but do not provide the same benefits as unique images. They are less likely to help your site stand out if used by many other websites.
- Google has adopted a permissive approach to AI-generated images. It focuses on transparency rather than prohibition by introducing labels for such images, including those altered with techniques like inpainting and outpainting.
- To audit your site’s images and get tips on how to optimize them, you can use SE Ranking’s Website Audit Tool and On-Page SEO Checker.
- To check if an image is available to Google, use the URL Inspection Tool in GSC for images hosted on your site. For images hosted on another domain, use the Rich Results Test.
What is Google image SEO & why is it important?
Image SEO is about optimizing each and every aspect of your website’s images to improve their visibility and ranking in SERPs. The effectiveness of this optimization is largely influenced by Google image ranking factors like image relevance and website authority.
Optimized images contribute to a better user experience. Fast-loading, relevant images enhance visitor satisfaction and encourage them to explore your site further. Search engines, in turn, reward user-friendly websites by giving them higher SERP positions.
Image search optimization can also bring visitors directly to your site. When your images rank high in the image pack or image search results, people can click on them and go straight to your page (bypassing the traditional text-based search results).
How Google image search works
Google Image Search operates in the three following ways:
- Image search by context.
- Reverse image search.
- Visual elements in SERPs.
Let’s review each method in more detail.
Image search by context
This is the most common form of image search. When a user enters a query, Google displays relevant images in the search results either on the “main” SERP or in the Images tab.
When an image accurately reflects a user’s search intent, it’s more likely to appear in Google image search results. Google encourages website owners to add more context to images because it helps search engines understand the image better and rank it higher.
Reverse image search
Unlike the traditional search where users input text, reverse image search allows users to input an image or image links. This feature can be used to identify the origin of an image, find similar images, or discover related content. You can also use Google Lens to perform visual searches. Just take a picture with your camera or upload any image from your library. The Lens button is present in both Google and Google Images search bars.
Visual elements in SERPs
Search results with visual elements attract more attention and clicks. This means that using relevant, high-quality images can greatly improve your website’s visibility and CTR. Here are the primary SERP features in which images appear:
- Image Packs
An image pack is a set of images related to the search query. They are typically displayed above organic results (or within the first several results).
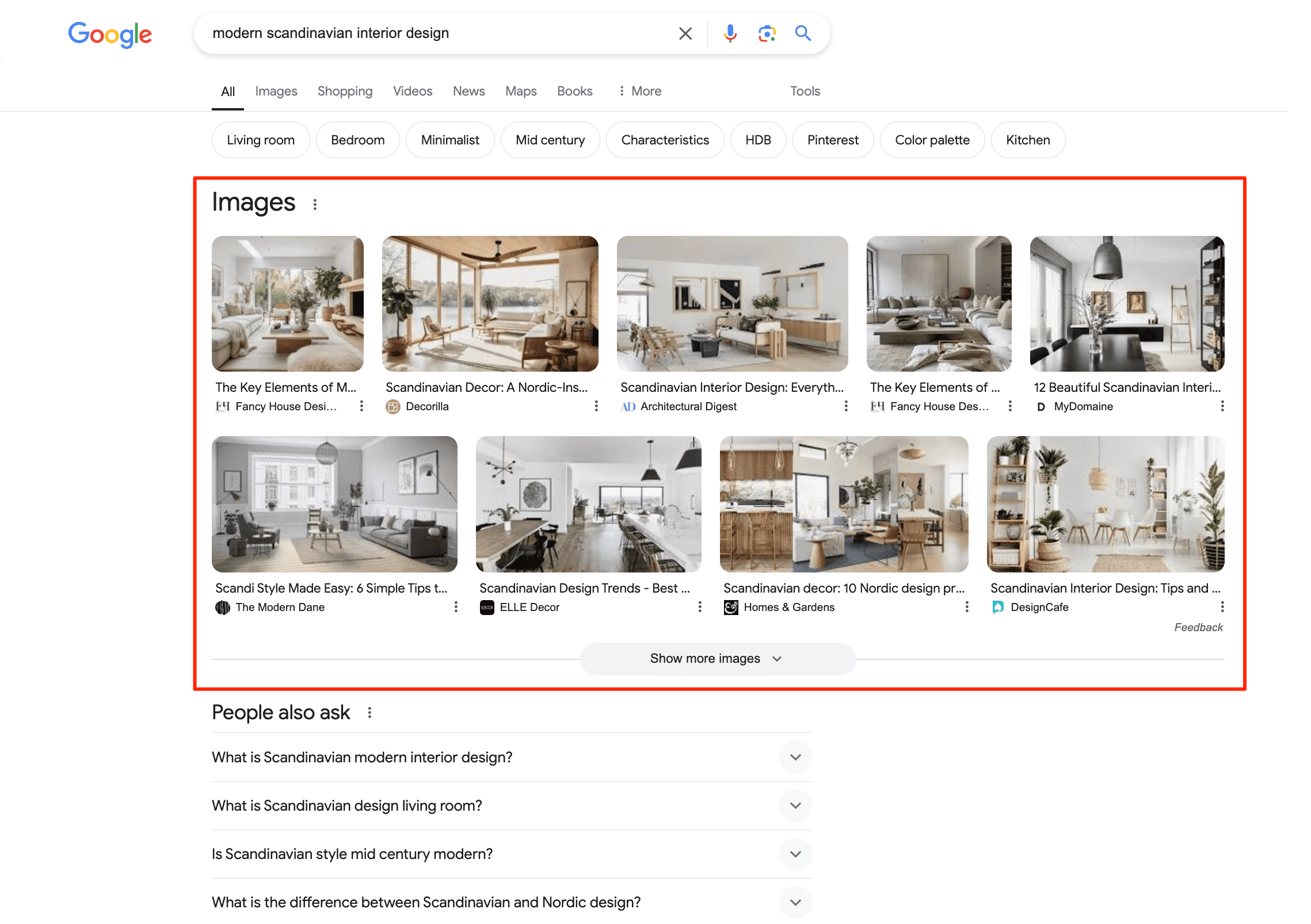
- Text result images
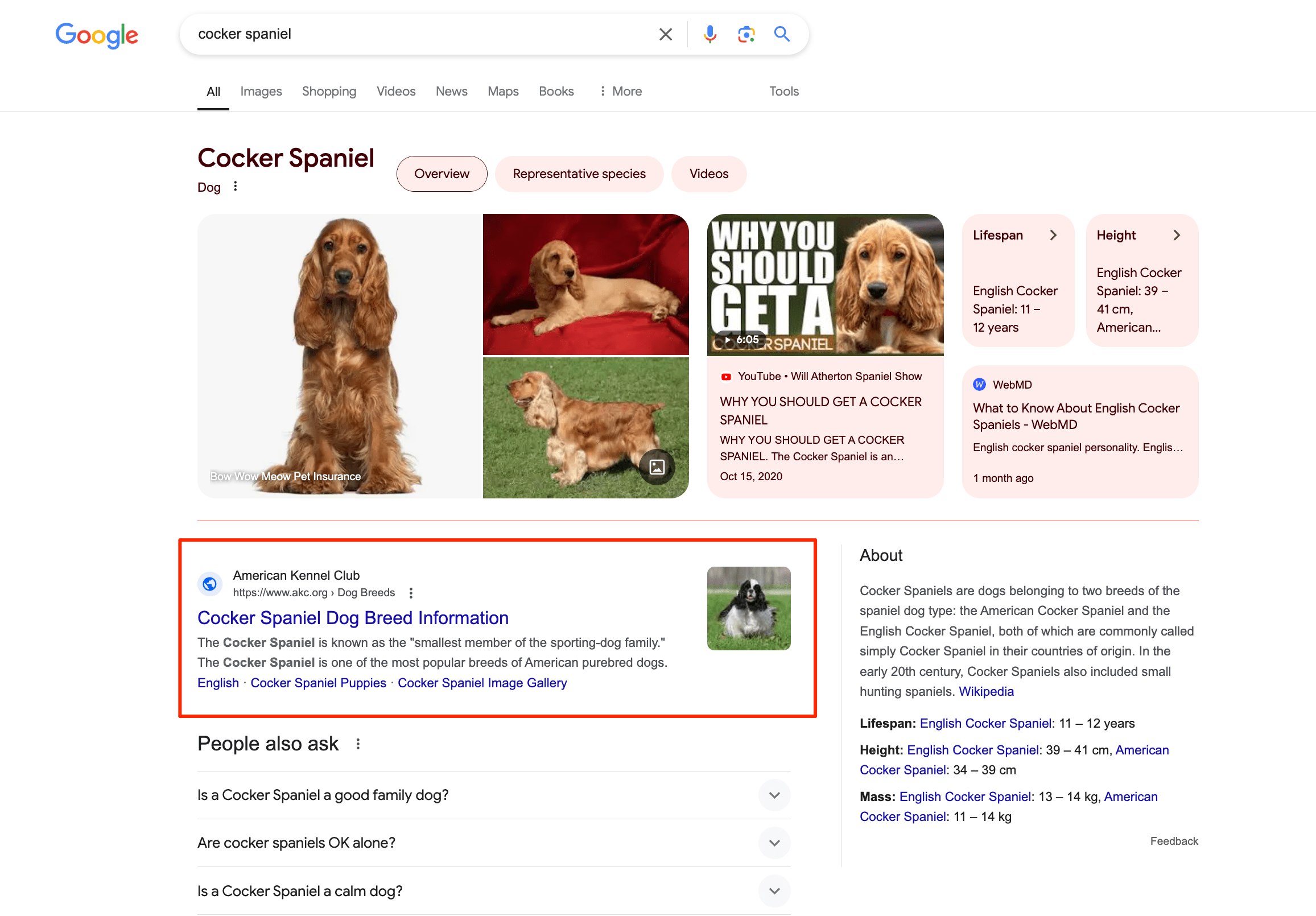
A text result image is the most relevant visual representation of a webpage’s content for a given search query. Clicking on it takes you directly to the source’s webpage. These images often appear next to the title and description of SERPs.
