Dofollow vs nofollow links and their value for SEO
There are hidden technical nuances that make a huge difference in how the links are perceived by search engines. These nuances are the link attribute values placed within the page code inside the link tag <a>.
By default, links are followed by search crawlers, allowing them to pass link juice to the pages they point to. But when the nofollow attribute value is specified, this default behavior doesn’t apply.
So, what exactly does it mean to nofollow a link, and when should you use this attribute? In this post, we’ll explain the SEO value of followed and nofollowed links, explore other available link attribute values, and provide guidance on building a safe backlink profile in accordance with link tag specifications.
-
Dofollow vs. nofollow links:
Dofollow links are regular links without the rel=”nofollow” attribute and pass authority to the linked site. Nofollow links include the rel=”nofollow” attribute and act as a signal to search engines not to pass authority. Google treats this attribute as a hint rather than a strict directive.
-
Impact on search engine optimization:
Dofollow backlinks from high-quality sources can significantly boost your search rankings. Nofollow links, though they don’t directly impact rankings, offer SEO benefits, such as driving traffic, increasing brand visibility, and building a natural link profile.
-
Additional link attributes:
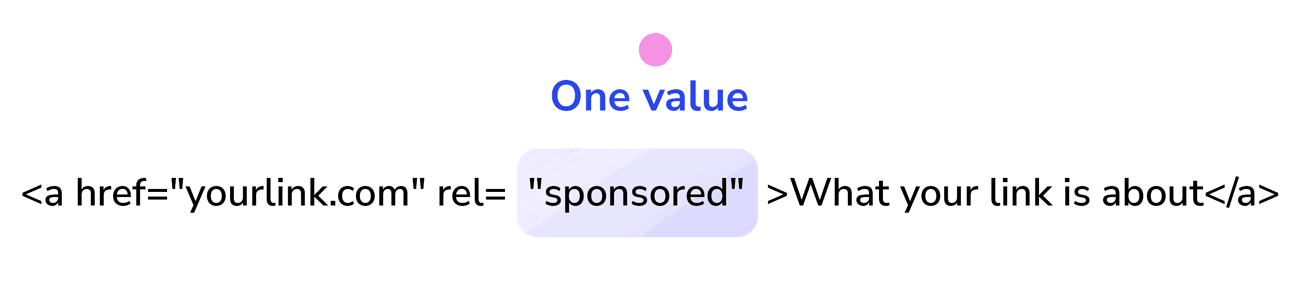
rel=”ugc” is used for user-generated content (e.g., comments, forums). rel=”sponsored” is used for paid or sponsored links, distinguishing them from editorial links.
-
When to use nofollow links and how to add them:
Use nofollow for untrusted links or links you don’t want to endorse. You can add rel=”nofollow” manually in the code or use plugins to manage link attributes easily within a CMS.
-
Internal links:
Generally, all internal links should be dofollow to maintain good website structure and visibility. Nofollow internal links are only recommended for non-essential pages like login pages or search results.
What is a dofollow link?
The dofollow value for the rel attribute doesn’t exist in HTML. A dofollow link (or a follow link, which is technically the more correct name for it) is, in fact, just a regular link without specific attributes. It’s commonly used as a descriptor in the context of the nofollow value only. This emphasizes that the link is not subject to any specific SEO instructions and that it should live up to regular expectations, i.e. pass link juice and authority to the referred sources.
To clarify further, let’s take a look at how a link appears in the code:


The first example is a followed, regular link, and the second example is a nofollowed link. As you can see, there’s no such thing as rel=“dofollow” in the code because it’s the default behavior.
This means that with no additional attribute values included in the code, links will work as the web intended. They work as authority signals that increase the importance of the web pages they cite. Back in the early days of search, Google was the first search engine to assign a key role to links. Since the introduction of the PageRank algorithm in 1998, Google started treating citations as votes that carry weight for web pages, making the most cited ones the most reliable and high-ranking. Although the algorithm and SEO practices have evolved over time, the main thing about links remains the same: getting high-quality external sources to link to you will increase your rankings.
How dofollow links help rankings
When discussing link value for rankings, we usually mean backlinks, which are the links you get from external sources. Search engines consider tons of ranking factors (we know that Google has more than 200), and high-quality backlinks are among the top two influential factors, alongside content. A Backlinko study even revealed that pages ranking first in Google had 3.8 times more backlinks than pages ranking in the top 2 to 9.
Backlinks bring all sorts of direct and indirect advantages to your website. This translates to an improved user experience with relevant and high-quality resource links, as well as increased referral traffic. But the primary benefit of dofollow backlinks lies in their capacity to pass link juice and reinforce your website’s authority and credibility. When reputable sites link to your valuable content, search engines interpret it as a positive endorsement, potentially leading to higher search rankings. As a result, SEO professionals often prioritize acquiring dofollow backlinks to strengthen their website’s online presence.
Check out our guide on link building for SEO to discover how to get valuable backlinks.
Now, let’s look into what happens when a link contains a nofollow attribute or other attribute values.
What is a nofollow link
Let’s say you prefer not to endorse some sources that you linked to. The nofollow attribute value tells search engines that you don’t intend to give credit to a specific web page that you referred to. Now, the nofollow attribute functions as a hint and not as a directive, and also differs from new attribute values designed for sponsored and user-generated content.
But let’s delve into the details step by step.
Nofollow was introduced in 2005 by Google as a response to the surge of comment spam. Website owners would leave links to their own sites in comment sections and forums, leading to higher rankings regardless of the relevance of the comment and the overall quality of their pages. Bing and Yahoo also adopted the concept and started treating the rel attribute values similarly.
