Programmatic SEO: What it is and how to make it work for you
Programmatic SEO is a smart strategy for building high-impact pages at scale. But to make it work, you need more than just templates and data. You need a thoughtful approach.
In this post, we’ll break down what programmatic SEO is and how to use it the right way. Let’s dive in!
-
Here’s a simple guide to setting up programmatic SEO to get high-ranking automated pages that bring in traffic and offer real value.
-
Step 1. Find scalable keyword patterns:
Focus on long-tail keywords. Create thousands of content opportunities by combining head terms with modifiers like location, intent, or features.
-
Step 2. Review search intent carefully:
Gauge user expectations for each keyword and tailor your page structure accordingly.
-
Step 3. Gather accurate, relevant data:
Use reliable sources like internal databases, public datasets, APIs, or web scraping to power your content and maintain quality at scale.
-
Step 4. Build strong page templates:
Design SEO-friendly, dynamic templates that adapt to each keyword while offering unique, useful experiences to users and search engines.
-
Step 5. Publish with top tools:
Automate publishing with platforms like WP All Import, Zapier, Softr, or Whalesync, but always test pages for broken links, formatting, and mobile responsiveness first.
-
Step 6. Track and optimize continuously:
Fine-tune your programmatic SEO strategy over time by monitoring keyword rankings, traffic, and engagement with tools like SE Ranking, Google Search Console, and GA4.
What is programmatic SEO?
Programmatic SEO is about using automation and templates to generate large volumes of optimized pages at scale, with long-tail keywords typically targeted.
It’s most useful for websites with product listings, directories, and location-based content.
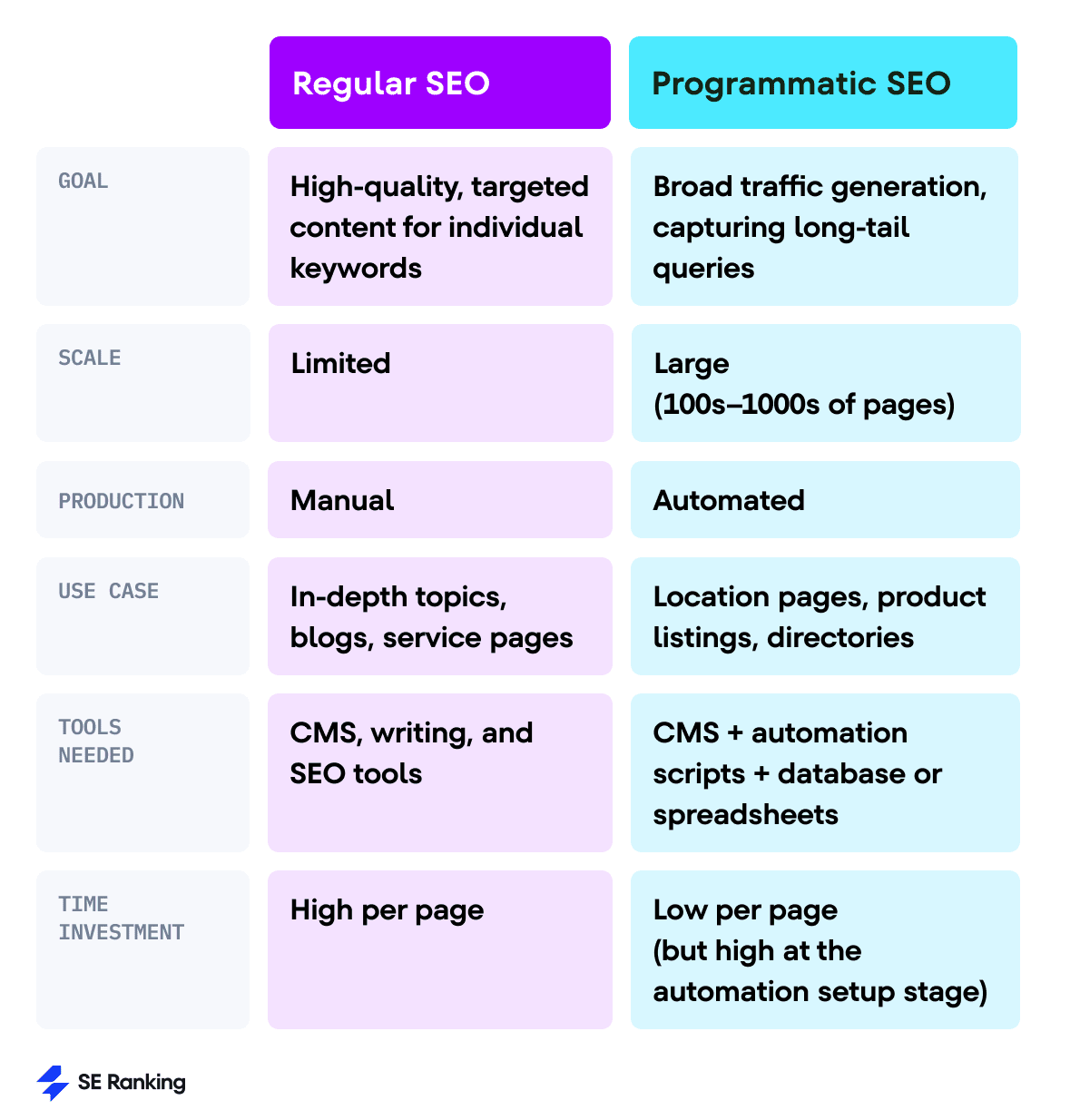
For a clearer understanding of programmatic SEO, let’s compare it with traditional (or regular) SEO.
Programmatic SEO and regular SEO differ mainly in how the content is created and scaled.
Regular SEO focuses on creating and optimizing individual pages manually. This means doing keyword research and content creation, optimizing metadata, adding images, and structuring internal links (all for one page). This method is most effective for blog posts, service pages, or landing pages where depth and originality matter most.
Example:
Let’s say you write an article and target the keyword “how to speed up a WordPress site.” You would manually create the content, optimize it, and then publish it.
Programmatic SEO is much different. Instead, you’re automatically generating several pages. The process involves identifying a keyword pattern and creating a dynamic template filled with data from a database or spreadsheet. Once the system is set up, you can scale SEO content across hundreds of pages (or even thousands), and do it much faster than with manual methods.
Example:
You would use a template and a database of cities and restaurants to create 500 landing pages that target keywords like “best restaurants in [city]”.
How does programmatic SEO work?
Let’s start by going over the key elements of programmatic SEO. We’ll look at them bit by bit to see how the process actually works.
- Keyword research & identifying patterns. Programmatic SEO works best when you target very specific search queries, like “best budget hotels in Paris” or “iPhone 13 cases under $20.” Scaling these pages is easy when you understand the keyword pattern.
- Structured data source. Programmatic SEO requires a database or spreadsheet with all key information. This includes product specs, location details, prices, and categories. This data fuels your template creations and lets you generate many unique pages.
- Template design. Another key pillar of programmatic SEO is template use. Think of it like a blueprint with all the key elements (like headlines, images, text blocks). All you have to do is fill it in with the details.
- Automated content generation. Specialized tools are used to automatically pull data from a database into templates and generate SEO-optimized pages at scale.
- General optimization. Even though it’s automated, optimization still matters. Make sure your pages are crawlable, indexable, and follow SEO best practices. Create unique titles and meta descriptions, use proper internal linking, and ensure fast load times.
Is programmatic SEO spam?
SEO experts like John Mueller and Lily Ray say that programmatic SEO can be easy to misuse. And yeah, some people have certainly used it to try to trick Google. But large-scale strategies themselves don’t go against Google’s guidelines. As long as you’re using it the right way and staying within the guidelines, you’ve got nothing to worry about.
The main thing is to create pages that actually help users. Generate relevant content with answers to common user queries. This ensures your pages aren’t ever seen as spam, even at scale.
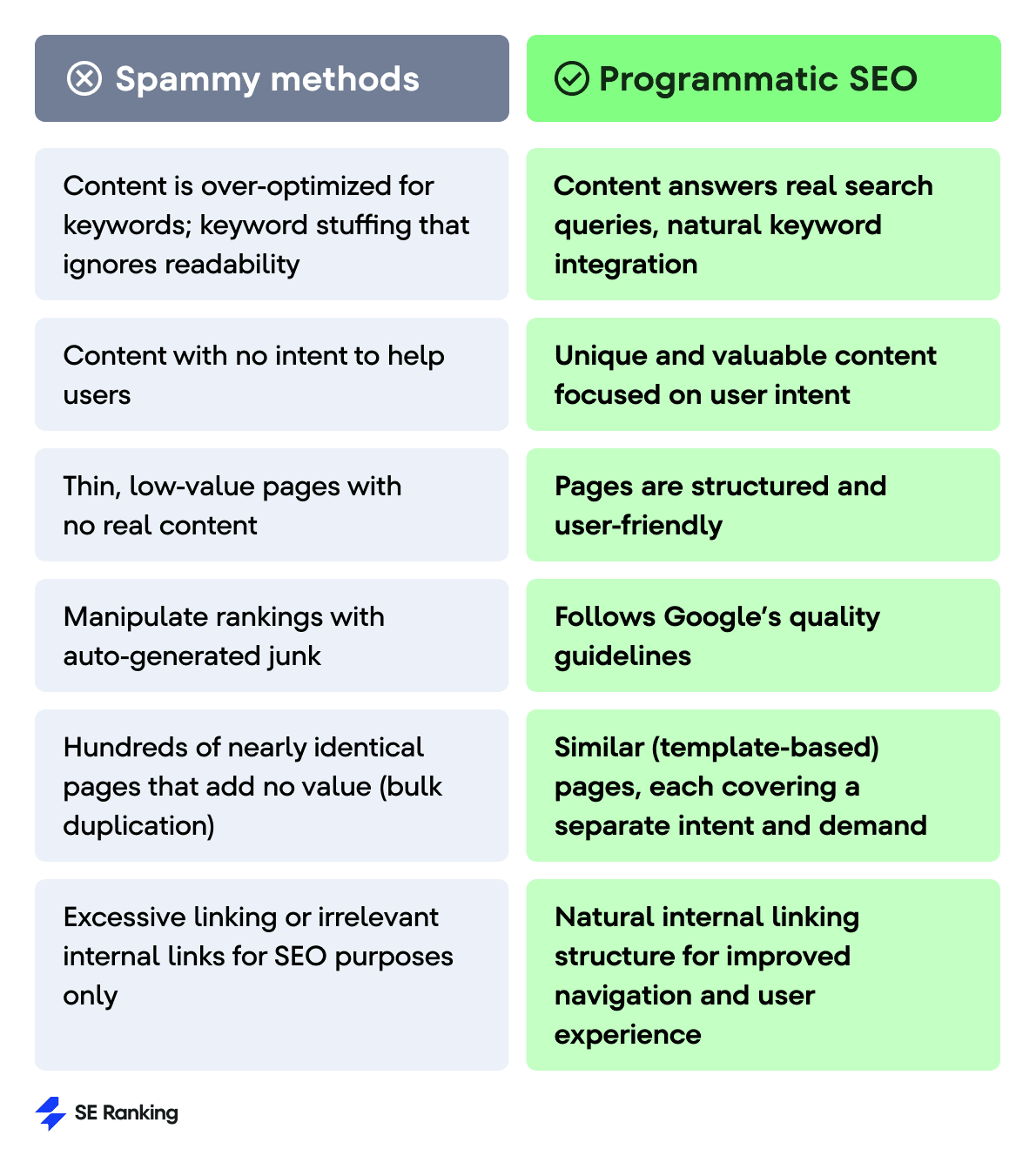
Think of programmatic SEO as a tool. It all comes down to how you use it. When used thoughtfully, it can be effective for scaling high-quality content. But it can backfire if used carelessly.