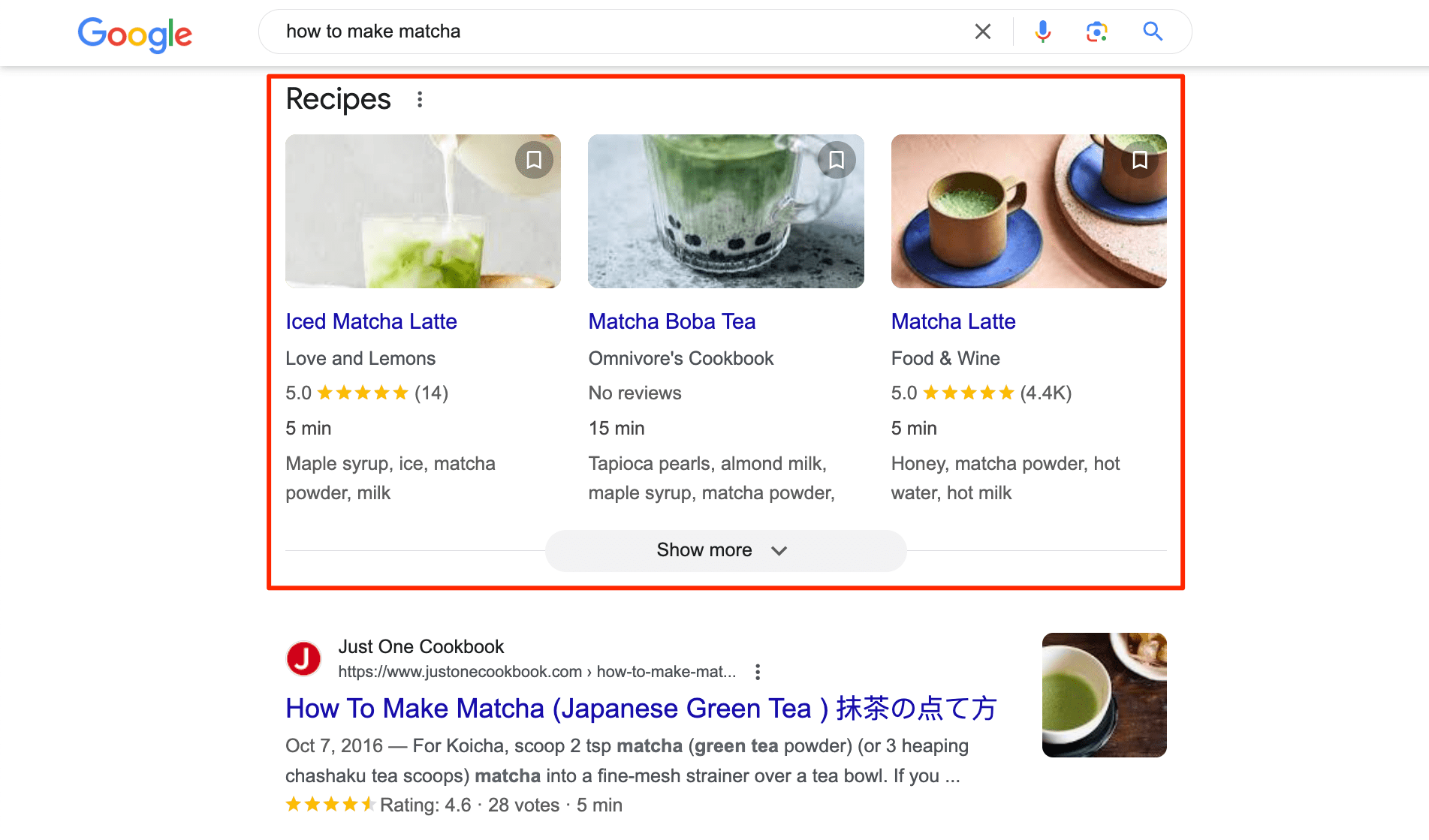
- Rich attributes
Rich attributes are data points that provide additional information about a product or entity. These include product images, ratings/reviews (accompanied by user-submitted images), recipes, events, and so on.
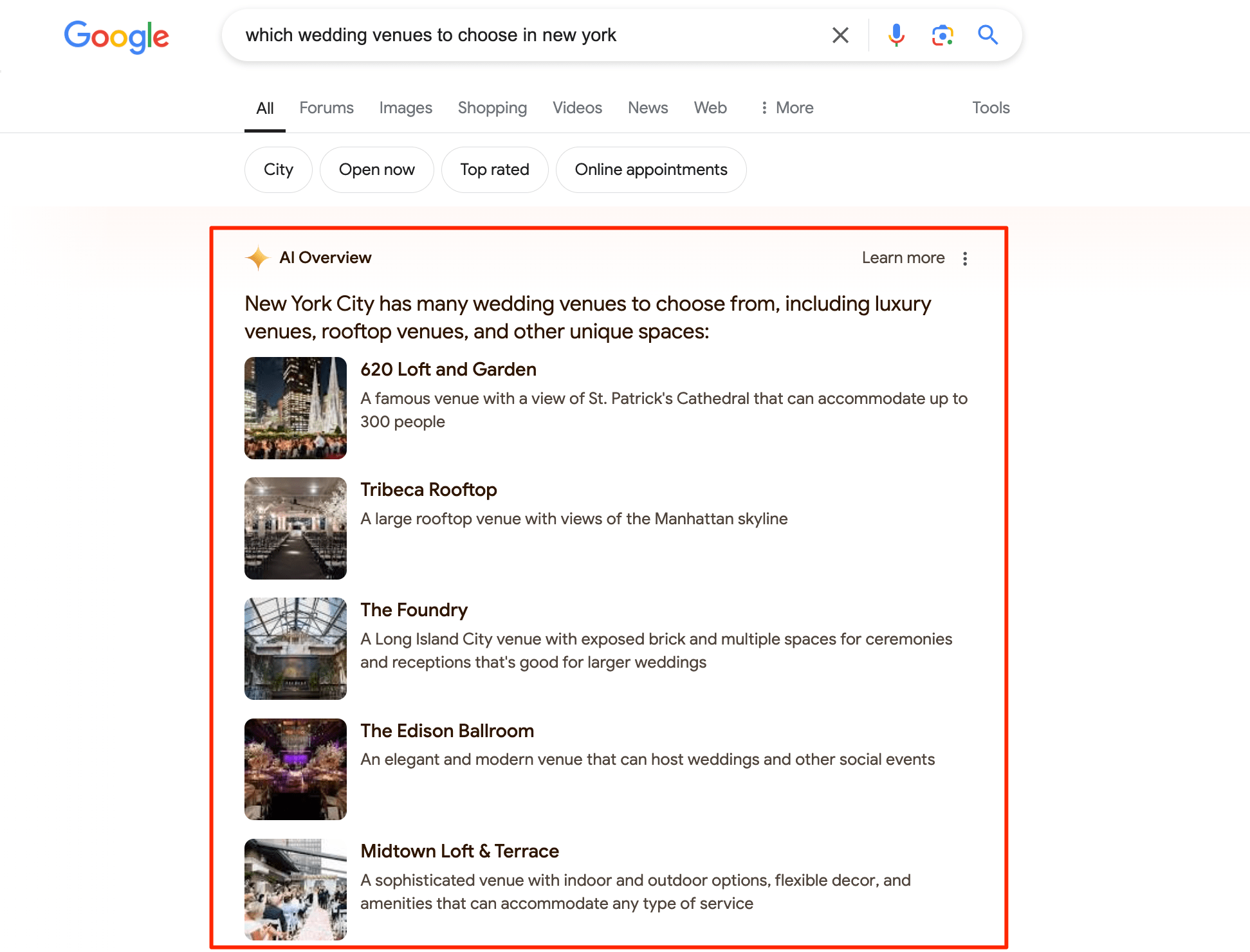
- AI Overviews
AI Overviews also tend to include images directly from websites. This is a great opportunity to increase your visibility and attract high-quality visitors. The thing is, according to Google, clicks from AI Overviews “are higher quality, and people are more likely to stay on that page.”
How the Google image algorithm works in 2025
Google is continuously enhancing its image search technology to deliver the best possible results. At the core of this process is Googlebot, a specialized crawler dedicated to “crawling image URLs for Google Images and products dependent on images.”
On May 16, 2024, Google introduced two new specialized crawlers to expand its data collection capabilities. These new bots, named GoogleOther-Image and GoogleOther-Video, “are versions of GoogleOther optimized for fetching image and video bytes respectively.” Google plans to use the data collected by these bots for internal research and development.