From 2005, nofollow functioned as a directive, and search engines would either ignore or downright refuse to crawl nofollowed links. This helped curb some manipulations, but it didn’t solve all the problems related to different types of links and the varying degrees of trust put on them.
In 2019, Google changed its approach to nofollowed links, making the nofollow attribute more of a hint. Google also introduced two new attribute values: rel=”ugc” for user generated content and rel=”sponsored” for sponsored content. This means that even if a link is marked as nofollow, search engines can still crawl it and include it in the ranking process.
Additional link attributes
Google introduced the rel=”ugc” attribute, which stands for User-Generated Content. It is intended for links contributed by users that originate from comments, forums, or other forms of user-generated content. Google introduced this attribute to distinguish user-generated links from editorially curated links. When website owners implement this attribute, it sends a signal to search engines that these links are created by users and may have different characteristics and relevance compared to editorially controlled links.
On the other hand, the rel=”sponsored” attribute is specifically designed to indicate paid or sponsored links on a website. It helps website owners and search engines distinguish these links from organic editorial links. By using rel=”sponsored,” website owners transparently disclose that the link is part of a paid partnership or advertising arrangement. This attribute serves the same purpose as rel=”nofollow” but it provides more specific info about the nature of the link.
It’s worth mentioning that website owners have the option to use multiple attributes simultaneously, allowing them to provide additional context and information about the nature of a particular link. For example, a link can have both the rel=”nofollow” and rel=”sponsored” attributes, indicating that it is a paid link that should not influence search engine rankings. This flexibility enables website owners to accurately describe the characteristics of their links, promoting transparency and aiding search engines in understanding the link ecosystem on a website.

The impact of nofollow links on SEO effectiveness
Websites aim to get as many followed backlinks as possible. Though this objective is completely understandable, it’s also beneficial to receive nofollow links. These links can increase your traffic, brand awareness, rankings, and provide more link building opportunities.
We asked Bibi Raven, a link building professional and founder at Bibibuzz, to share her opinion on the value of nofollow links:

Nofollow backlinks can improve your SEO in the following ways:
- They can directly impact rankings. Since Google treats nofollow as a hint, it can follow the nofollowed link and include it in ranking calculations.
- They drive traffic and increase awareness. Links placed on popular sources will definitely receive clicks from visitors. If the linked source seems interesting and helpful to the context, users will visit it and possibly even navigate to other pages on the website.
- They help build a natural and diverse backlink profile. The dofollow-only backlink profile will raise suspicion in search engines because it might seem that all links are paid and agreed on instead of being earned by the quality of content itself.
- They give opportunities to get dofollow backlinks. The more links a website gets in general, the more it’s recognized by users and SEOs. When you grow your backlink profile with nofollow links, your chances of getting followed links increase.