Next, we’ll walk you through how to create programmatic SEO pages that actually deliver value.
How to create programmatic SEO pages
Let’s move on to the more practical part of this guide. We’ll show you how to set up programmatic SEO to keep your automatically generated pages ranking well, driving traffic, and providing real value.
1. Find keywords that scale
Programmatic content targets thousands of semantically similar keywords (namely keyword patterns). Start by finding relevant keywords with many variations to scale your content.
This consists of batches of long-tail keywords, with a head term combined with different modifiers: location, intent, or product features. For example, you might start with the head term “best restaurants,” and then add various locations as modifiers:
Best restaurants in London
Best restaurants in New York
Best restaurants in Kyiv
You can combine the head term with three modifiers to create three distinct long-tail keywords. Each would require its own page. Then you can scale this almost endlessly by adding more secondary modifiers, like “Best restaurants in Kyiv pet-friendly”, “Best restaurants in London for dates”, “Best restaurants in New York with pizza”, etc.
But to find out which modifiers drive traffic and are relevant to your audience, you’ll want to use SE Ranking’s Keyword Suggestion tool, which is ideal for finding keyword patterns.
Start by entering your seed keyword into the Keyword Generator tool. Let’s use “guided tours” as an example.
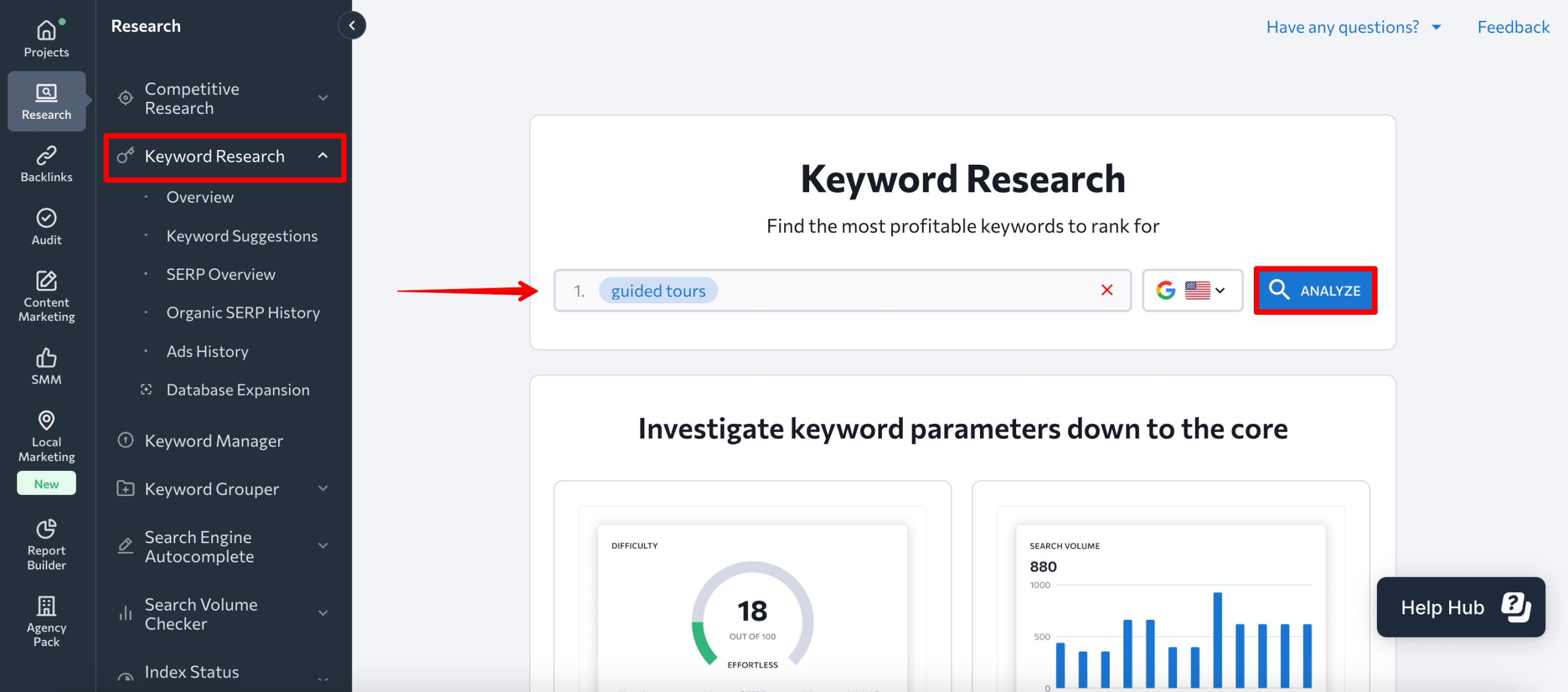
Go to the Keyword Suggestions section to see a list of long-tail keywords.
On the left side of the table are a bunch of repeating terms. Those are your keyword patterns.
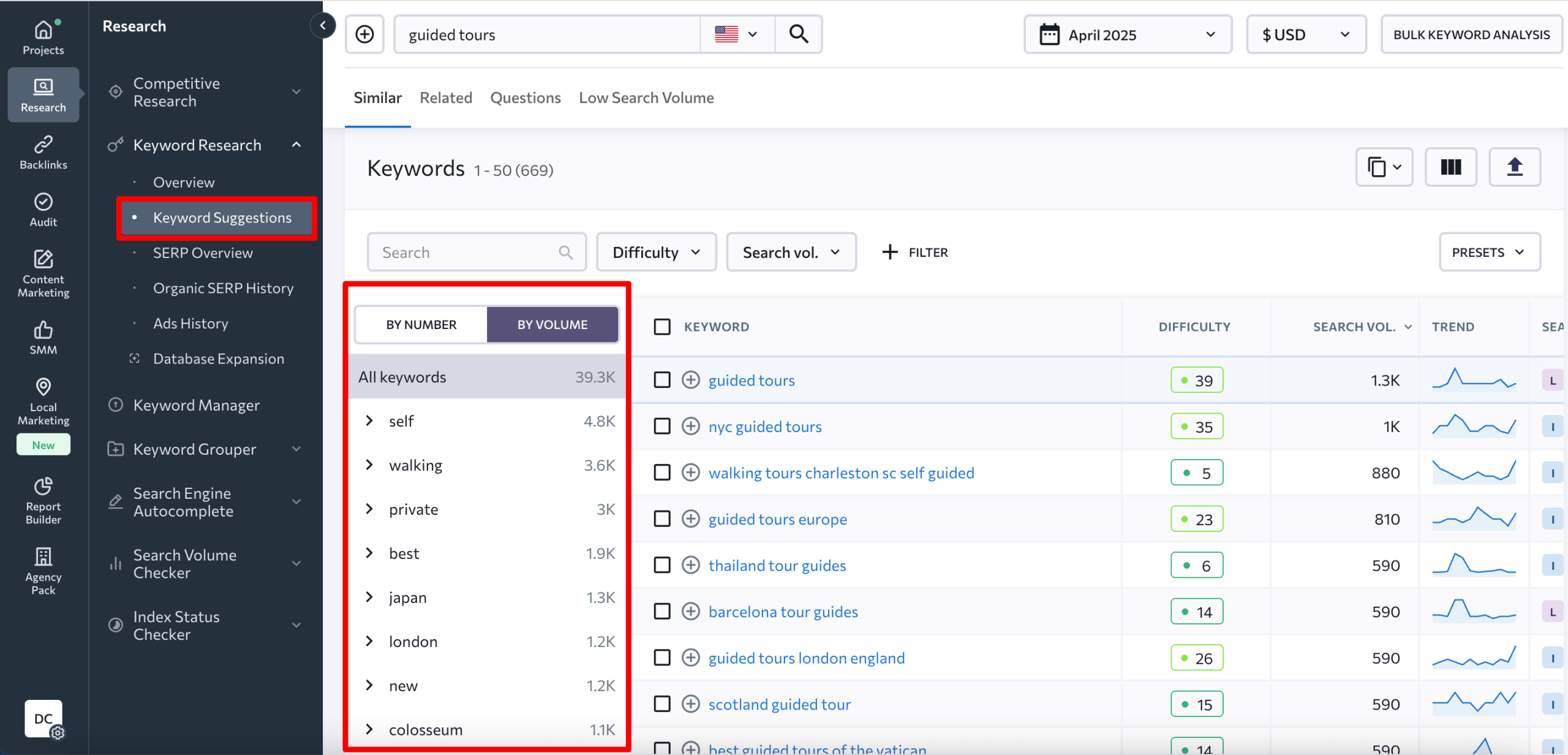
Look through the list to get a better feel for what users are searching for. Notice that in our analysis, there are intent-based patterns like self, walking, private, best; location-based patterns such as Japan, London, NYC, Rome; and even price-based patterns like free.
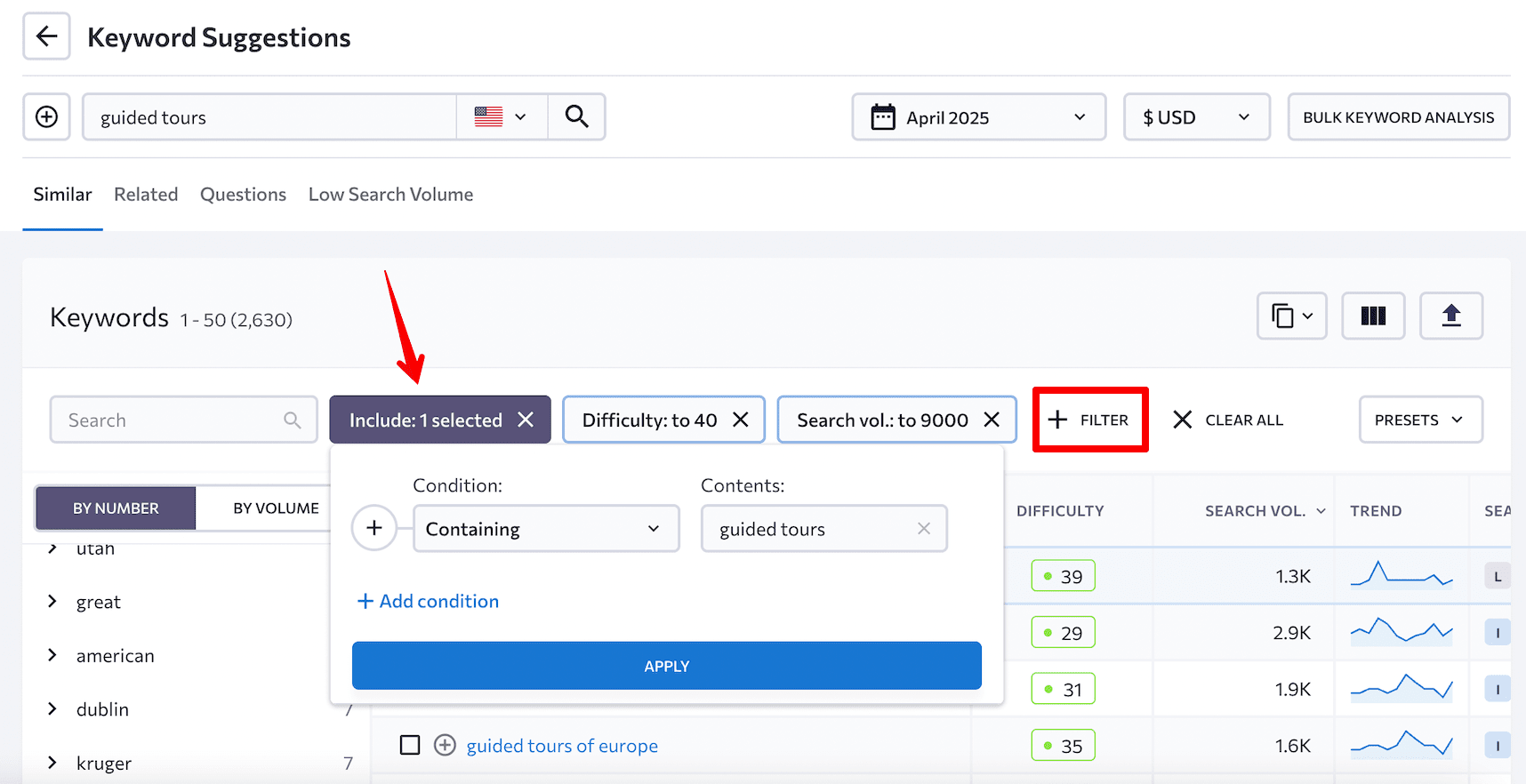
You can also run this kind of analysis by reviewing the main keyword table. Just focus on keywords with low difficulty and decent search volume. We recommend setting the difficulty to 40 or below. As for search volume, what’s considered low will vary depending on your niche.