So, how does this process work?
First, search engine crawlers explore websites and collect information from them. For example, they examine image metadata (information about the image, like size, format, and alt text). Next, Google stores data about billions of images in its massive database. Finally, using complex calculations, it ranks images based on the relevance of an image’s metadata and context to a query. It also looks at website authority, among other factors.
How to optimize for Google Image Search
SEO steps, such as choosing the right image, making sure that it’s high in quality, and optimizing it with relevant keywords, are all essential. However, the overall optimization level and quality of your website also significantly impact how Google ranks your images.
Let’s discuss the various aspects of image search optimization below.
Produce useful and unique images
Set your website apart by creating unique and valuable images, whether they are photos, screenshots, illustrations, or infographics. Unique visuals not only differentiate your site from competitors but also kep your already existing users more engaged. High-quality, relevant images make your content more appealing and enrich your users’ experiences.
Are stock images bad for SEO?
According to Google’s John Mueller, stock images are not necessarily bad for SEO.
“If you want to use stock photos as a decorative element on a page, it’s perfectly fine. It adds a little bit of flavor, a little bit more color to the post, or to whatever content we have there.” However, producing unique visuals is your best bet if visuals are central to the page’s purpose, or if you plan on showcasing your product or service in a unique way.
Note: Experiment with stock image sites like Unsplash, Shutterstock, Depositphotos, or other galleries. Compare them to see how many licensed images each one has available to download and in what resolution.
For example, let’s say you run a travel website and use a specific stock photo, but this photo is also featured on 10-20 other sites. Technically, this photo is acceptable from an SEO standpoint, but it does nothing to help your site stand out.
In fact, people searching for travel destinations usually prefer to see authentic, up-to-date photos. Generic stock images, especially ones used in dozens of other local guides, are nowhere near as capable of intriguing users.
So, if images are a key part of your page’s content (and not just decorative elements), opt for unique photos rather than stock images. This also enhances your site’s uniqueness overall.
Can you use AI-generated images?
Google has taken a surprisingly lenient stance on AI-generated images. Instead of banning them outright, they’ve opted for transparency. To enhance user trust, Google has introduced a system to label AI-generated and manipulated images. This includes specific tags for images that have been altered through techniques like inpainting and outpainting.
However, there are limits to this openness. Creating fake screenshots using AI, for instance, might cross the line.
“I think the tricky part would be if you’re showing screenshots of specific things, and you’re piping that into some machine-art-generated thing, then maybe you don’t necessarily get actual screenshots.” – said John Mueller.
Check if Google thinks your images are relevant
There is no direct way to see Google’s exact perception of your images. However, there are some indirect steps you can take to assess their relevance:
1. Search for keywords related to your images, analyze your ranking (a higher position indicates better relevance), and track image clicks (using GA4).
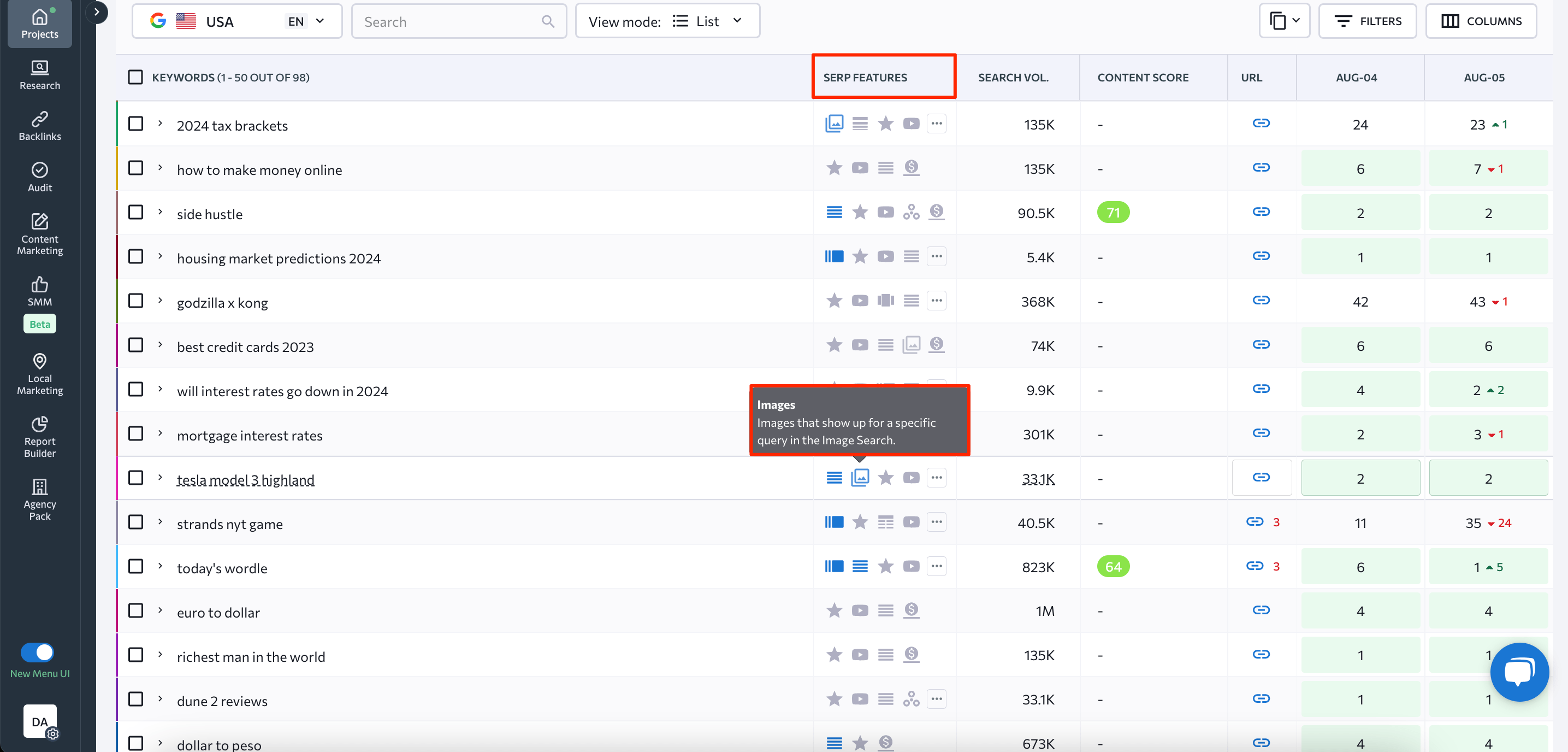
To track your rankings on different search engines over time, use dedicated tools like SE Ranking’s Position Tracker. With its help, you can identify what keywords bring the most traffic to your site and discover which search terms you appear for in Google’s Image search results.
To find this information, start by setting up your project. Then, navigate to the rankings table within the Detailed tab and look at the SERP Features column.
2. Use Vision AI (a tool that can extract insights from images and videos). For example, consider using this tool’s API if you run an online store and want to home in on a photo to use to sell bicycles.
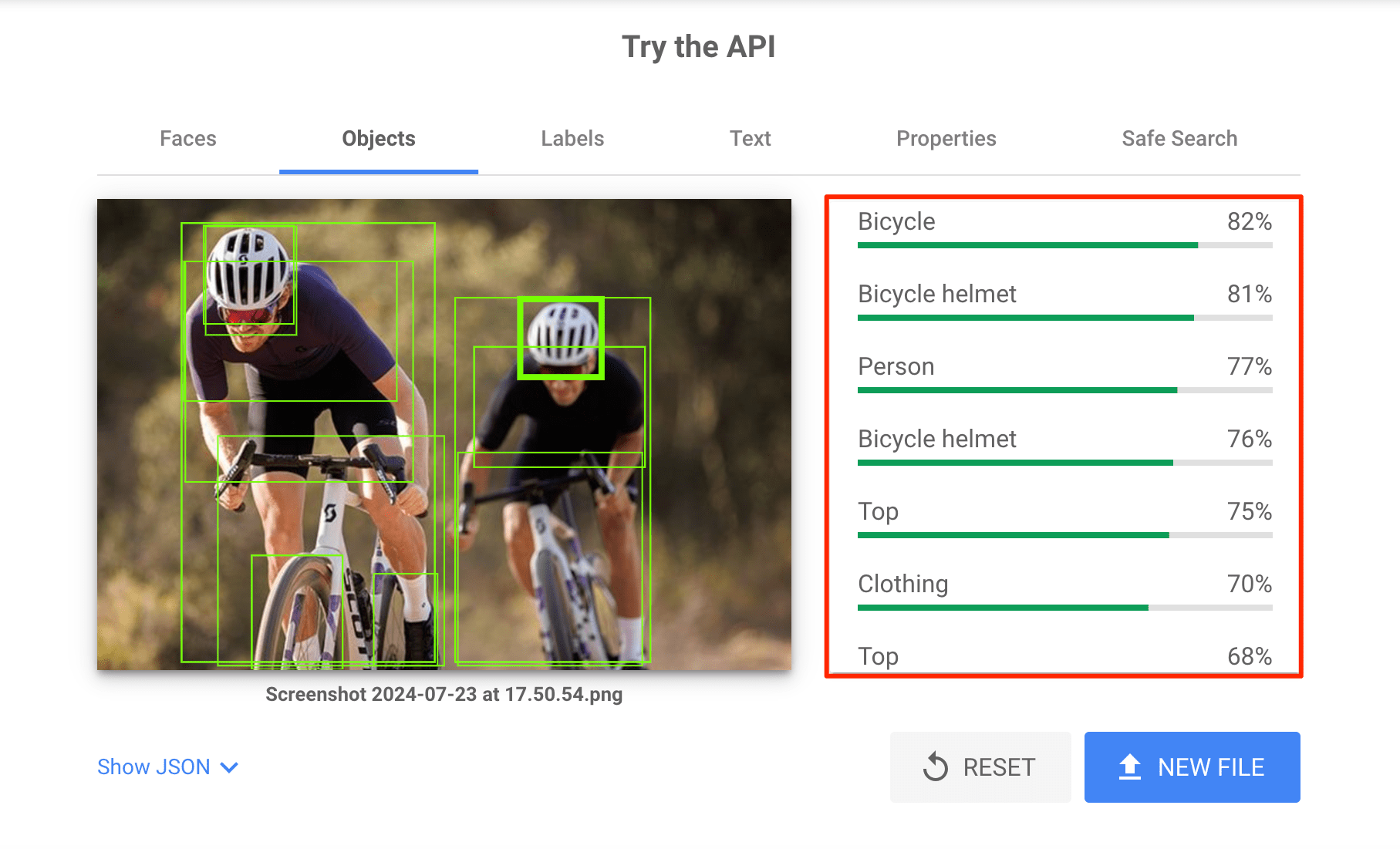
As you can see, Google is 82% sure that your image depicts a bicycle, which is great. However, the analysis also suggests the image strongly resembles a bicycle helmet (81%), a person (77%), and even clothing (75%). These additional identifications don’t align with our desired focus for this photo.