How to know if the link is nofollowed?
To examine the rel attribute and its values, which remain hidden from users within the page code, you can use various methods. Here are some ways to check backlinks and their attribute values:
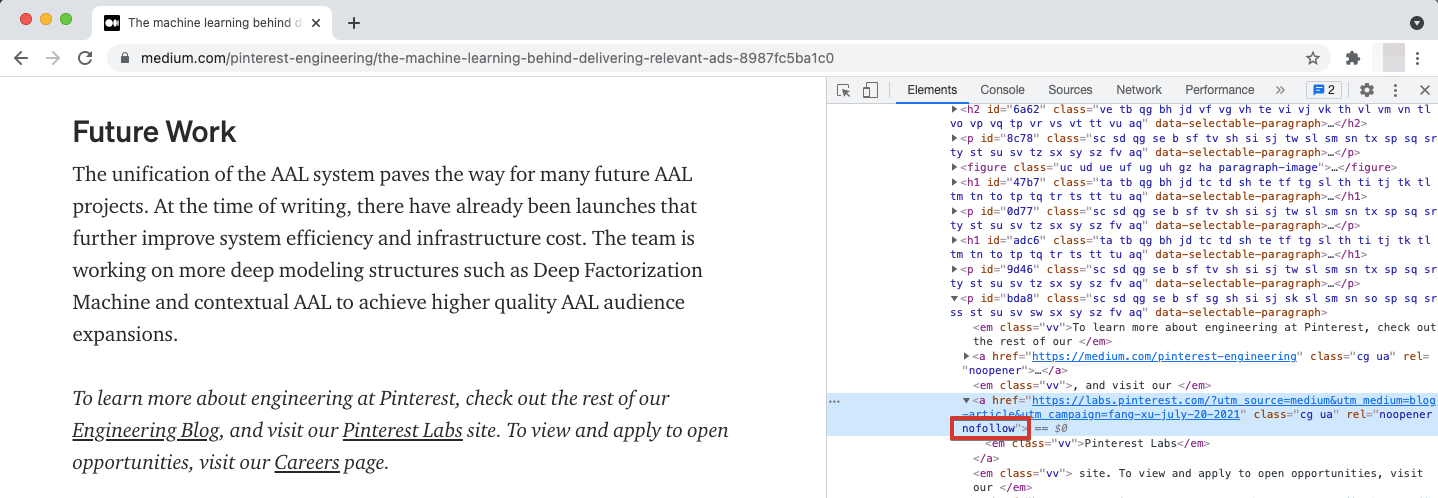
- By viewing the code in the Chrome browser. By right-clicking on a link and choosing Inspect, you can view the page code with the link code highlighted. If the rel attribute is absent, it signifies a regular, followed link. If the attribute is present, look at its value:
- By using browser extensions. Many extensions highlight either dofollow or nofollow external citations on a page. With the NoFollow extension in Chrome (it’s also available on Firefox), nofollowed links are highlighted in red, while others aren’t marked at all. Here’s how it looks:
Some more complex extensions not only highlight the linked sources but also generate a report with backlink and domain parameters. For example, you can filter followed/nofollowed links using SEOquake:
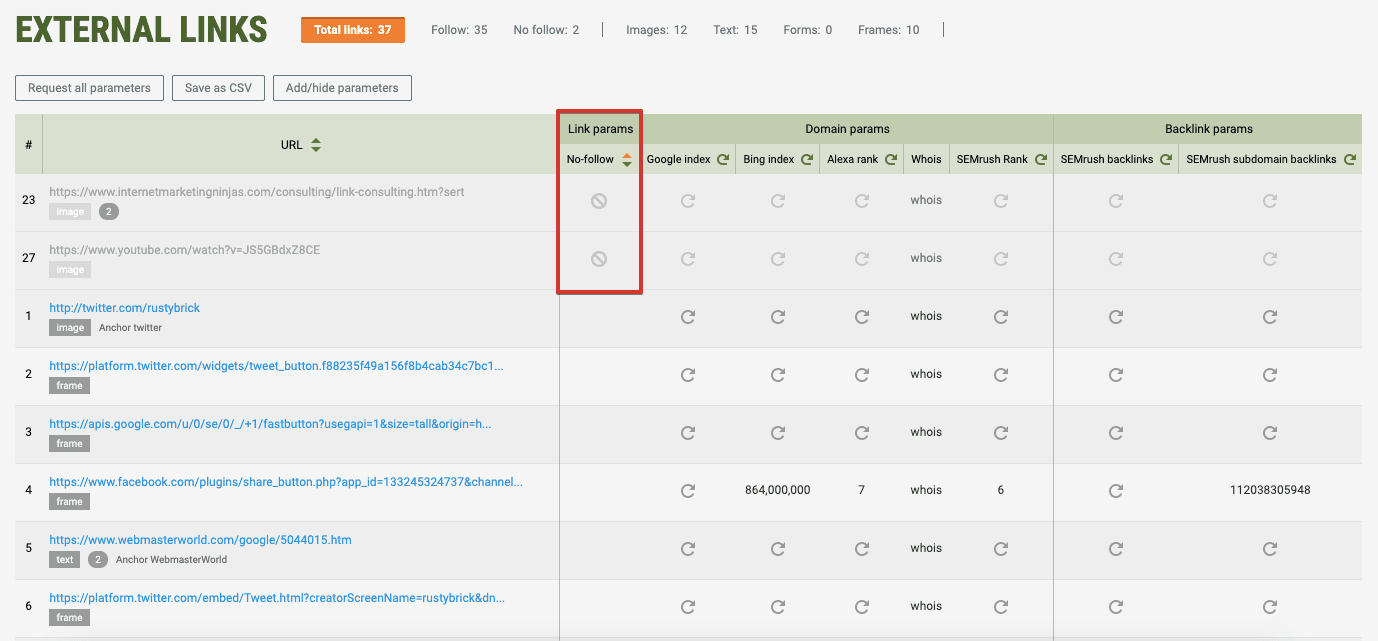
- By using an SEO tool. This method is not for checking citations on any given page but for checking all the backlinks on your website or on another domain. SE Ranking’s Backlink Checker allows you to analyze your backlink profile and review major link parameters, including whether they are followed.
In the Backlinks section of the tool, the Type column indicates whether a backlink comes from a text or an image, as well as whether it’s followed.
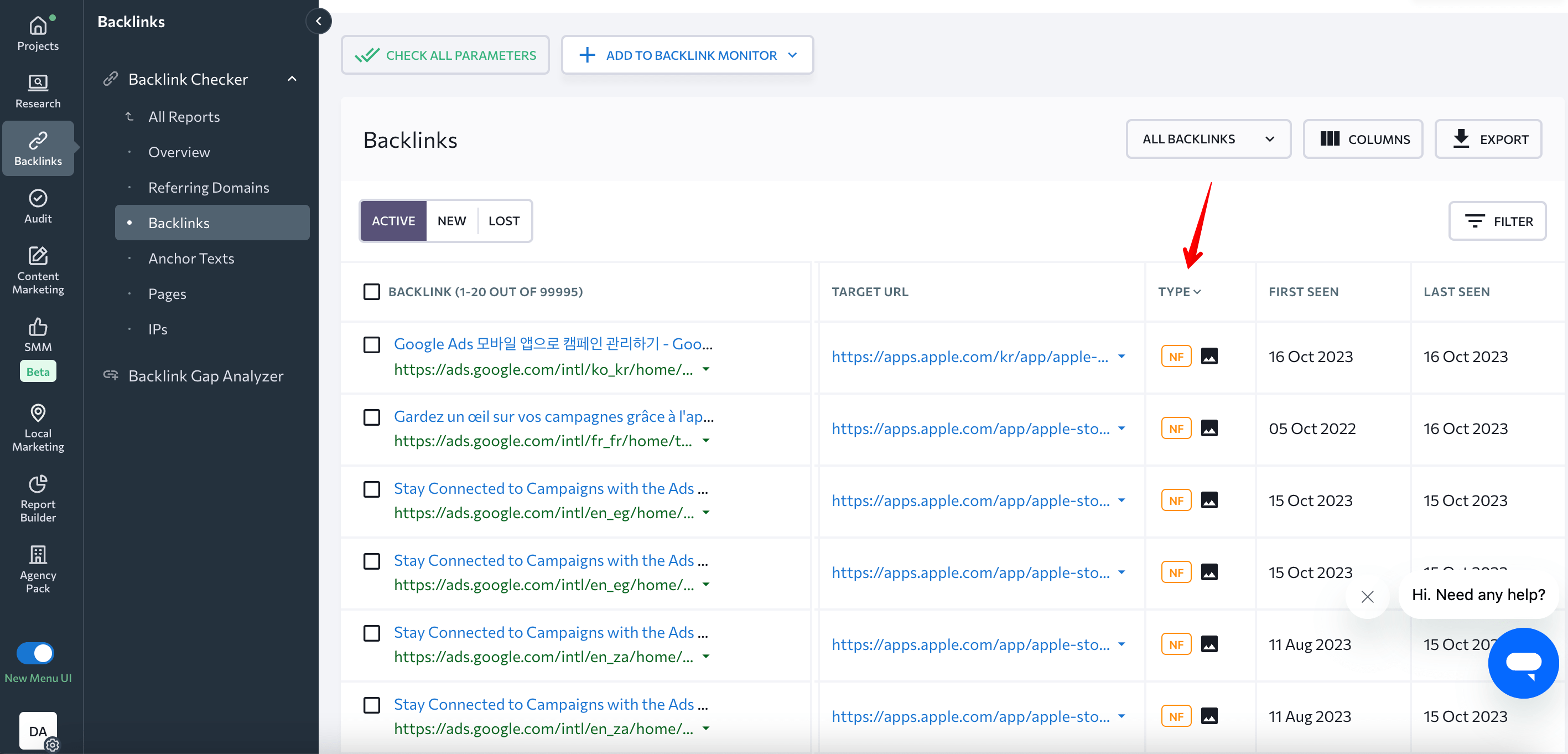
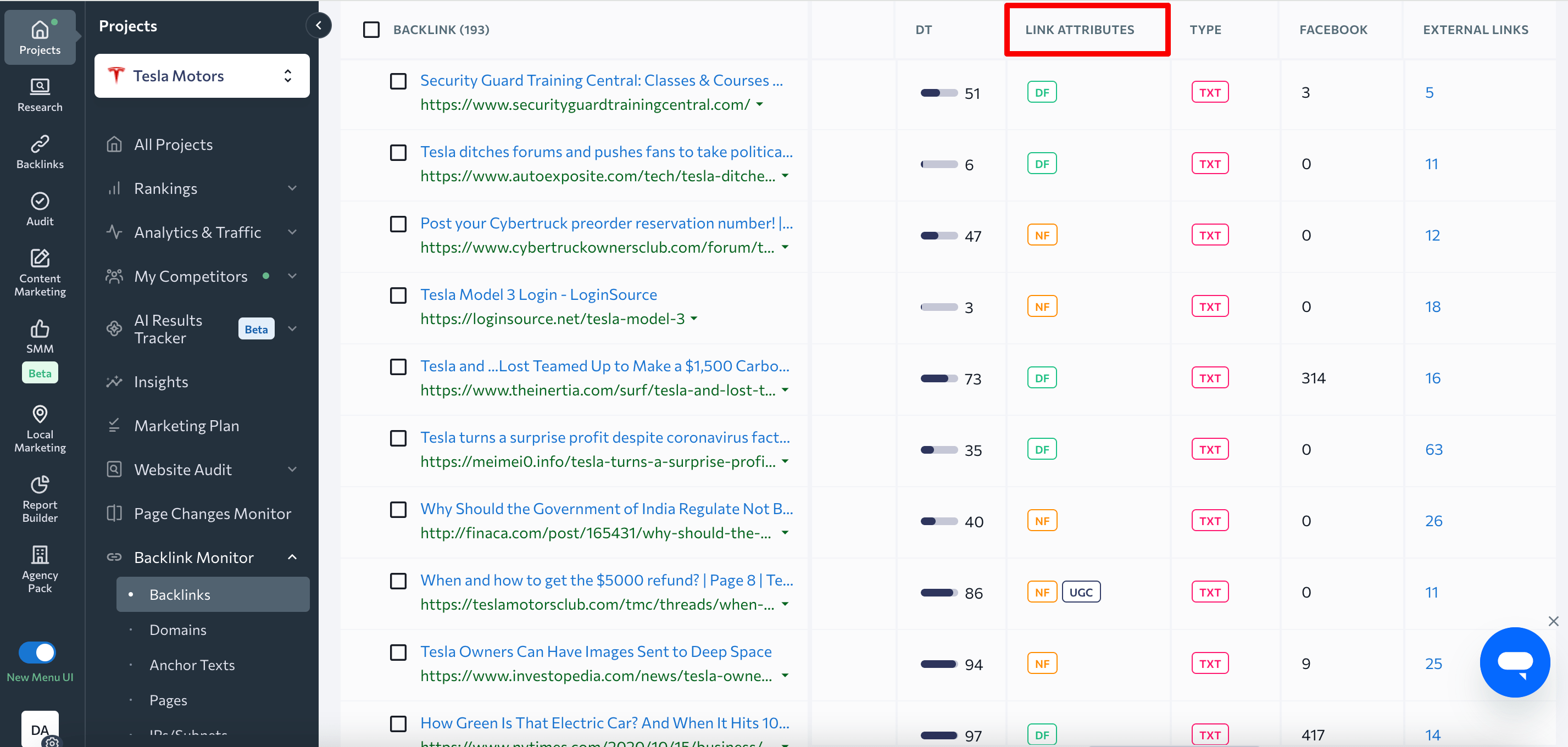
Or you can add your inbound links to SE Ranking’s Backlink Monitor and see this data in the Link attributes column.