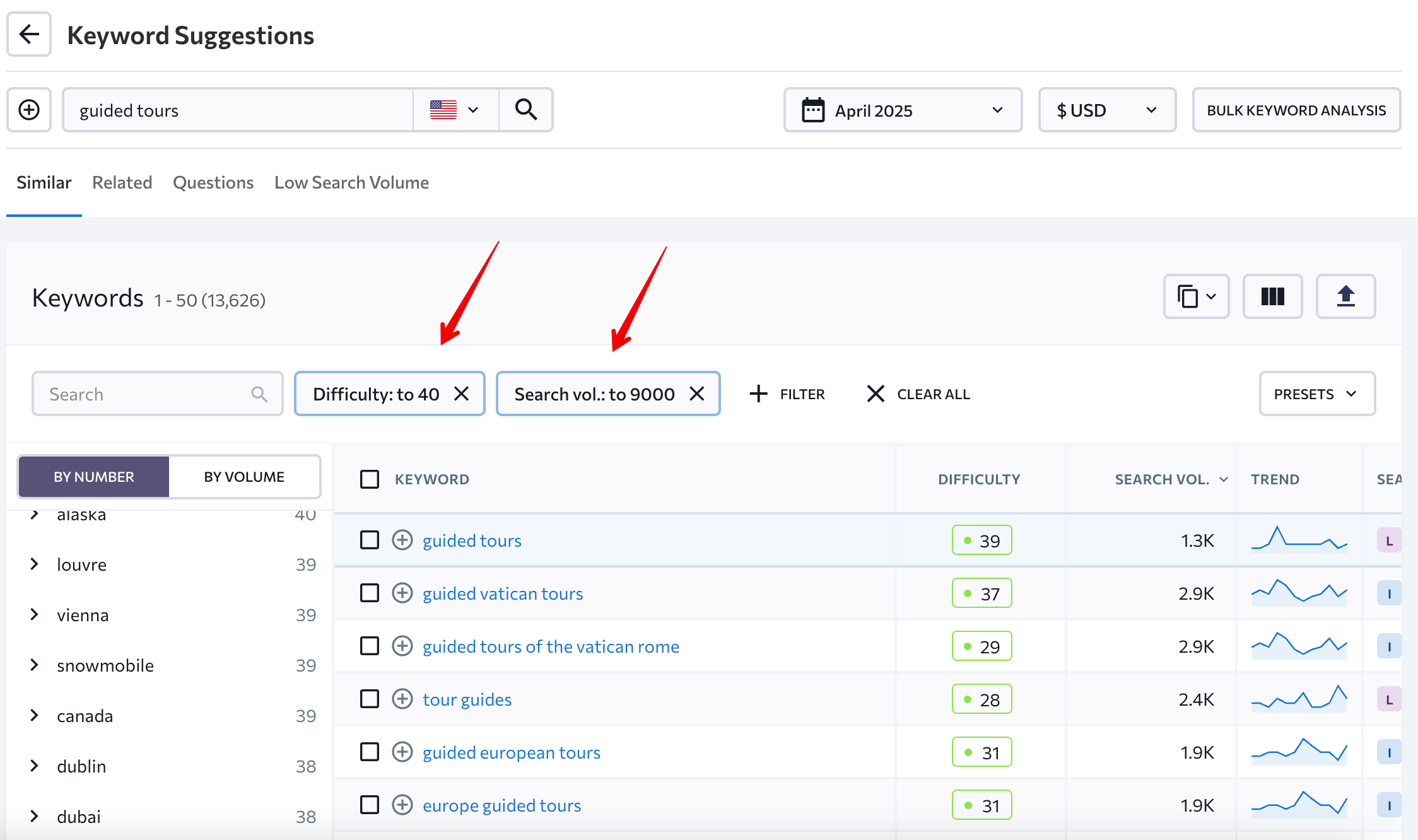
You can focus on exact matches of your main keyword by filtering the list under that specific criterion.
2. Analyze search intent
It’s possible to generate thousands of programmatic pages that technically match the query, but this isn’t what users want. That’s where understanding search intent becomes essential. It shapes not just your keyword list, but the entire structure and content of your programmatic SEO pages.
Search intent is the why behind a query. It’s what the user is trying to accomplish:
- Buy something? (Transactional)
- Learn something? (Informational)
- Go somewhere? (Navigational)
- Compare options? (Commercial)
Creating effective content means knowing exactly what users expect to see. For instance, if someone searches “best budget laptops 2025”, are they looking for a comparison, a curated list, or a single product page? Knowing the intent helps you figure out if you need to build a listicle, a comparison table, or skip the keyword entirely.
It also helps you build smarter, more targeted templates. If users searching for “best laptops for students” want specs, price comparisons, and pros & cons, your template should include all of it. If the query is location-based, add maps or local details. If it’s product-focused, include filters or CTAs.
Search intent + keyword insights = blueprint for scalable, useful content.
See the table below. It shows the intent behind each keyword.
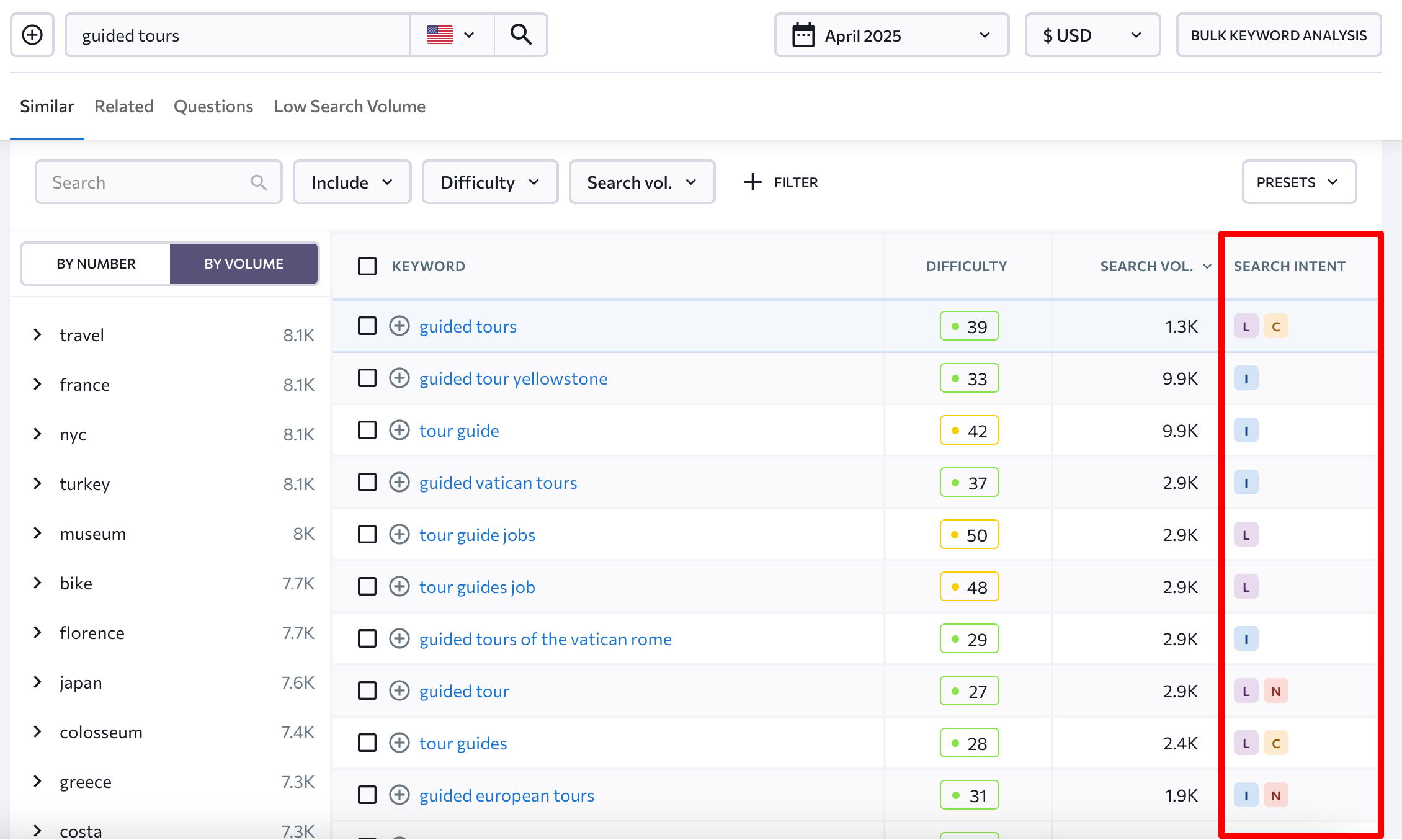
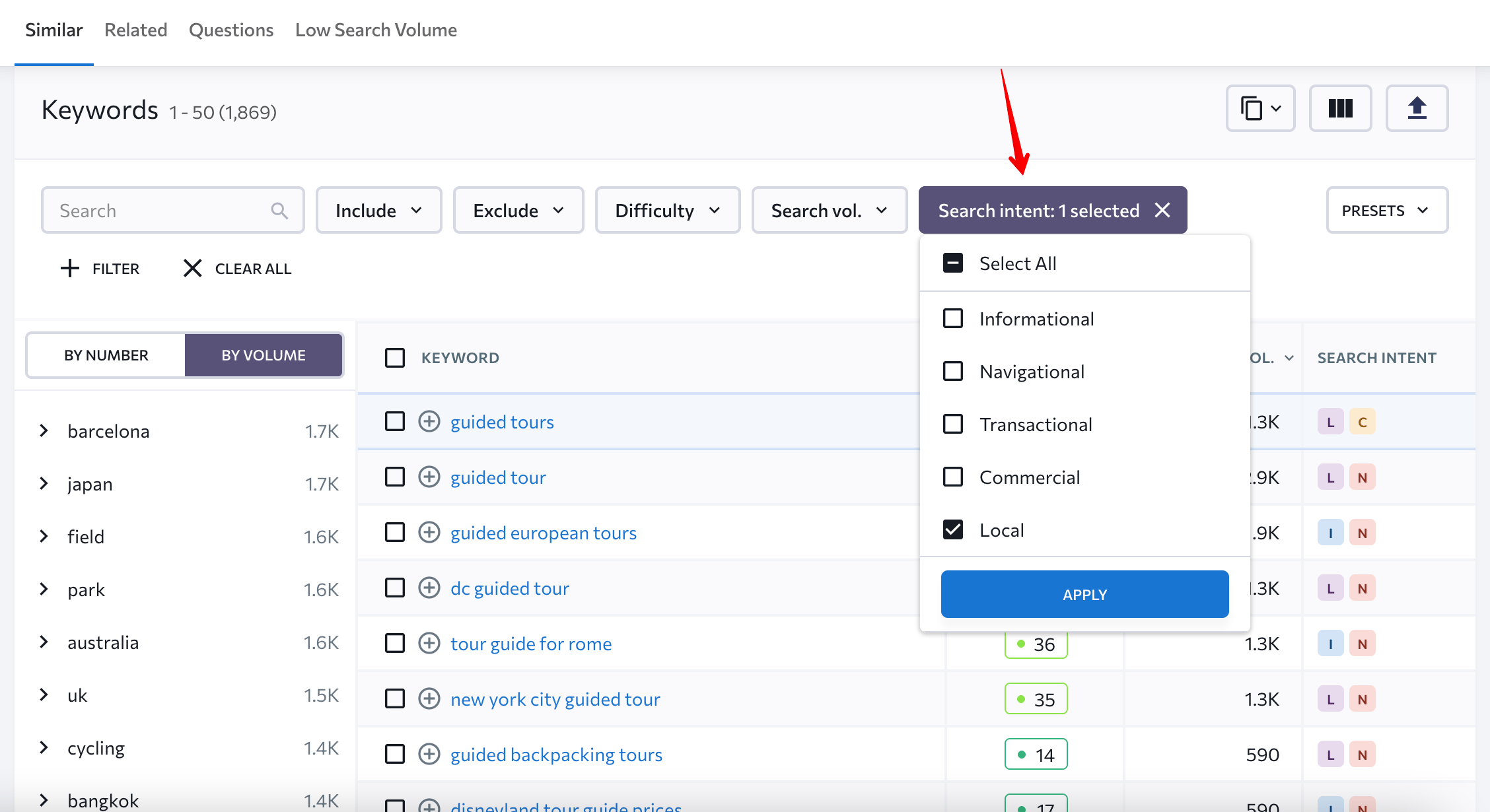
You can also filter by intent and look at the keywords for each intent separately.