Now, let’s use a more specific picture of a bicycle where it’s depicted as the main object.
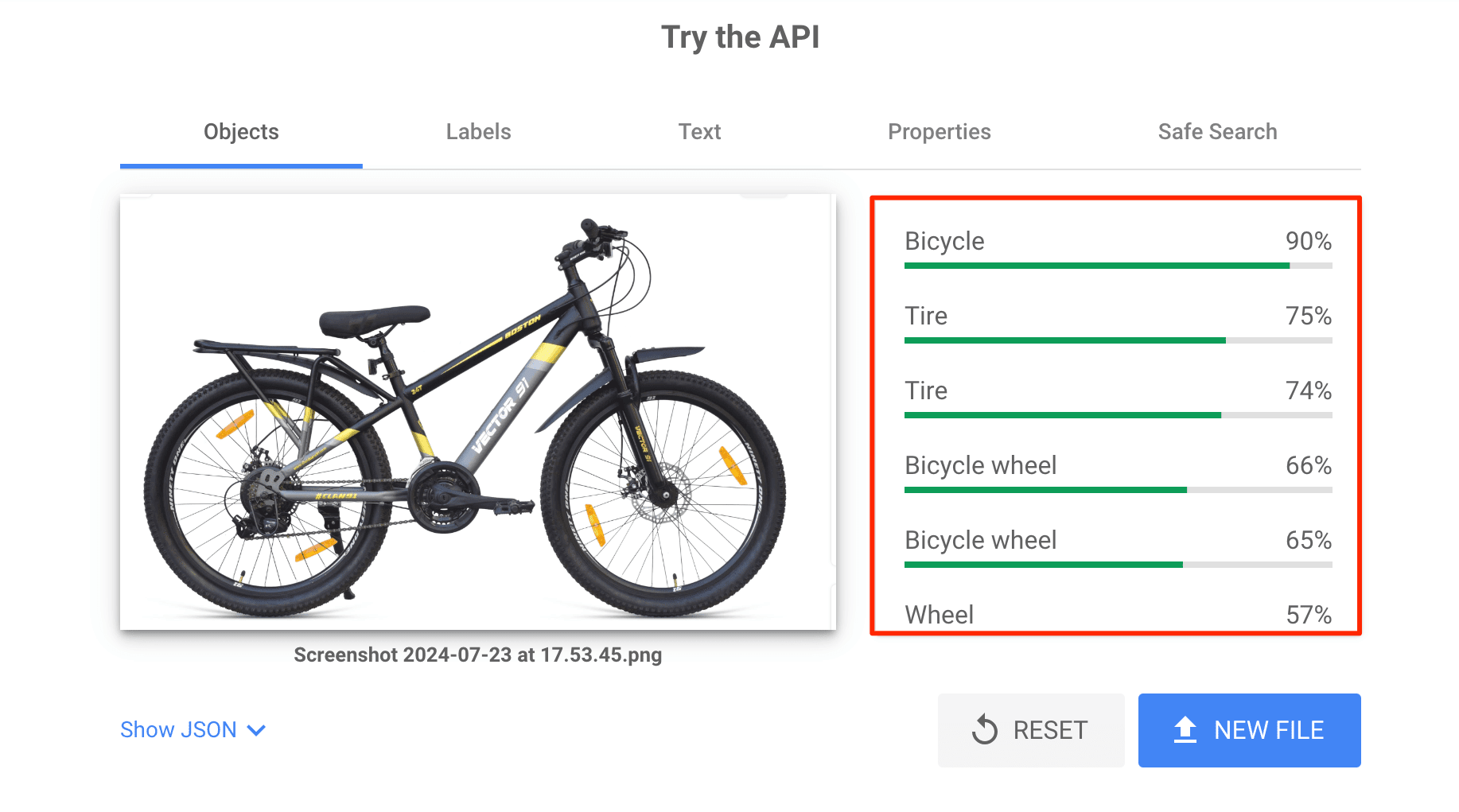
Now, Google is 90% sure that your picture depicts a bicycle. The other suggestions are strongly related to your product and include tire and wheel. So, this image could be a great choice for your online store.
Keep your image quality and resolution high
Search engines prioritize high-quality, high-resolution images. This means that the images should be clear and sharp, with no blurriness or pixelation. High-quality images help in making your website look professional and polished.
Best image sizes for Google
To optimize images, Google recommends providing “multiple high-resolution images (minimum of 50K pixels when multiplying width and height) with the following aspect ratios: 16×9, 4×3, and 1×1.” These ratios ensure that your images display well across various devices and formats.
Large images require a width of at least 1200 pixels. Enable them through the max-image-preview:large setting, or by using AMP. This also increases your chances of appearing on Google Discover.
Additionally, ensure that your images are not wider than your users’ screen resolutions. Check common screen resolutions in GA4 to resize images accordingly (Reports > Tech > Overview).
Use descriptive filenames
Search engines also scan the names of image files, so make sure to name them properly. Google’s official guidelines state that the filename should be descriptive but not very long. For example, if the photo shows a smoothie, it’s best to name the file tropical-green-smoothie instead of leaving the default name generated by a camera like IMG_7489.
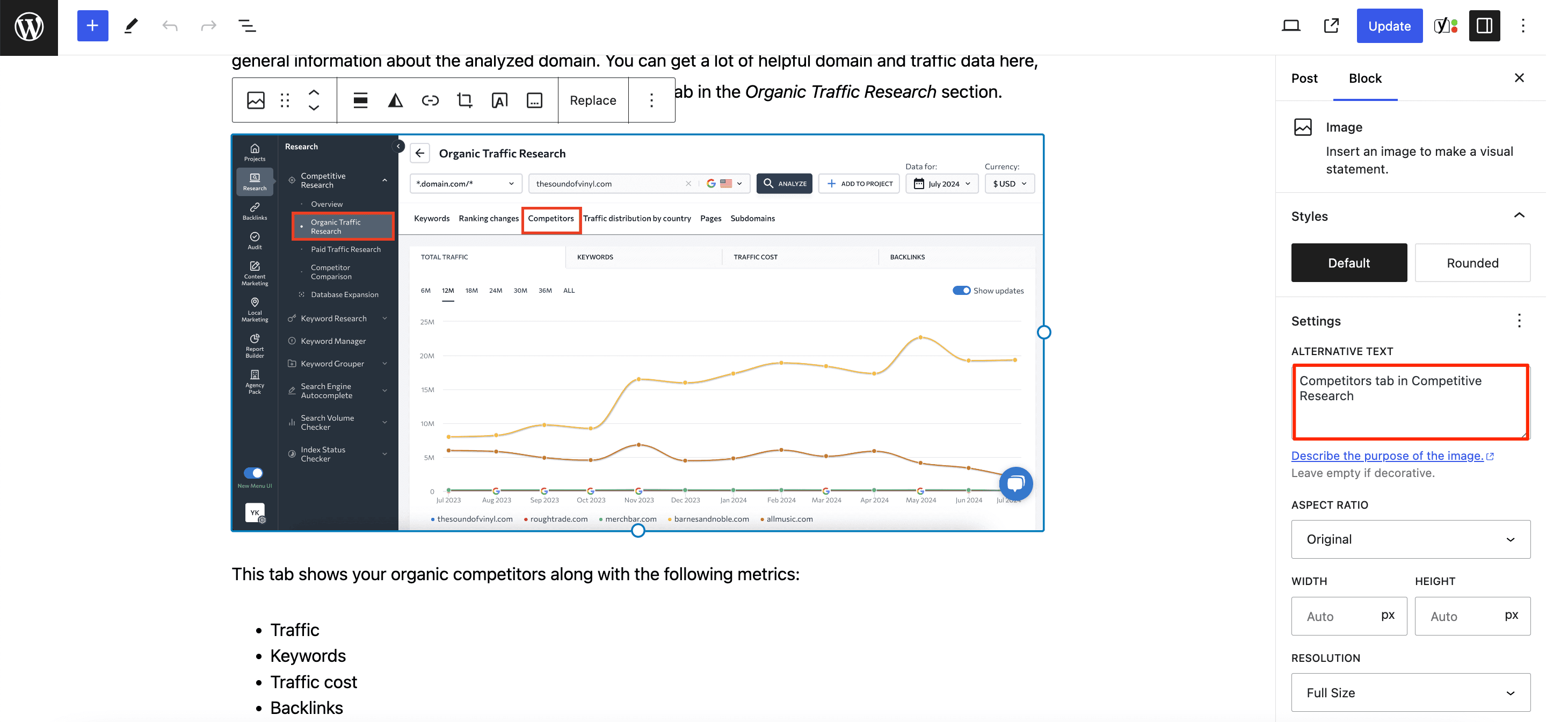
Add alt text
Adding a descriptive alt text can help you improve your rankings by associating your images with relevant queries. It’s also an accessibility requirement since alt text is the only option for people who can’t see the image. If an image has the alt attribute but no text, Google will assume the text on the page closest to it is the alt text.