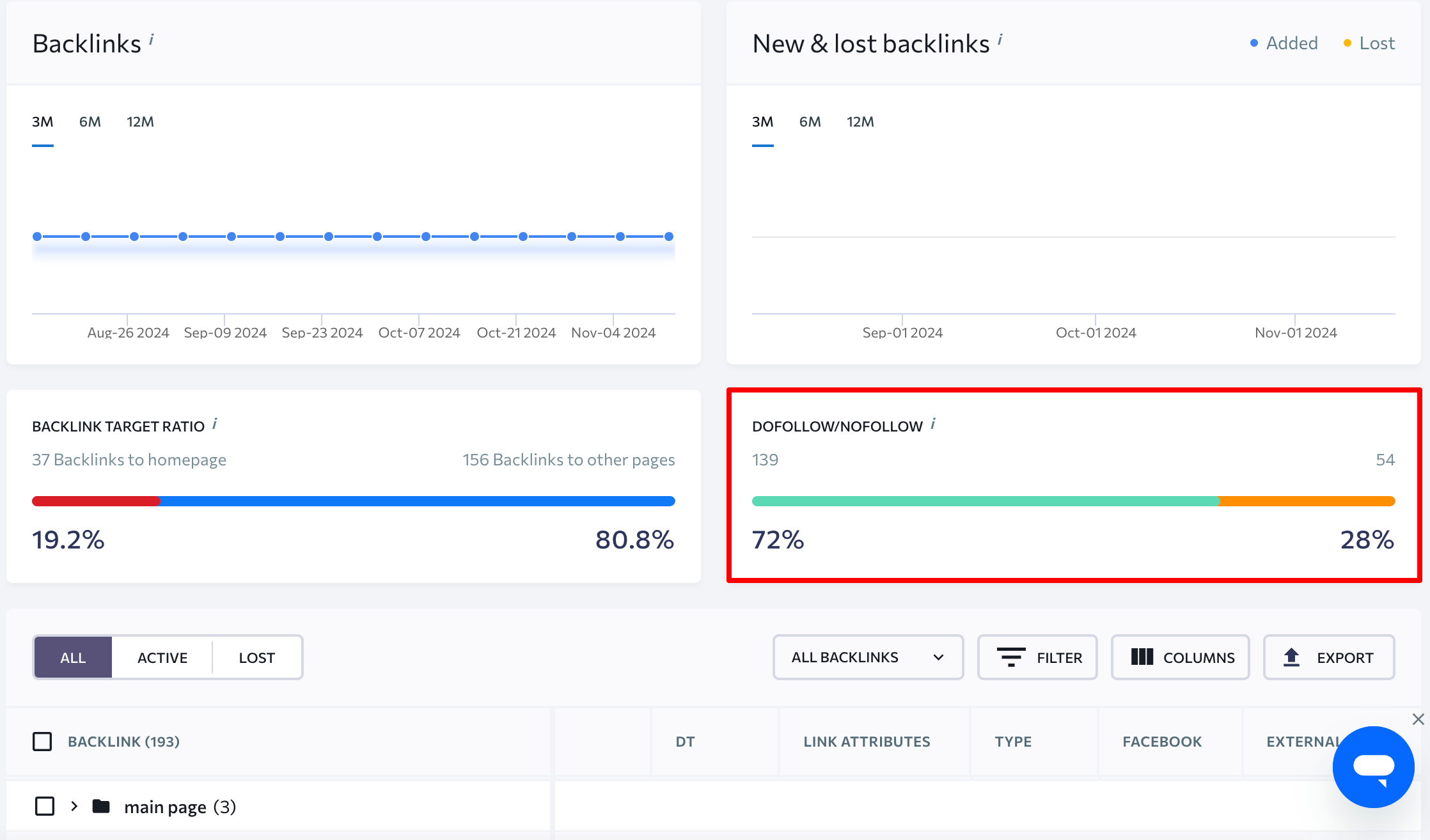
You can also view the distribution of followed and nofollowed backlinks and filter the table by this value:
Now that we’ve outlined the differences between the rel attribute values, let’s discuss the SEO value of nofollowed links and why it’s important to check if a backlink has been followed.
How Google and other search engines treat nofollow links
We now understand that when Google encounters a nofollow link, it doesn’t completely ignore it. Instead, Google treats the nofollow attribute as a hint that indicates it should not pass PageRank or link equity through the link. However, Google reserves the right to still follow the nofollowed link and consider it in ranking calculations if it perceives the link to be of high quality or relevance. In other words, while the nofollow attribute provides a signal to Google, it doesn’t necessarily prevent the linked page from being considered for search rankings.
Other search engines such as Yahoo, Bing, and DuckDuckGo also use links to evaluate website authority and relevance. While there is less information available regarding how Google alternatives perceive the rel attribute values, we can assume that nofollowed links may hold even greater value if you’re targeting these search engines.
For example, Bing places a strong emphasis on the quality and relevance of the backlinks rather than the dofollow or nofollow attribute. Bing recommends getting “quality links […] from a website Bing knows already and trusts.” This means that obtaining a high-quality link from a website trusted by Bing, whether it is a dofollow or nofollow link, can have a significant SEO impact on a website’s ranking in Bing search results.