You can also analyze the search results to understand what users are really looking for.
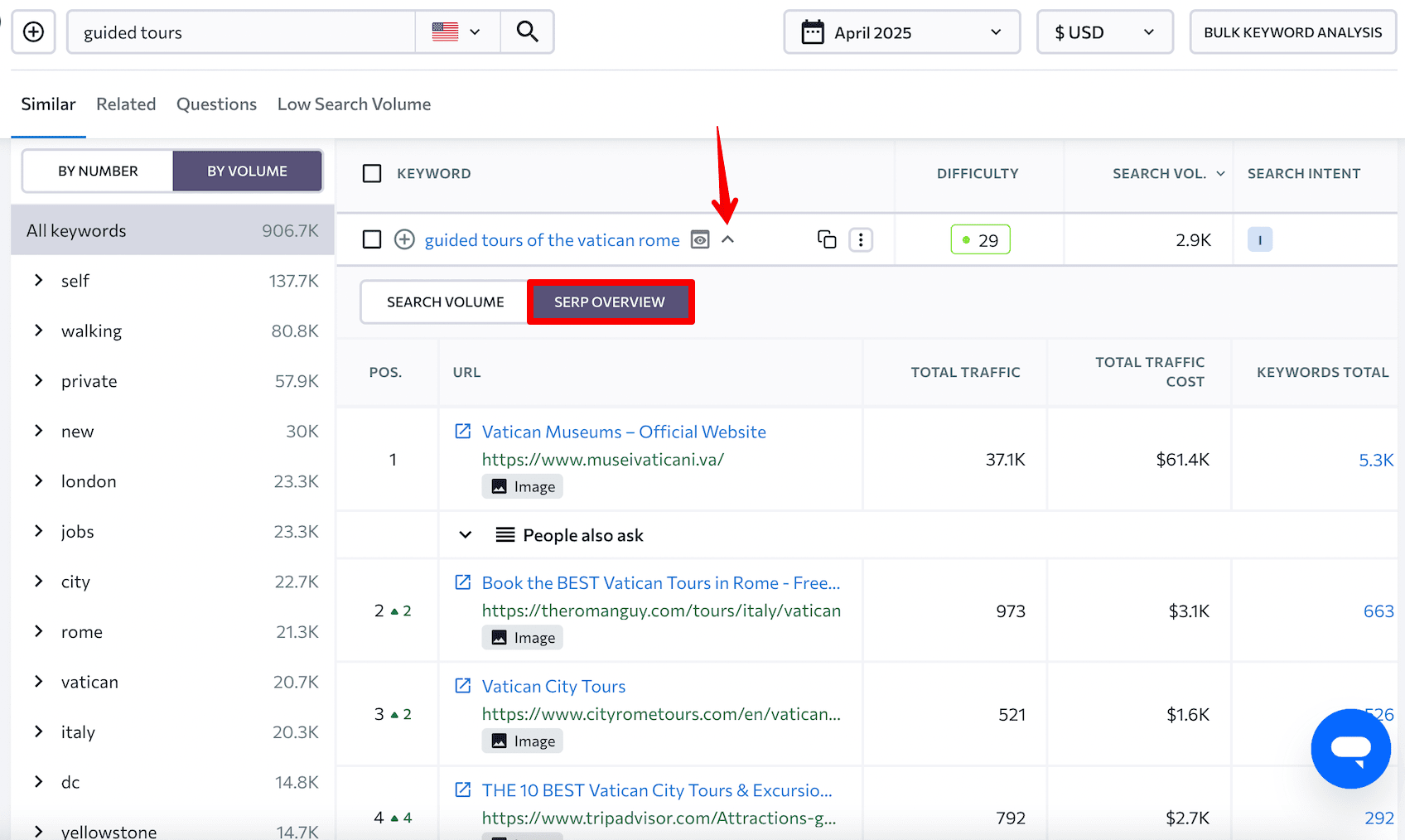
For example, the informational query “guided tours of the vatican rome” returns top results of tour lists and ticket options. You’ll need to create a similar content structure to rank well and convert users for this keyword.
3. Identify and collect relevant data
Once you have your keyword lists ready, find reliable data sources for your content.
Data accuracy and relevancy are crucial in programmatic SEO, where content is created at scale using automation.
Users (and search engines) quickly lose confidence in outdated, misleading, or false content. Inaccurate data can lead to lower rankings, higher bounce rates, or even penalties. That’s why selecting dependable databases is so important.
Below is a list of the most common data sources. Whatever you choose should depend on your topic and business goals, among other factors:
- Internal databases. This data is unique to your business. Your competitors can’t replicate it. It’s often the most valuable and desirable.
- Publicly available datasets. These are widely available and easy to find, but others may be using them too. Plenty of datasets are available on nearly any topic. Examples of websites with different databases include: data.gov, EU Open Data Portal, Kaggle, Github, KDnuggets, Open Data Inception. You can even use Google to search for datasets, but it’s only a small sample of what’s out there.
- APIs. APIs allow you to pull structured data directly from external sources. Examples include the Google Search Console API, SE Ranking’s API (SEO data), OpenWeather API (weather), and Yelp or Google Places APIs (local business information).
- Web scraping. If APIs or datasets don’t work for you, use web scraping (which means extracting data from websites) to build your own dataset. It’s useful for gathering competitor insights, reviews, pricing data, or product catalogs. Some useful tools for this include Scrapy, Beautiful Soup and Puppeteer.
Once you’ve gathered all the data, create a page to pull it in.
4. Build and structure your programmatic pages
The next step is to build a well-designed page template. This will serve as the foundation for your entire programmatic SEO project.
Use keyword research to shape the page’s layout and structure. Check the layouts your top competitors use in search results to see what works. If you didn’t do this in step 2, open the SERP Overview tab in the Keyword Research tool.
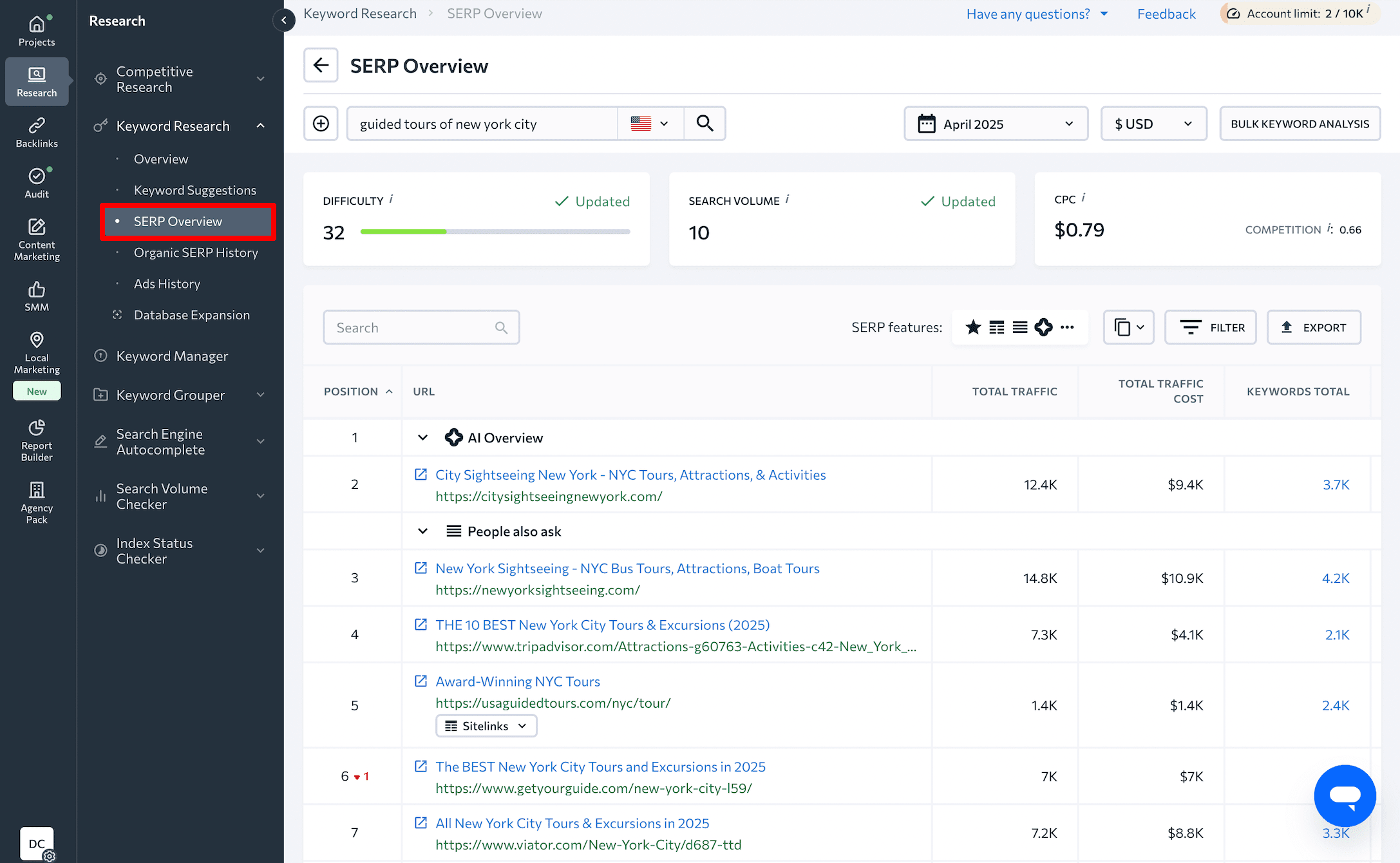
For example, if you search for guided tours of new york city, you’ll find websites featuring tour cards that display key details like images, descriptions, prices, durations, and ratings. Most sites in this niche also let you view a detailed tour page with booking capabilities, plus a search bar and filtering options.