Here’s how adding alt text works in WordPress:
Examples of good alt tags include:
- For a product image:
<img src="red-shoes.jpg" alt="Pair of red running shoes">
- For an infographic:
<img src="seo-tips-infographic.jpg" alt="Infographic showing top SEO tips for 2025">
Use a descriptive image title
The Title text is shown when a user hovers over an image. It’s not as crucial for SEO as the alt attribute, but Google recommends including it anyway. Contrary to the alt text, you can write a title that describes the context rather than the individual image. But keep it short and don’t stuff it with keywords.
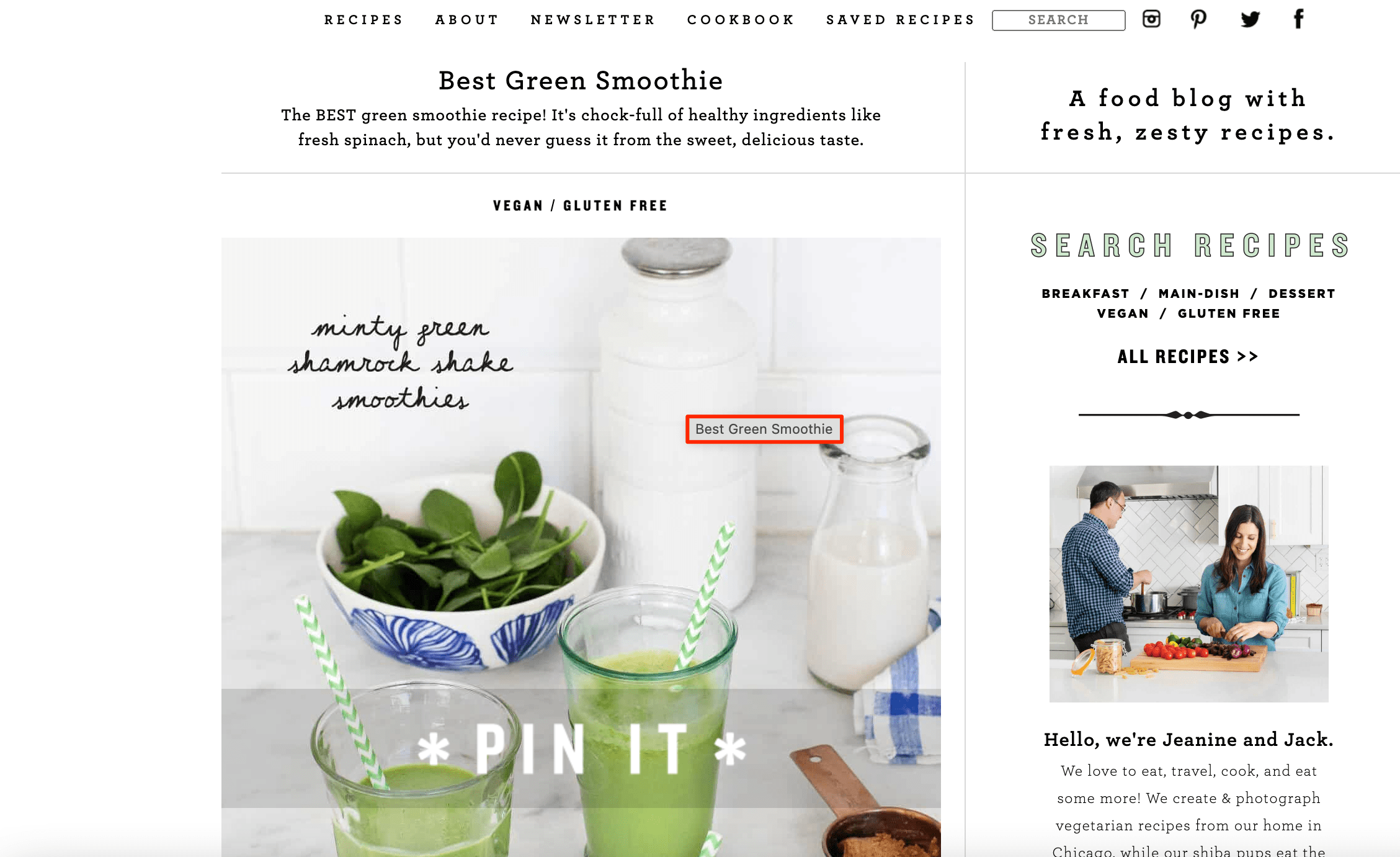
Use captions
Captions provide context about an image. They also provide extra information to make your visual content more compelling and informative.
Here’s how it looks on a website:

Use the right image file format
Choosing the right image format is essential to balancing image quality, site speed, and SEO performance. Different formats offer various benefits, and selecting the right one can enhance your website’s efficiency and user experience.
The best image formats for SEO
- JPEG: Common format, balances quality and size. Ideal for photos.
- PNG: Higher quality with larger file sizes, supports background transparency. Best for infographics and design elements.
- WebP: Offers excellent compression and faster load times, although not all browsers support it.
- SVG: Great for logos and icons, but can have design issues (e.g., problems with fonts).
- GIF: Google crawls and indexes GIFs like any other image type, but GIFs can slow down websites.
- AVIF: High-compression image format that offers superior quality and reduced file sizes compared to JPEG and WebP, with support for transparency and HDR.
Compress your images
If done correctly, compressed images load faster without sacrificing quality. This can help you avoid unexpected layout shifts, which can affect Core Web Vitals and frustrate users.
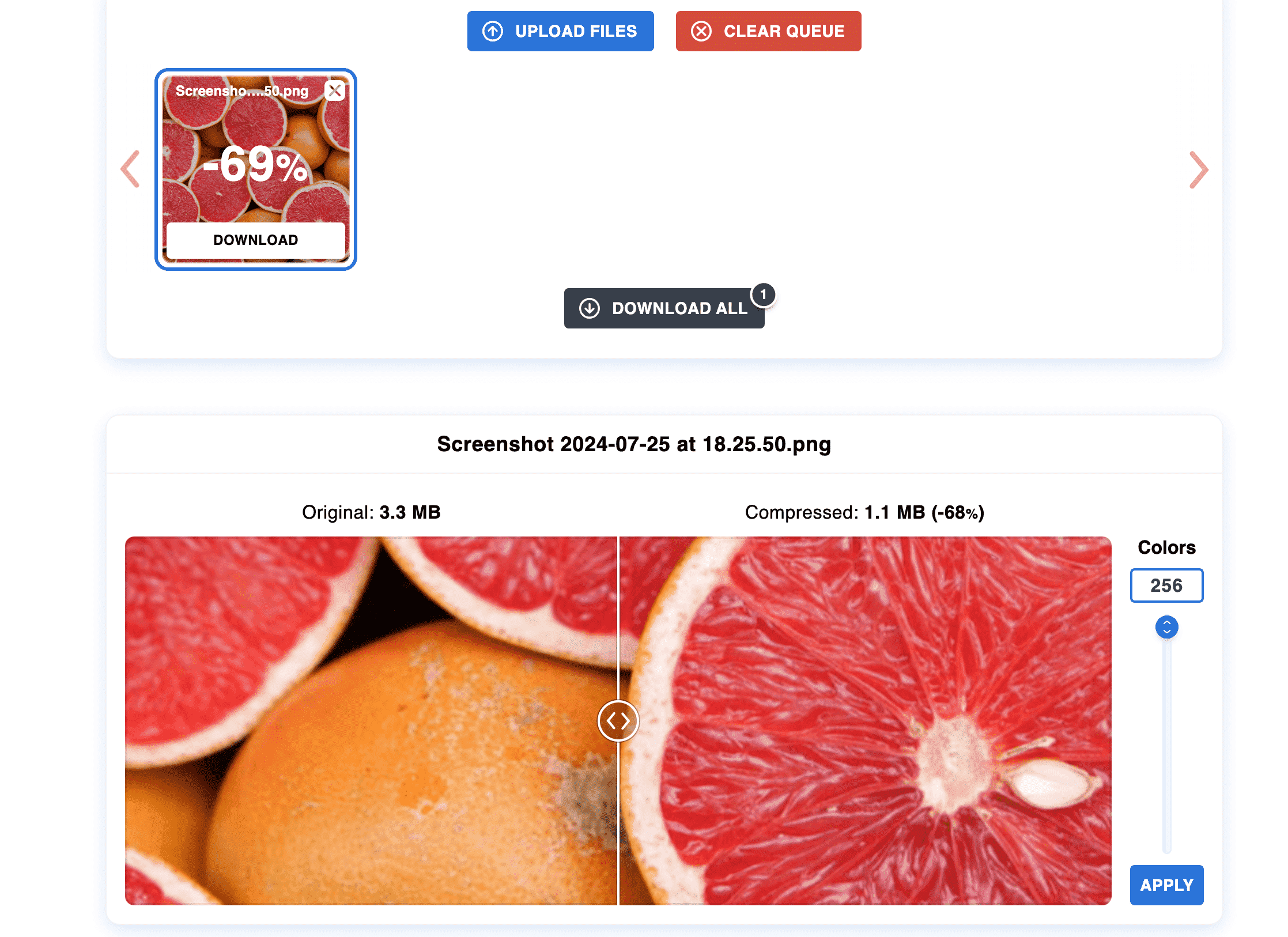
There are several compression tools that you can use to get desirable image file sizes (from Photoshop to online services like Imagify). For example, the SEO image optimization tool, Optimizilla, lets you adjust colors and shows a preview of the compressed image:
You can also use WordPress plugins to improve website speed by optimizing images. For instance, EWWW Image Optimizer allows you to optimize all your existing images and automatically optimize new ones.