Similarly, DuckDuckGo focuses on high-quality backlinks from relevant and trustworthy sources as a key factor in its ranking algorithm, regardless of the dofollow or nofollow attribute. DuckDuckGo claims that “links from high-quality sites […] are the best way to get good rankings.”
Overall, while the specifics of how each search engine treats dofollow and nofollow links may differ, the importance of high-quality backlinks remains consistent.
Can nofollow links hurt your website?
When it comes to nofollow backlinks, Google’s stance on them has been the same since 2013: they do not harm your website unless they are obtained from spammy link exchanges (black hat SEO strategies). You should prioritize getting backlinks from high-quality sources and regularly monitor if spammy websites link to you. In Backlink Monitor, you can filter them by the Domain Trust score, which indicates the level of authority that a referring domain has:
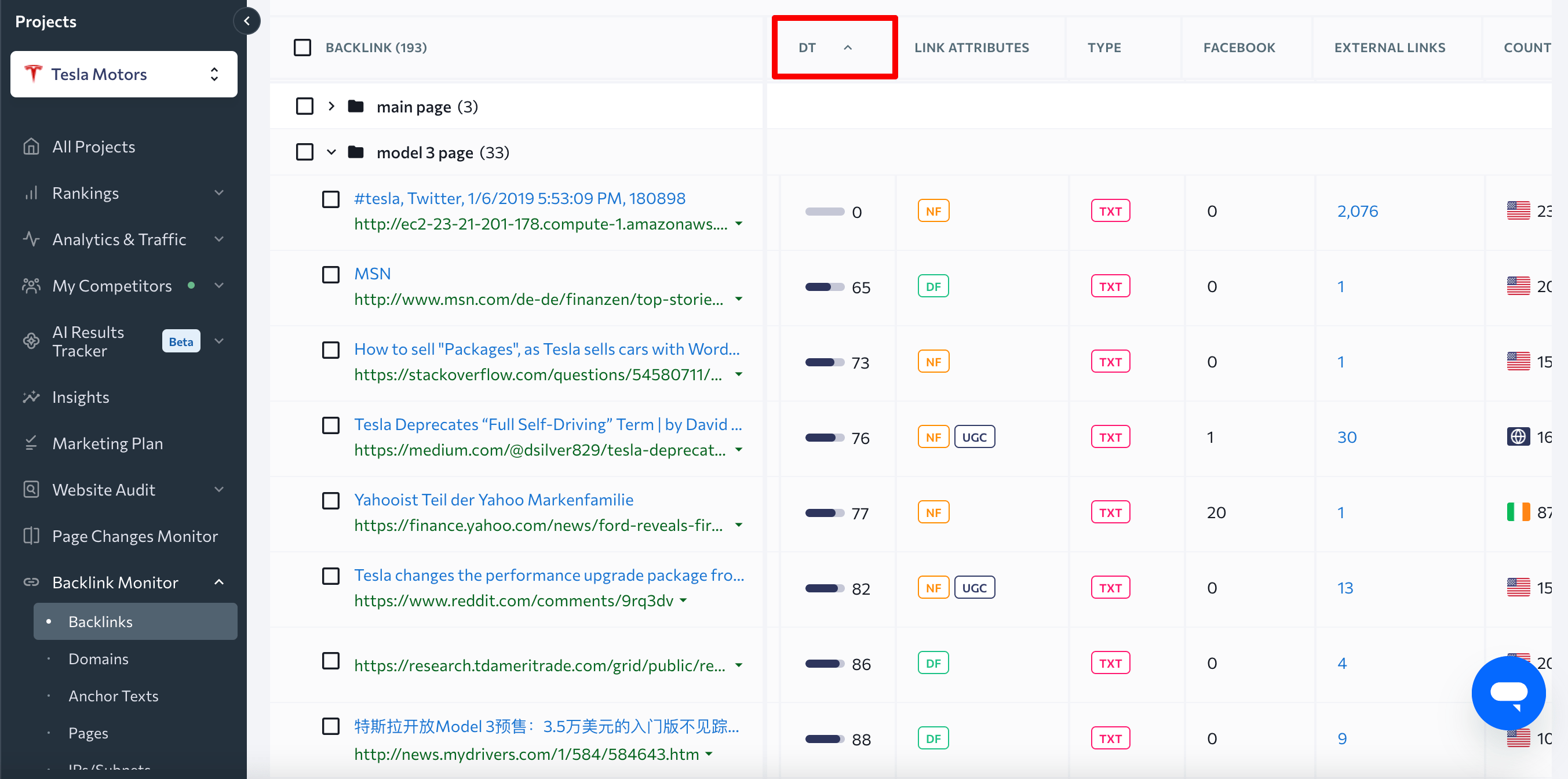
To remove potentially harmful backlinks, you’ll have to contact the websites that are referring to your site.
The best ratio of dofollow and nofollow backlinks
With the abovementioned benefits in mind, you should work on receiving both follow and nofollow backlinks. But how should you treat the nofollow value in the context of your outbound links (links placed on your webpage that refer to other sources)?
We reached out to Alex Wright, SEO & Performance Marketing Director at Clicky Media, to share his thoughts on combining dofollow and nofollow links in your backlink profile.

When to nofollow external links
The nofollow value is good for when you don’t want to associate your site with the linked sources and you don’t want to validate their authority. But when you refer to a web page in your content, this means you found it interesting and that it has the potential to help your visitors. There is no reason not to endorse this source. Let’s elaborate on this a bit more in our post on external linking.