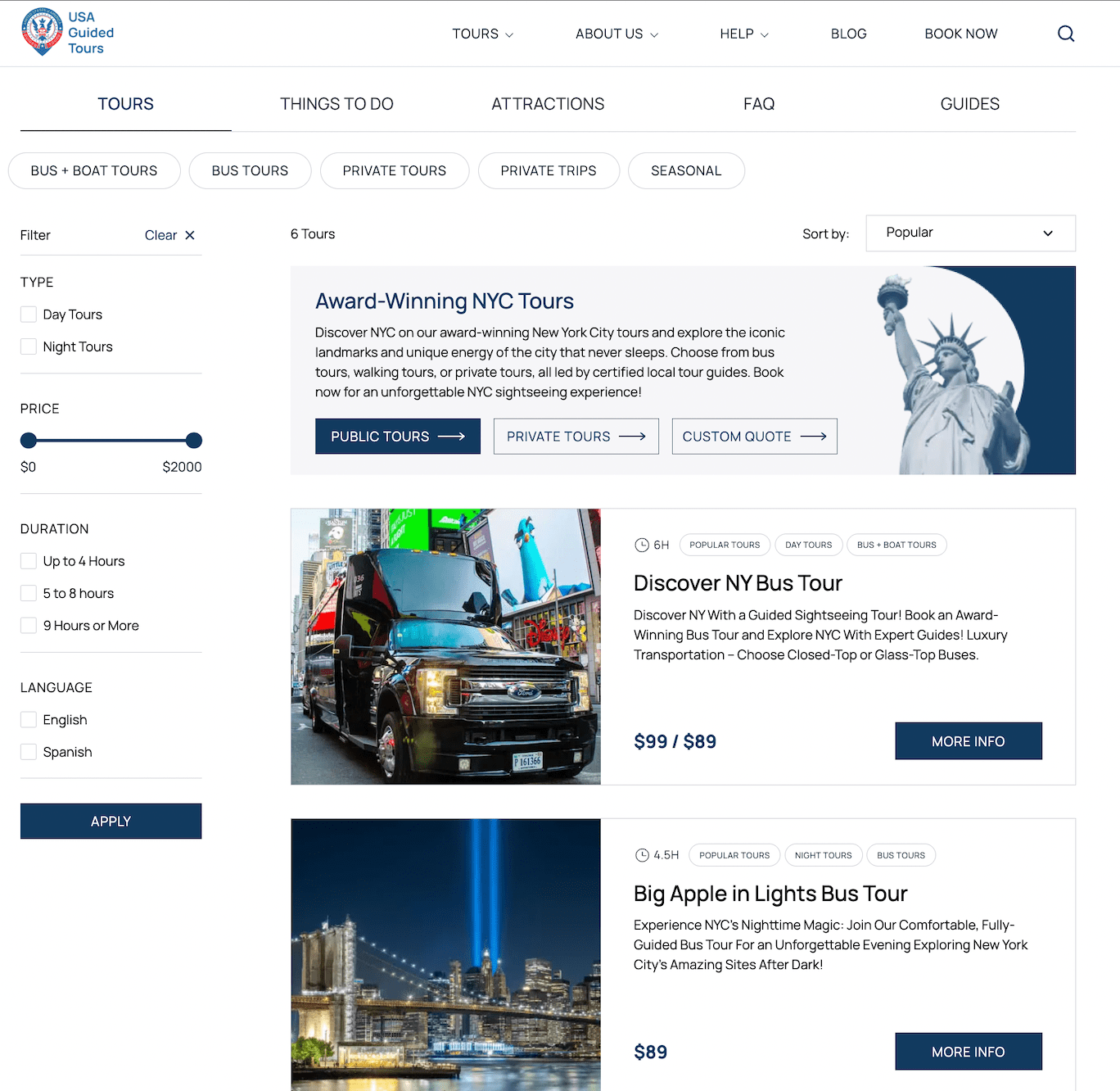
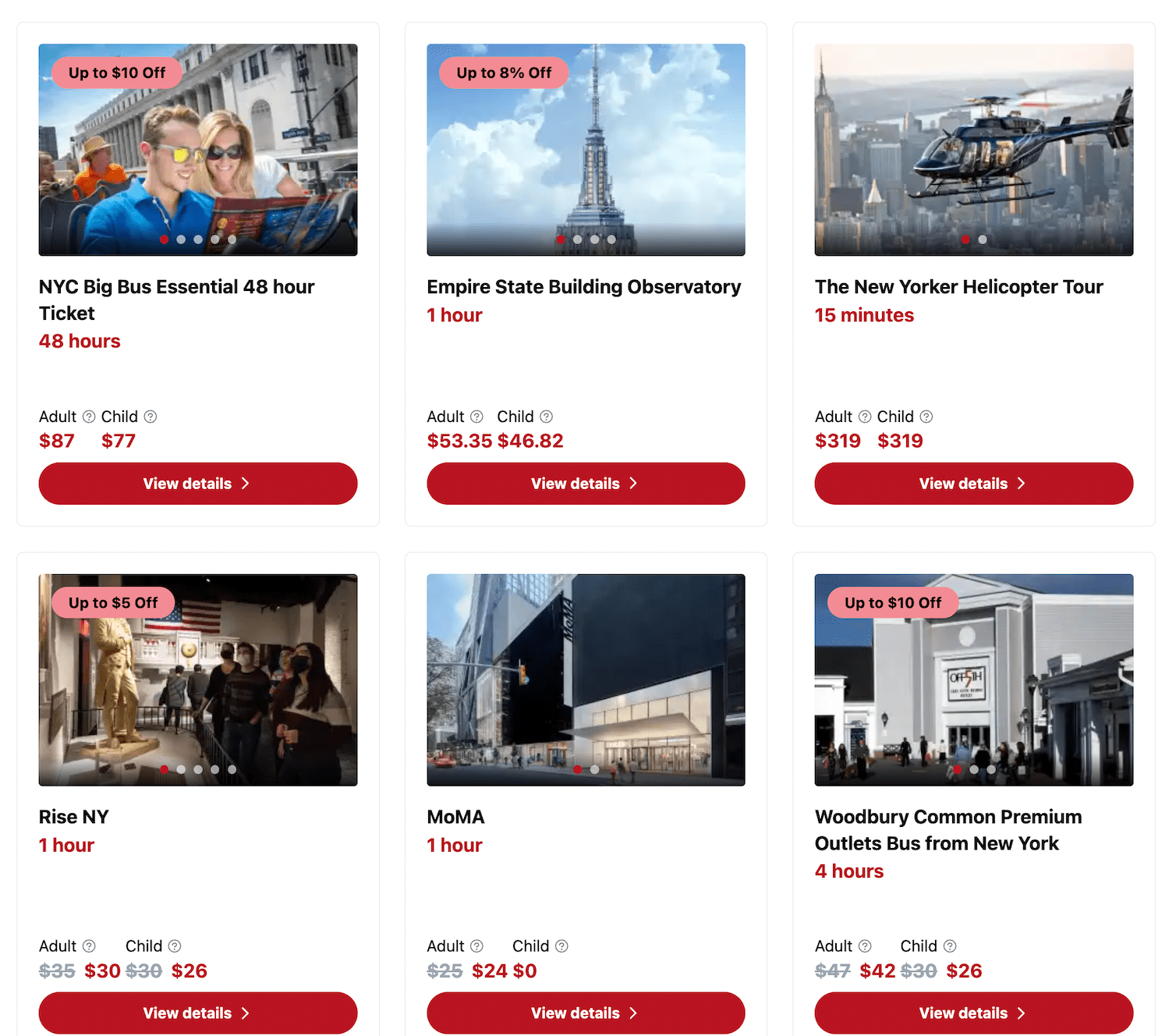
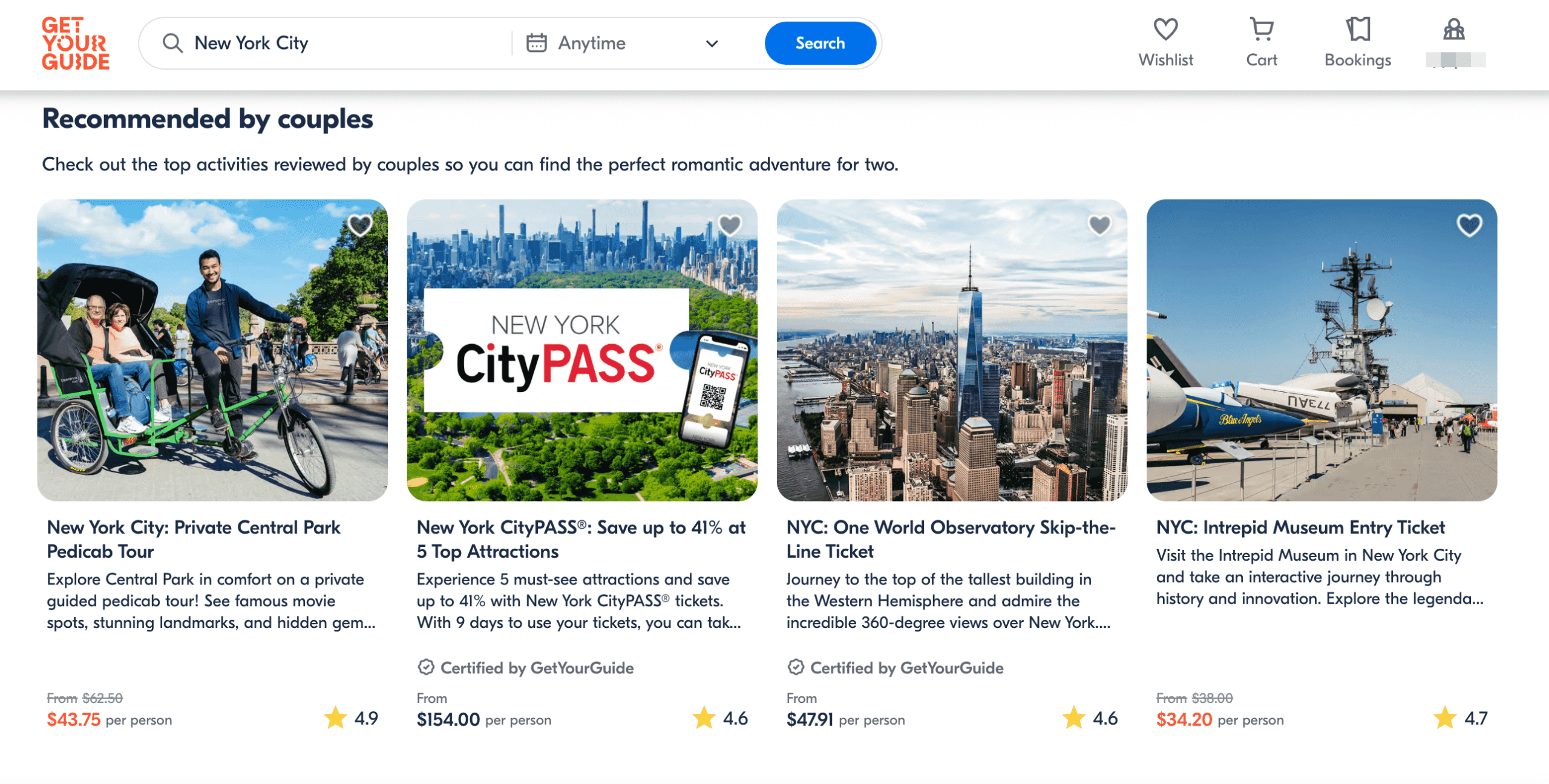
The design you choose should align with two things: what you’re offering, and the landing page type.