Use responsive image scaling
When performing SEO for Google images, make sure your images are responsive. This means that your images should scale appropriately for different screen sizes and resolutions. One effective way to achieve this is by using the srcset attribute.
This attribute allows you to specify different images for different screen resolutions and sizes (e.g., showing a 2x image on a 2x display). This ensures that users get the best possible image quality for their device while minimizing unnecessary data usage.
For more insights on responsive image scaling, check out this dedicated guide on the responsive images syntax in HTML.
Use lazy load
The technique involves making images load asynchronously. This means that your users won’t see the page’s full content unless they scroll down to look for it. You have likely already seen this feature multiple times. For example, lazy loading is active when image placeholders are replaced with images in sync with you as you move down the page.
It only makes sense to use lazy load if your page has many images. To apply this technique, you can either use plugins like Native Image Lazy Loading or manually add it to the code. Make sure to add the lazyload class to the img tag, and specify the placeholder and the original image in the src and data-src attributes:
<img class="lazyload"
src="placeholder.jpg"
data-src="image.jpg"
alt="image description">
JavaScript handles image lazy loading, but a <noscript> tag is necessary for browsers without JavaScript support for image display.
Many popular CMSs have automated responsive image handling. WordPress led the way in 2015, automatically generating srcset and sizes attributes upon image upload. Shopify and Magento followed suit. Other CMSs like Drupal offer their own special tools for this purpose.
For a comprehensive overview of CMS capabilities, refer to our blog post on how to select the most SEO-friendly CMS.
Create an image sitemap
You can include information about images in a website sitemap or create a separate .xml file. This helps Google navigate your content. There are plenty of services and plugins that generate sitemaps and can help create an image sitemap. You can also learn more about image sitemaps from Google Search Central.
Optimize image metadata
Adding image metadata enhances your appearance on Google Images. For example, the image may feature information about its creator, usage guidelines, and credit information (to prevent image theft). Also, including licensing details can qualify your image for a Licensable badge. This is a clear signal to Google that the image is yours and yours only.
There are two ways to add image metadata:
- Structured data: This involves adding code to the webpage where the image is displayed. This code provides details about the image and its usage.
- IPTC Photo Standard: This information is embedded directly into the image file itself. It travels with the image regardless of where it’s used online.
Optimize Open Graph meta tags
The Open Graph protocol helps you control what content will be displayed on social media when your page is shared. Setting a particular image for platforms to load is crucial. Otherwise, they may scrape something irrelevant or not show anything at all.
Images for social shares can be set automatically by a CMS but if you don’t use any, you’ll need to manually assign the og:image tag for each web page.
Serve images via CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a global network of servers that stores and delivers your website’s content. This means users download files from the closest server to their location. This significantly improves download times and page loading speeds. Most of them can also help you better handle traffic spikes, enhance security against attacks, and get detailed analytics for monitoring image performance.
To use these benefits, you can install a CDN plugin on your website. Popular options include Cloudflare, ImageKit, KeyCDN.
Enable browser caching
Browser caching is a technique that significantly improves website performance by storing static resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript files locally on the user’s device. When a visitor returns to your website or navigates different pages, the browser can load these cached files directly. This results in faster page load times, a better user experience, and decreased server load.
To learn more about cache browsing and how to implement it, check out Google’s browser caching guide.
Follow the SafeSearch guidelines
Image search on Google has a SafeSearch filter for users to block explicit content. Be careful with the images that might have some indicators of adult or violent content. If Google’s algorithms identify your image as objectionable, your page will be hidden from search results for users who turn on the SafeSearch filter.
The Vision AI image SEO tool, already mentioned above, can give you insights into how Google detects images. If you do have adult-only images, group them separately in the URL structure and add metadata like <meta name=”rating” content=”adult” /> to your pages.
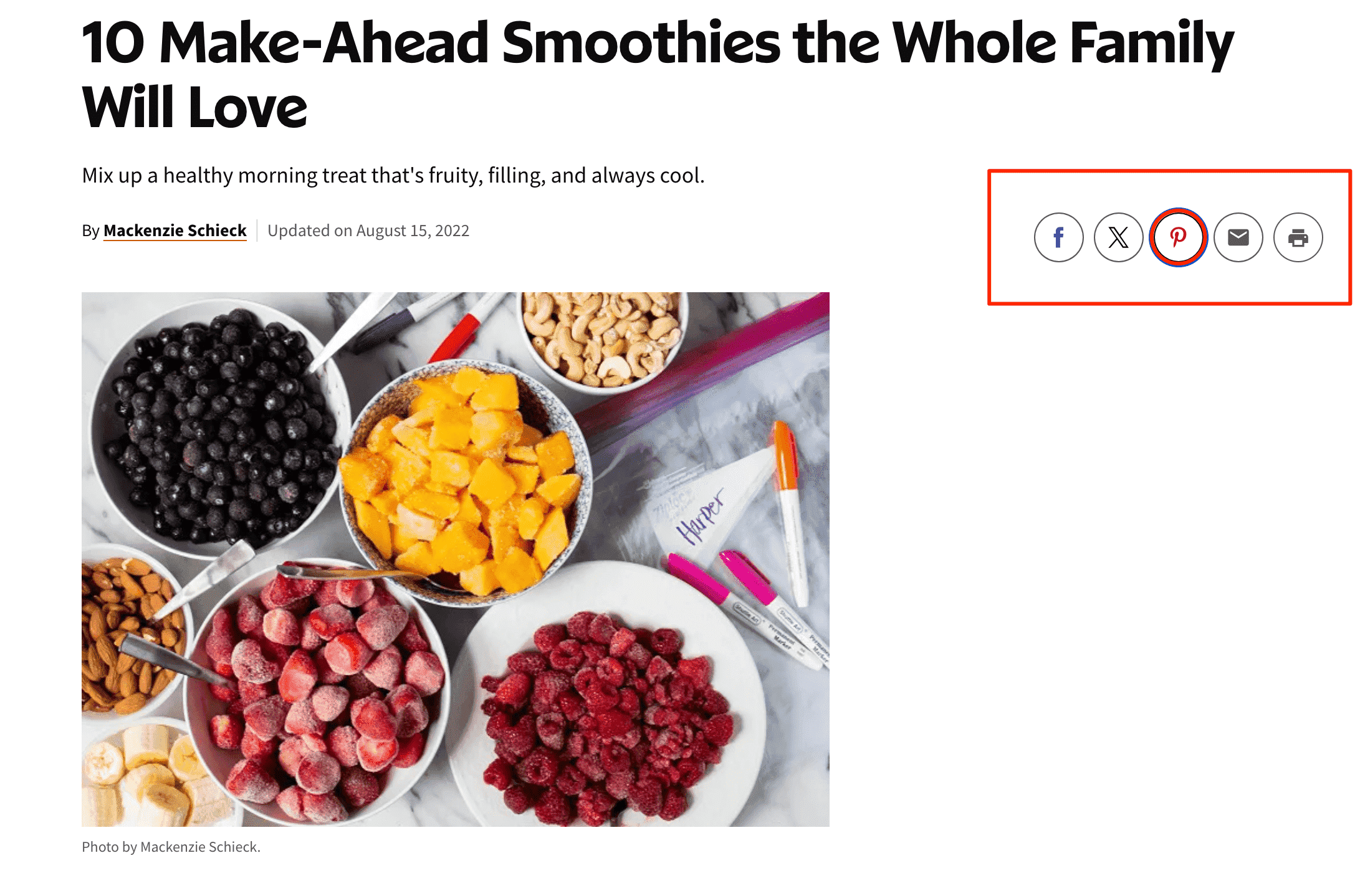
Add a Pinterest Save button
Adding a Pinterest Save button to your visuals encourages users to share your content with their followers. This simple action can significantly expand your reach and introduce your business to a wider audience.