It’s important to use the ugc attribute for links in comments while using sponsored content for affiliate or other paid links, either instead of using nofollow or in combination with it. Many popular CMSs set ugc in the comment section by default, eliminating the need for manual intervention every time someone leaves an unsolicited link. With the sponsored value, you’ll have to monitor it and apply it to each particular link.
Alex Wright shared his perspective on nofollowing external links:

When to nofollow internal links
Nofollowing internal links is typically not necessary in most cases. Internal links play a valuable role in facilitating navigation and establishing the website’s structure. They help search engines discover and index content within the website.
Improve your internal linking with breadcrumb navigation—it helps users and search engines follow your site’s structure. Learn more here.
However, there might be specific scenarios where using the rel=”nofollow” attribute on internal links could be useful.
For example, you might consider nofollowing internal links to login or registration pages or internal search results pages. This way, you can help Google crawl your website correctly.
But if you don’t want certain pages to be included in the index, including login pages, filters, etc., then you need to block crawling by using the noindex directive in the robots meta tag.
The difference between nofollow and noindex
Nofollow and noindex serve as technical rules to communicate with search bots regarding the access to your pages or links. Inexperienced users sometimes confuse the two. The main distinction between them is that nofollow rules simply control the crawling of links, whereas noindex tags control the indexing of website pages.
It’s also important to understand that there are two variations of the nofollow rule. Firstly, it can be applied as an attribute within the <a> tag, allowing you to prevent a specific link from being crawled. Secondly, it can be utilized as a rule within the <meta> tag, commonly appearing as <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,nofollow”>. In the latter case, it instructs search engines not to follow any of the links present on the entire page.
By understanding and distinguishing between these two approaches, you can selectively control the crawling behavior of individual links or apply a broader nofollow rule to all links on a page.
Ensure that all the internal links that are intended for ranking purposes are followed. SE Ranking’s Website Audit provides the option to access and download a full list of your URLs, allowing you to filter them based on dofollow/nofollow values or other parameters. Go to the Found Links section and verify whether any of the important links are not marked with the nofollow attribute.
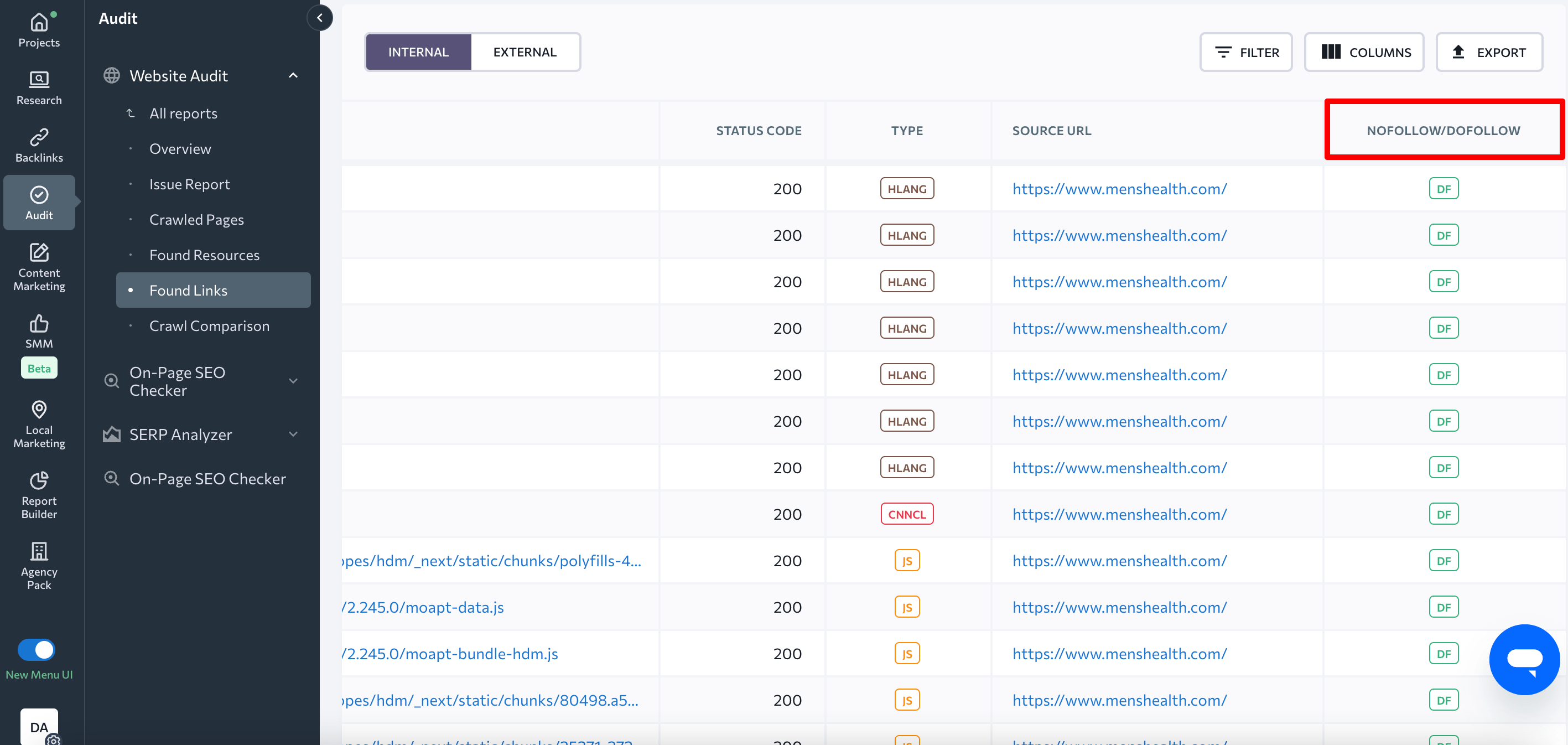
Nofollowed internal links can damage your site’s search visibility, especially if they are leading to important pages that you want to rank in the SERPs.