Use ready-made templates. Many CMS platforms let you choose from a wide selection. Platforms like Wix, GoDaddy, and Hostinger provide built-in template libraries. Popular CMSs such as WordPress, Shopify, and Joomla also have thousands of pre-designed templates that are easy to integrate. This makes getting started quickly easy, and you don’t even have to build from scratch.
Even though programmatic pages are built using a single template, each one must feel valuable, relevant, and unique to both users and search engines. Otherwise, you risk creating thin or duplicate content that fails to rank.
Here are several ways to make your content unique:
- Dynamic content: Automatically pull in data for each keyword or location. This includes pricing, product specs, local statistics, and availability, and ensures each page looks tailored and informative.
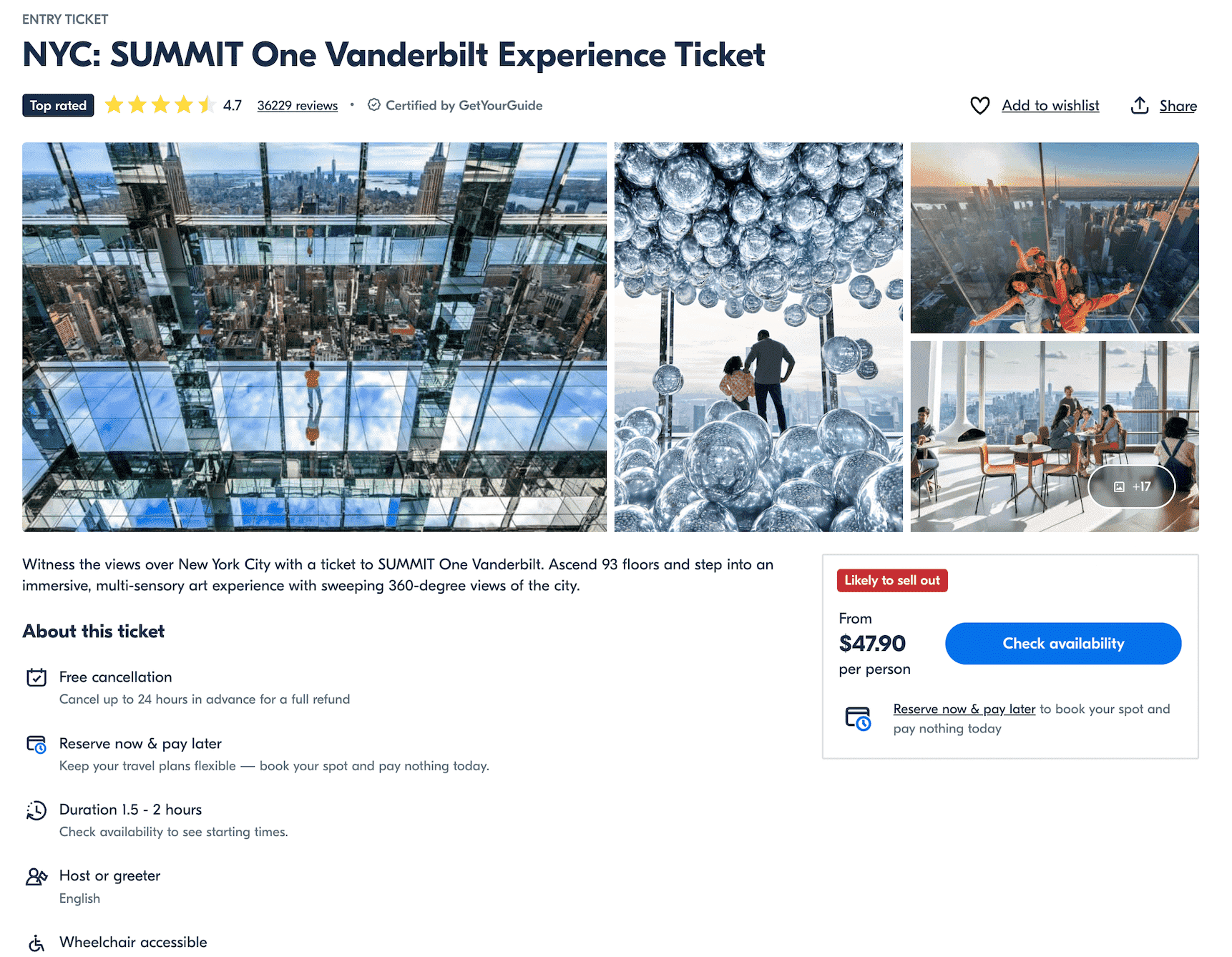
- User-generated reviews: Display authentic reviews and ratings about the product, place, event, or feature on the page.
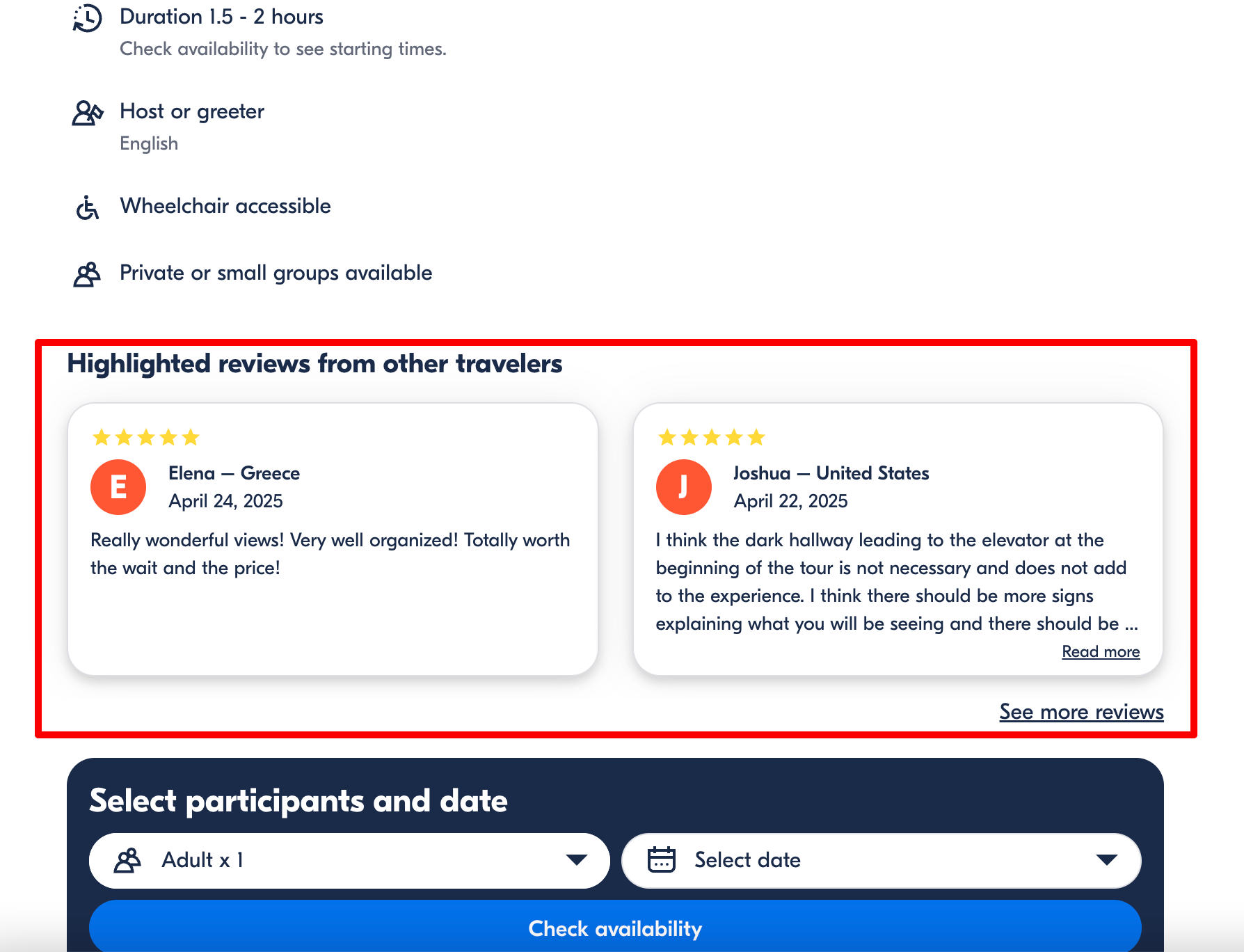
- Data tables and visualizations: Use your dataset to generate comparative tables, charts, or lists with stats that differ from page to page. Embed relevant images.
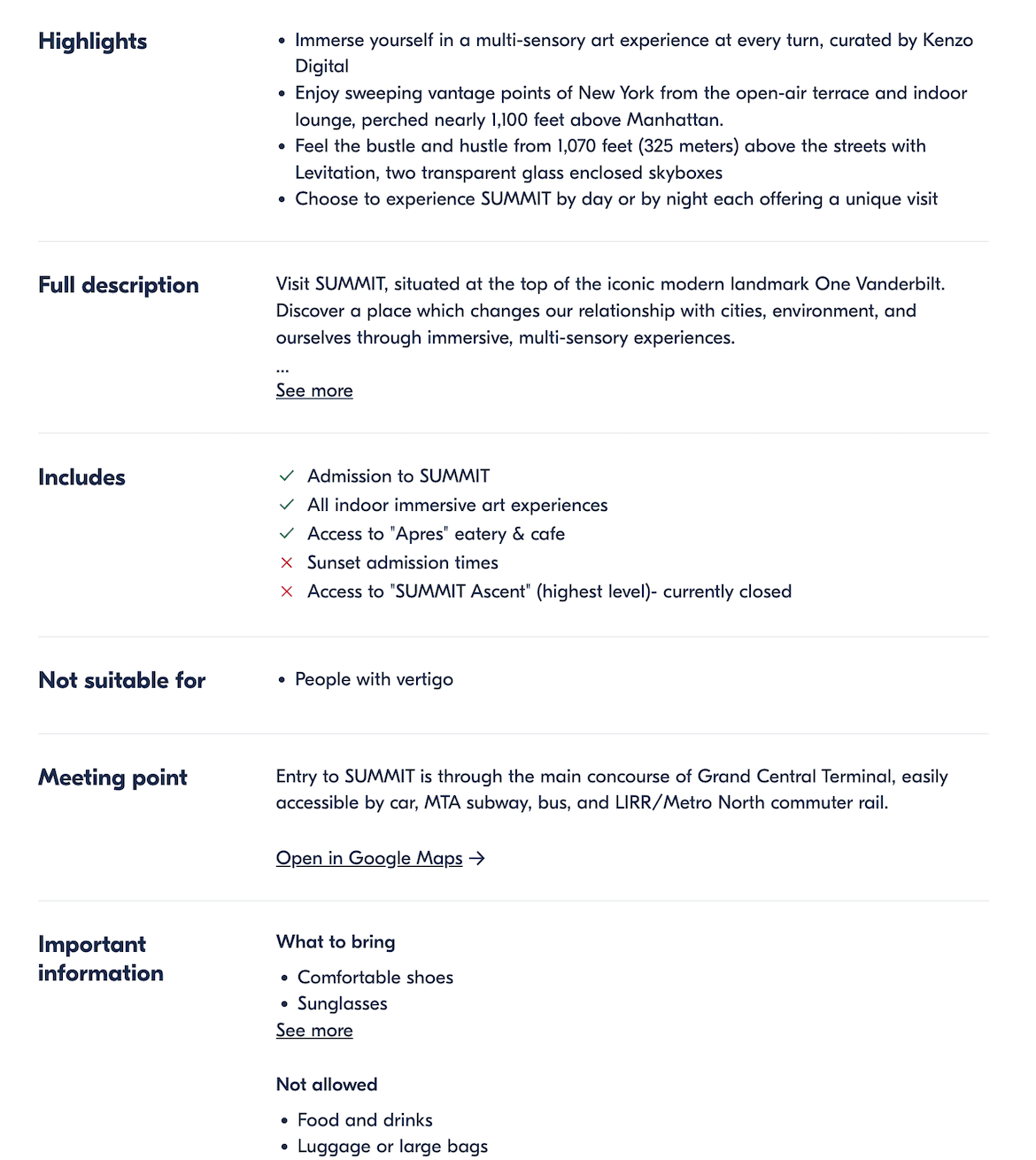
- Custom summaries or descriptions: Create short, unique blurbs based on the data on each page. This could look like key benefits, comparisons, or insights to give each page an editorial appeal.