Pinterest provides instructions on how to add their Save button to web pages, however, many CMSs provide easier options for this. For instance, you can use a plugin in WordPress.
The screenshot example below shows a Pinterest button at the top of the screen:
Use Schema markup for images
Images can help identify a specific type of content on a page, such as product, recipe, or video. Each has a label and is displayed in search results on desktop and mobile devices.
Structured data, or schema markup, creates these labels. Optimize images on specific content pages to help users find what they need more easily in search results.
To add schema markup to your images, you’ll need to incorporate the ImageObject properties into your HTML. Below are some of the most important properties for rich metadata sets:
- contentUrl: The URL of the image.
- caption: A text description of the image.
- creator: Information about the creator of the image, which can be a person or an organization.
- license: A URL to the license under which the image is published.
- thumbnail: A URL to a thumbnail version of the image.
Plugins like Schema App Structured Data can simplify this process. Alternatively, you can follow our in-depth guide on schema markup for more detailed instructions.
Keep your page optimized for search engines
When it comes to image optimization for search, ensuring that the content surrounding your images is relevant and informative is key. In fact, search engines analyze the text around images to understand their context. Always use descriptive headings, subheadings, and paragraphs that naturally incorporate relevant keywords.
The technical SEO health of your pages also impacts image visibility. Factors such as internal linking, page experience, usability, and mobile-friendliness can influence image rankings.
To ensure your pages are fully optimized, use SE Ranking’s On-Page SEO Checker. This tool provides comprehensive insights into the optimization level of your pages for search engines (using its own page quality score) compared to top-performing competitors. It also identifies optimization issues and offers actionable recommendations on how to improve your page quality score and search engine performance.
How to audit images on your site
You can audit your site images using SE Ranking. In the Issue Report section, you’ll find the image analysis block. This section provides information about images missing alt text and those that are excessively large.
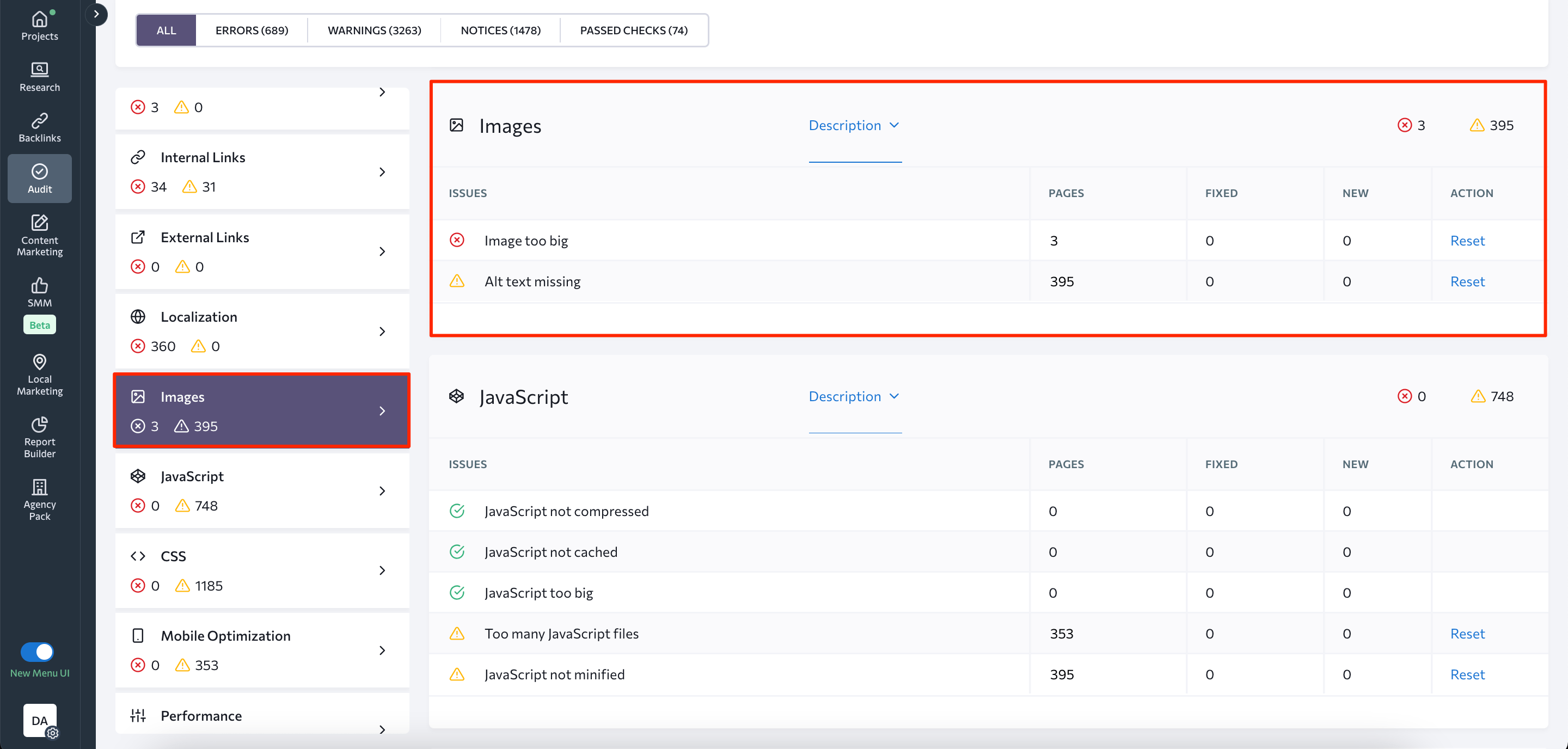
Make sure to fill the alt tags for each picture on your website and reduce their size to speed up your website’s load times. Learn more about what other aspects to check from our article on doing a site audit the right way.
On-Page SEO Checker also checks if the alt text is there. Besides, the tool analyzes if the visuals are unique and makes recommendations on how to optimize image file names.
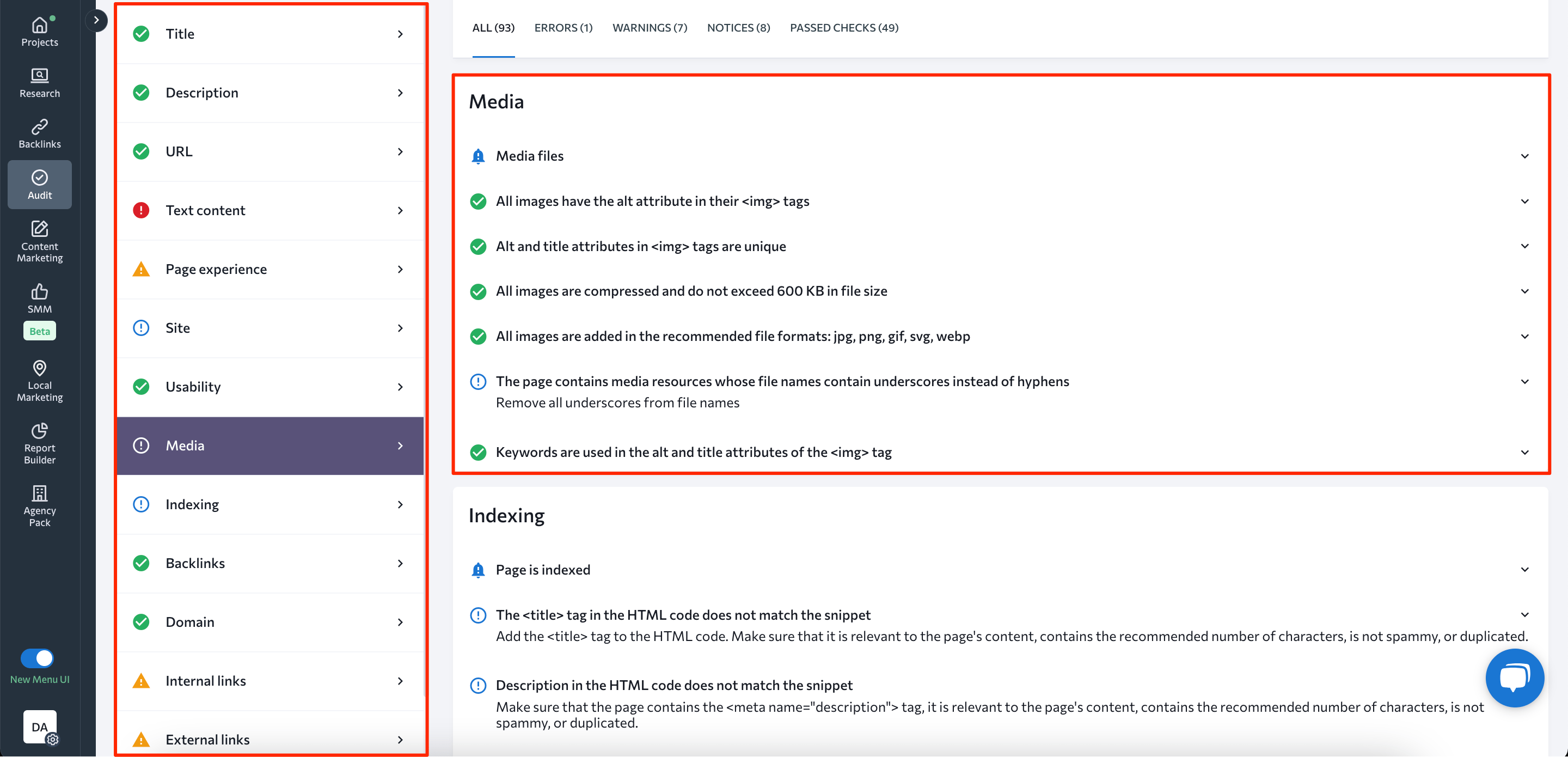
Since the main purpose of SEO tools like this one is to assess how well a given page is optimized for a target keyword, you’ll also see if your images contain that keyword in alt and title tags.