How to add the nofollow attribute value
To make a specific link on your website a nofollow link, there are two main methods you can use. The first option is to manually edit the page code and add the attribute rel=”nofollow” to the link. The second option is to install a plugin for your CMS that automatically offers a nofollow checkbox for each inserted link. For instance, the Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress opens a menu with three options for each link, allowing you to mark it as nofollow or sponsored:
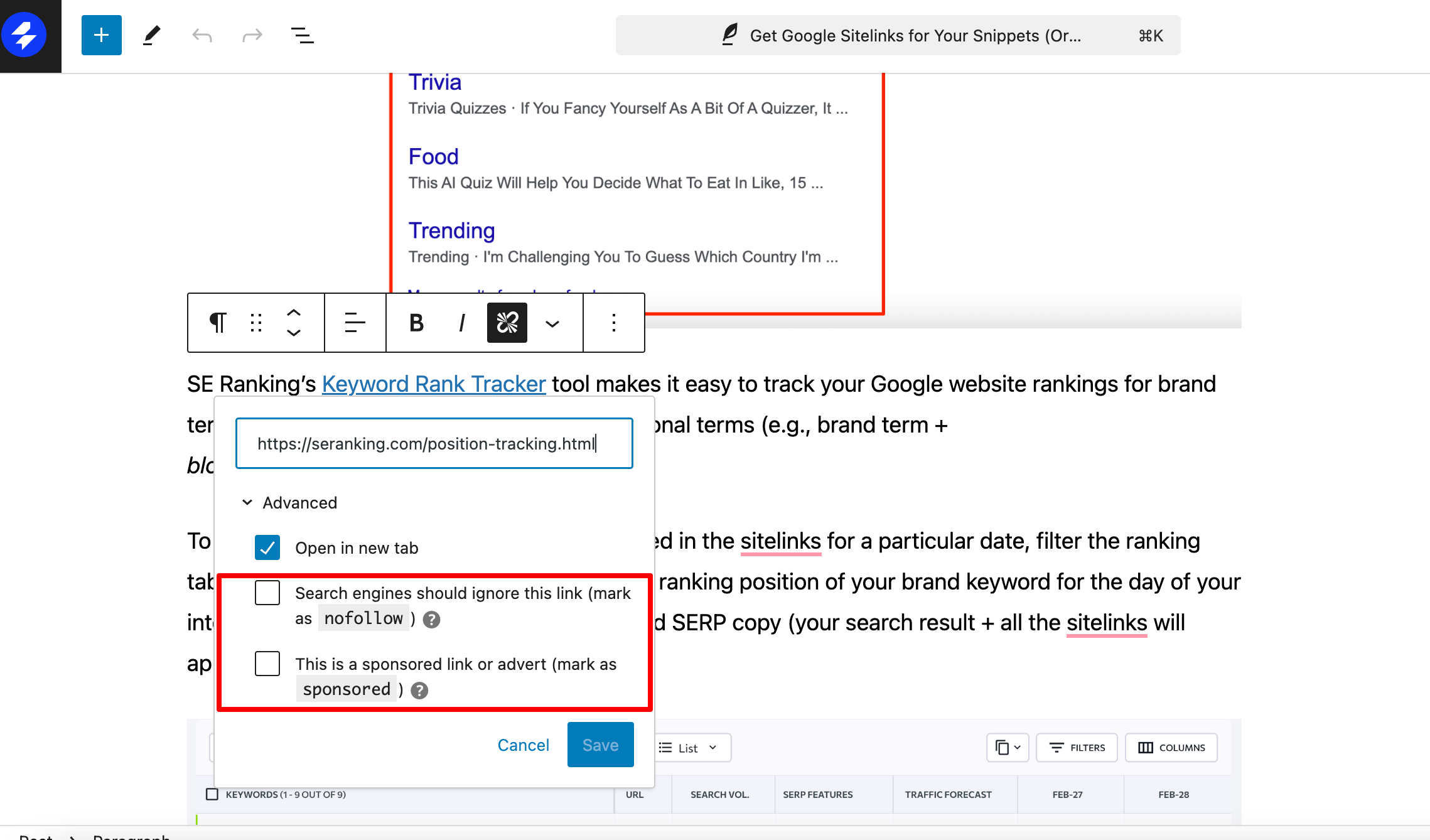
Other plugins with similar functionality include External Links, All in One SEO, and Rank Math SEO.
Wrapping it up
By default, search engines follow all links on a webpage to crawl, index, and use them as a signal of the linked source’s authority in ranking calculations. Sometimes, websites indicate that they don’t necessarily endorse the linked page, and that’s when the nofollow value of the rel attribute is put into action. Google interprets nofollow as a hint, but we have limited knowledge about how other search engines treat this value. This means that nofollowed backlinks can still be discovered and impact rankings.
Here are some key recommendations regarding the rel attribute values:
- Build a natural backlink profile that includes a majority of followed backlinks while also having a fair share of nofollowed ones.
- When linking to external sources, use UGC and sponsored attributes when appropriate. Avoid marking trusted citations as nofollow.
- With internal linking, ensure that all important URLs are followed.