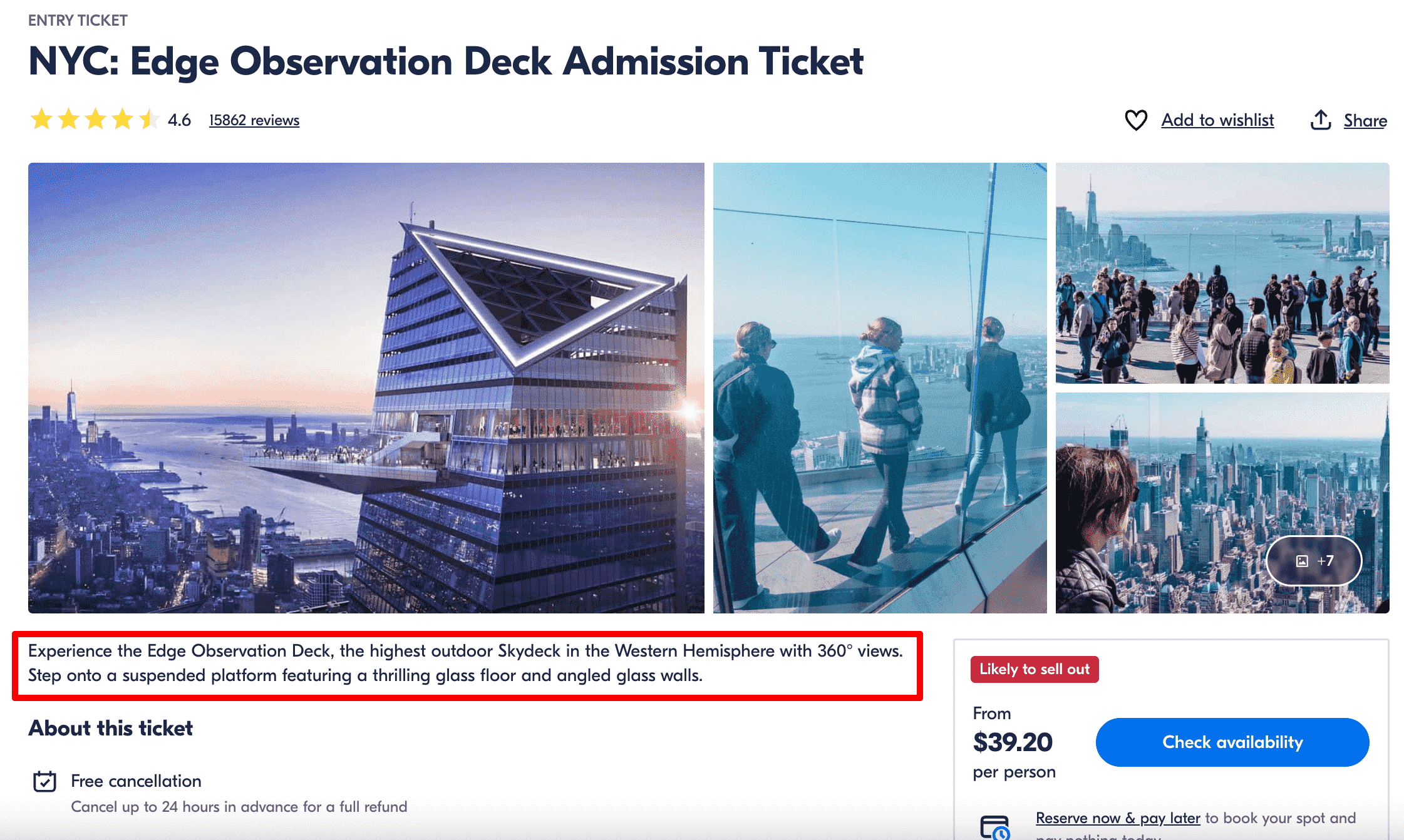
Combining these elements makes the experience and content feel tailored, even if you have already used the same format.
You’ll also need a template for your metadata. Here’s an SEO-friendly template for the title and meta description of location-specific or service-specific pages:
- Title tag:
Top [Service] Providers in [Location] – Updated for [Year]
- Meta description:
Explore the best [service] options in [location]. Compare features, prices, and user reviews to find your perfect match.
Don’t overlook the basics. Core fixes to on-page SEO are the backbone of every high-performing page.
- Use keywords naturally in headers and other content, while avoiding keyword stuffing. Use variations and keep the language natural.
- Break your content into clear, scannable sections like overviews, key stats, FAQs, or comparisons.
- Strengthen your site’s structure and SEO by linking to related pages and including breadcrumbs. This improves navigation and crawlability.
- To prevent duplicate content issues, use canonical tags, and don’t forget to add descriptive alt text for all images or dynamic visuals.
- Add relevant schema markup to help search engines better understand and display your content as rich results. Learn more in our structured data guide.
Check out this in-depth On-Page SEO guide to explore best practices and get actionable tips.
5. Publish content on your website
The final step is to publish the content on your website. There are plenty of tools available to help you display your data on the pages and streamline the process. Here are a few top picks:
- For WordPress users, WP All Import makes uploading data directly from spreadsheets easy.
- Set up a Zapier integration to pull content from your spreadsheet automatically. Or you can give Softr a try.
- Use Whalesync if you use Airtable database and Webflow—any updates you make in Airtable are reflected on your site automatically.
After setup, adding a new row to your spreadsheet triggers the tools to publish a new page automatically.
Before hitting publish, make sure you test and validate your pages.
Start by looking for broken links—both internal and external—as they can harm user experience and negatively impact SEO. Next, check the formatting: check all headings for consistency, lists for proper stylization, and tables or dynamic content for correct display. Also, confirm all visuals load correctly.
Don’t forget responsiveness. Test your pages on different devices and screen sizes. For example, a page that looks perfect on a laptop might break on mobile devices. Always optimize the site’s desktop, tablet, and mobile versions.
Use SE Ranking’s Website Audit to run all these checks. You’ll get a complete health overview plus detailed recommendations for fixing issues.
Validate your pages upfront to catch small issues before they become bigger problems. It keeps your site professional, user-friendly, and search engine-ready.
6. Monitor rankings and performance
Publishing your pages isn’t the finish line. To gauge performance, keep tracking keyword rankings, traffic, and user behavior. This helps you spot changes early, adjust your programmatic SEO strategy, and improve your pages over time.
Monitoring traffic helps you measure the actual impact of your SEO efforts on user visits, while engagement metrics like bounce rate and dwell time show how visitors interact with your content.
Use SE Ranking’s Rank Tracking Tool to track your keyword rankings across multiple search engines, devices, and locations. Use its CSV/XLS import feature to add thousands of keywords. It will display daily position data in user-friendly tables and graphs, with metrics like average position, share of voice, visibility, traffic forecast, and the presence of SERP features. All of these features together help you monitor the progress of your programmatic SEO strategies.
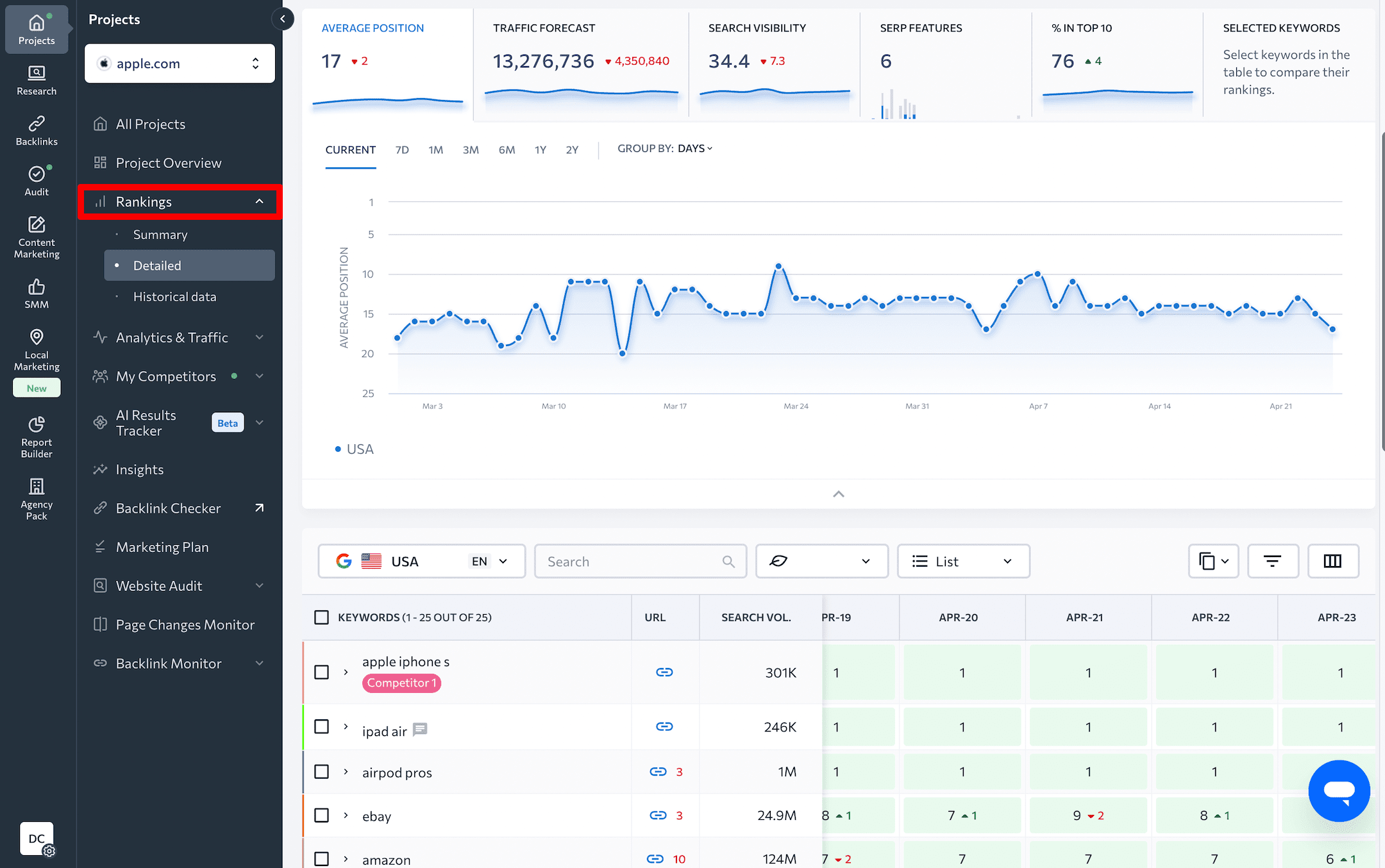
To stay on top of other key performance indicators, use Google Search Console and GA4. SE Ranking works as an SEO hub, which means you can integrate Google’s data into the platform and display information like rankings, traffic, and engagement.