How to check if Google has access to your image
There are two methods to checking if an image is available to Google:
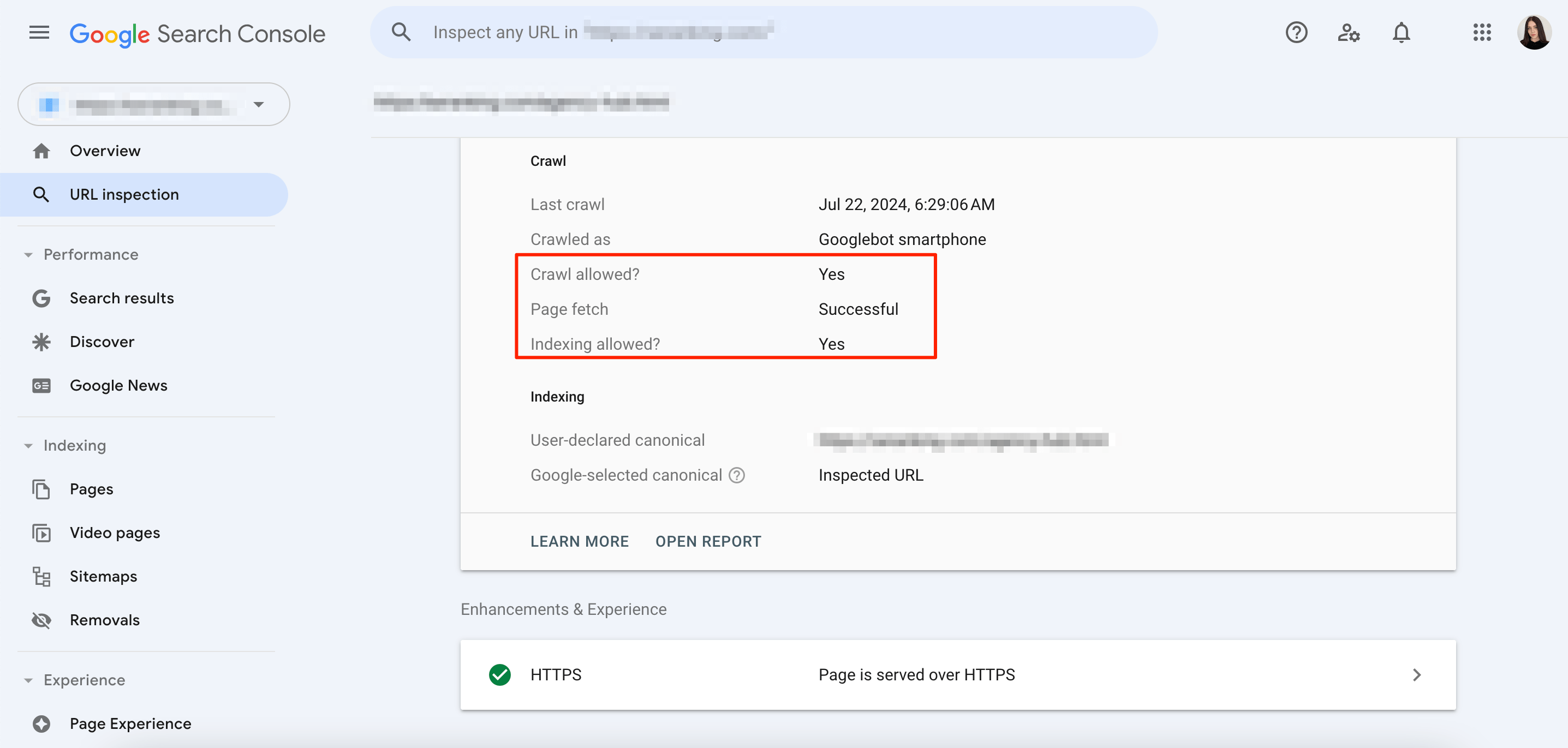
- URL Inspection Tool.
If the image is hosted on your site, open the URL Inspection tool in GSC. Then, enter the image URL and expand the Coverage section. Now, the Crawl Allowed section should be displaying Yes and Page Fetch should be Successful.
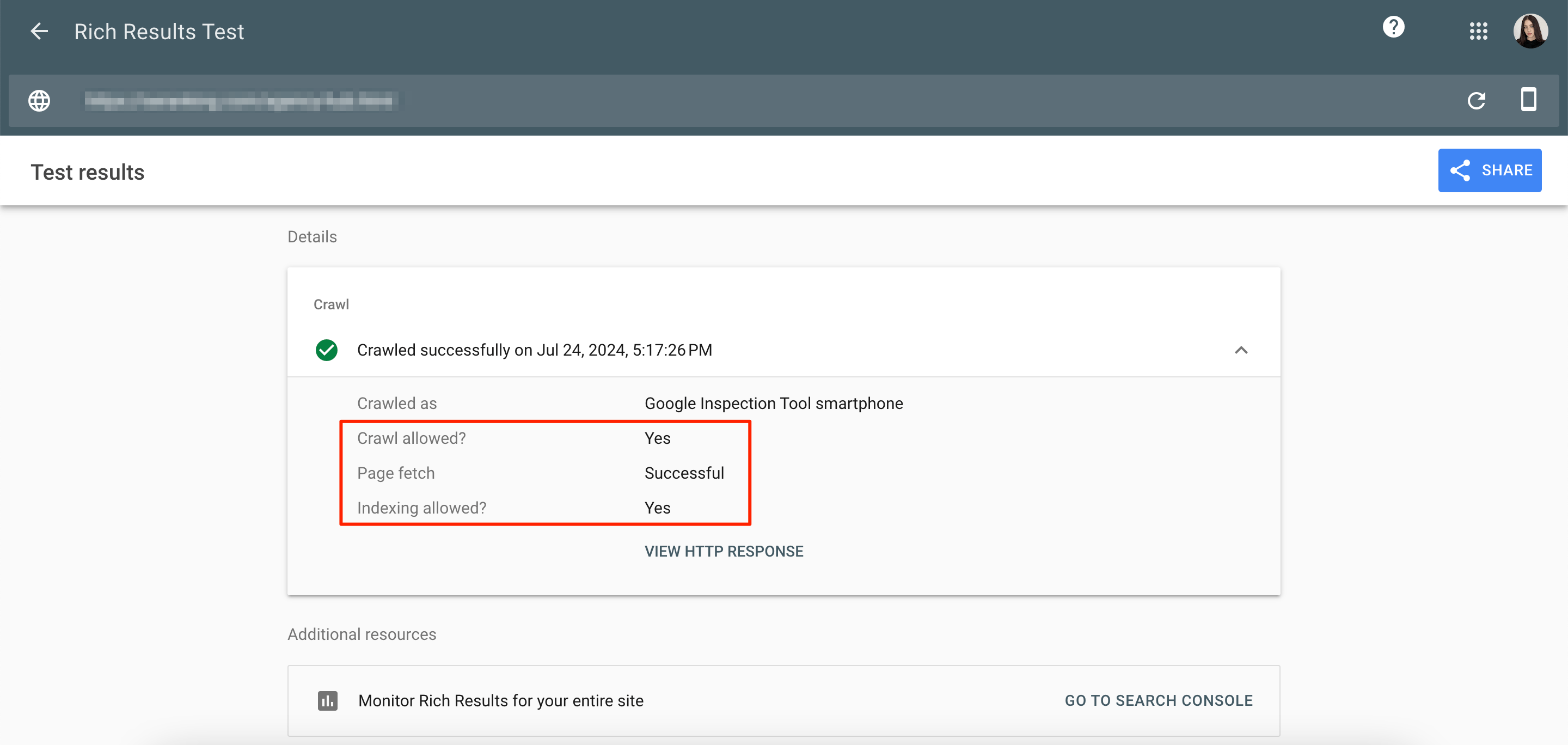
- Rich Results test.
If the image is hosted on another domain, open the Rich Results test. Next, enter the image URL and click Test URL. Now, expand the Crawl section and follow the same steps as in the case above – verify that Crawl Allowed displays Yes and the Page Fetch shows Successful.
Conclusion
Navigating Google images SEO in 2025 may be a complex and difficult process, but the payoff is worth the effort.
By carefully optimizing your images, you can significantly improve online visibility, increase search engine rankings, enhance user experience, and drive more traffic to your website.