Real-world programmatic SEO examples
Chances are, you’ve already seen programmatic SEO in action. Some possible unintended instances include searching for services, places to visit, restaurants, tours, and more. Below are three real-world programmatic SEO examples.
SE Ranking’s Agency Catalog
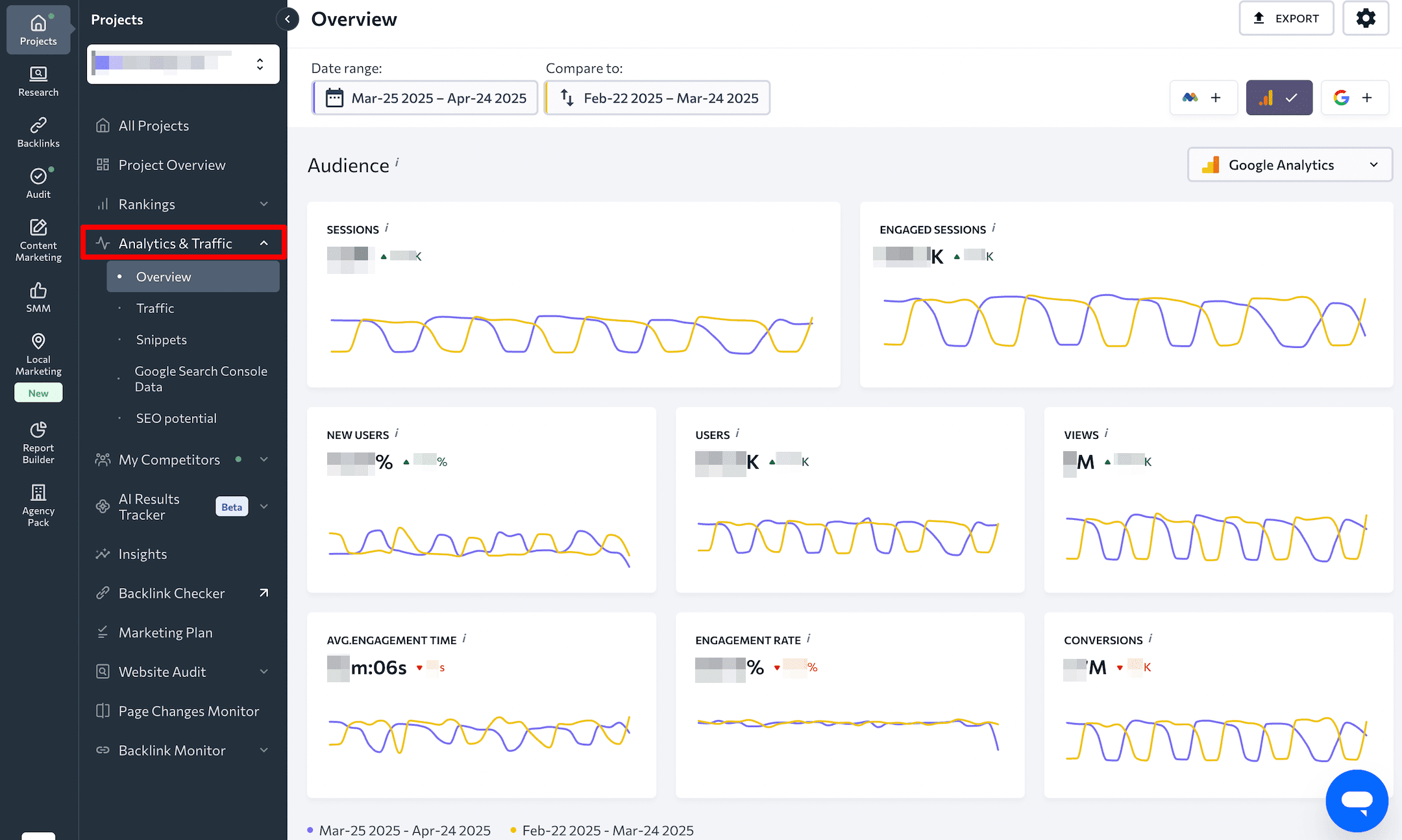
SE Ranking has an Agency Catalog designed to connect businesses with trusted digital marketing agencies that use SE Ranking in their SEO workflows. Agencies featured in the catalog can showcase their services and areas of expertise. It’s a win-win: businesses get reliable support from verified professionals, and agencies gain exposure and potential leads through SE Ranking’s website.
The catalog automatically generates optimized landing pages for digital marketing agencies. Opening an agency’s profile takes you to a structured template that displays key details, like the services offered, location, contact info, year of establishment, team size, payment methods, pricing, awards, and client reviews.

Each page is dynamically generated using structured data from agency profiles (submitted earlier by agencies after purchasing the Agency Pack), combined with location- and service-specific keywords. These pages are interlinked within the catalog and optimized with unique titles, meta descriptions, and H1s. This allows SE Ranking to rank organically for hundreds of long-tail queries.
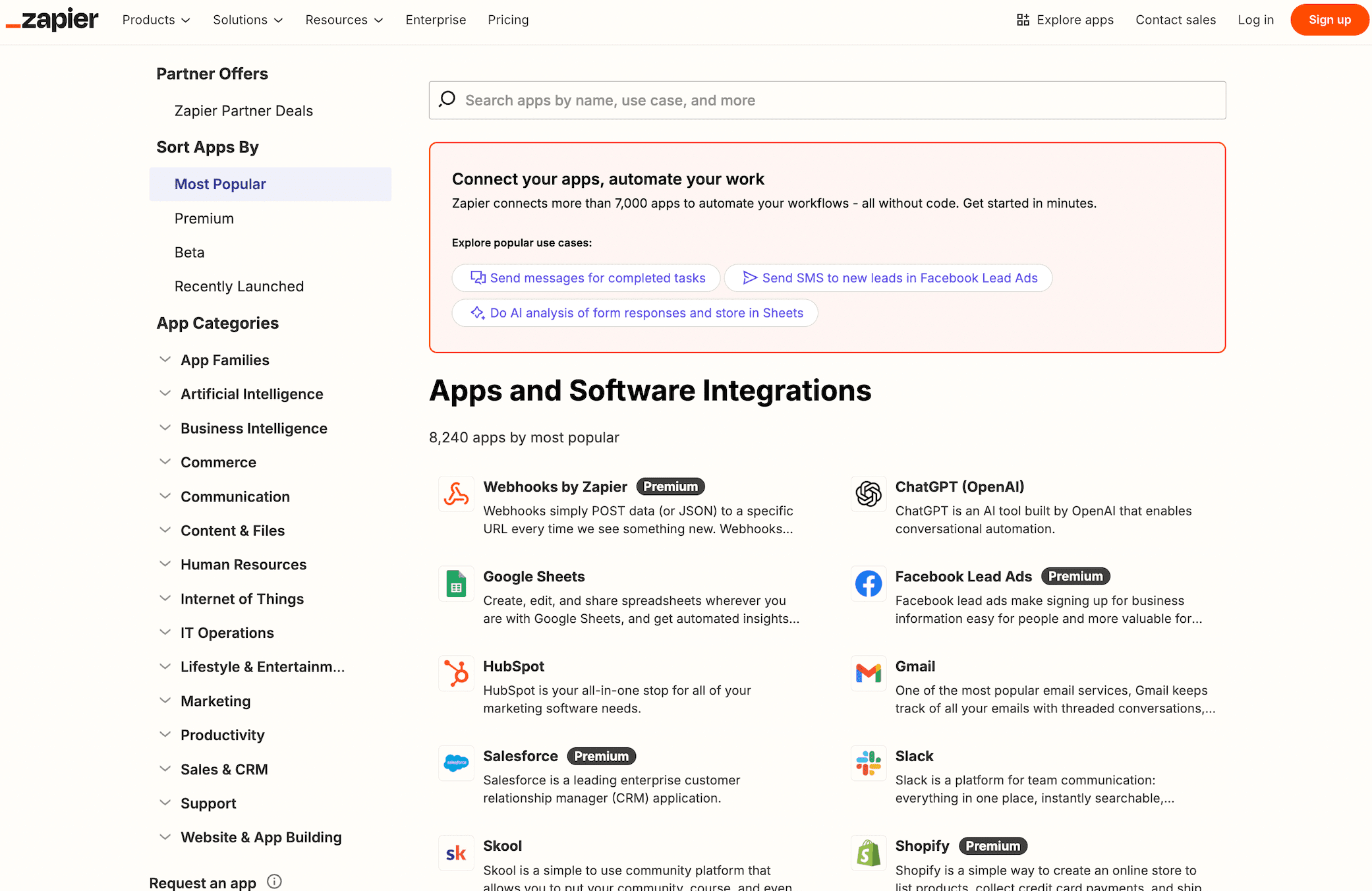
Zapier’s App Directory
Zapier is a great example of how programmatic SEO can help grow organic traffic. They created landing pages for every possible supported app combination. Zapier uses a flexible template that automatically fills in information, like what each app does, how they work together, ready-to-use workflows (called “Zaps”), and clear calls to action.
Each page is designed to rank for specific search terms such as “Connect Notion to Gmail” or “Google Sheets and Slack integration.”
Thanks to this programmatic approach, Zapier ranks for thousands of integration-related searches. This brings in relevant traffic and helps strengthen its reputation as a top tool for app automation.
Webflow’s Website Templates
Webflow has grown in popularity as a no-code website builder, praised for its designer-friendly interface and powerful CMS capabilities. One of Webflow’s standout features is its Website Templates, which offer ready-made structures for different site types, including portfolios, blogs, and full-scale marketplaces.
Instead of manually creating a unique page for each template, Webflow uses dynamic CMS collections to build hundreds of pages automatically. Each page targets specific long-tail keywords like “Agency website template,” “Portfolio website template,” or “Landing page builder,” but follows a consistent structure.
Use of AI in programmatic SEO
Traditionally, programmatic SEO involved manually building templates and filling them with structured data. Today, AI can automate nearly every part of the process.
- AI tools can create unique, high-quality page content at scale, including meta titles, descriptions, introductions, FAQs, and body text tailored to specific keywords, locations, or product attributes. Recently, we conducted an experiment generating content with AI, and the results were quite impressive. Take a look here.
- Instead of using one static layout for all programmatic location pages, AI can dynamically adjust page templates based on content type, user intent, or industry. This improves both UX and SEO performance.
- AI-driven SEO tools can analyze generated pages for readability, keyword density, internal linking, schema markup, and other SEO best practices to get every page to meet high technical standards without manual review.
- As data changes (e.g., new products, new cities, price updates), AI can automatically refresh pages to keep content up-to-date. This solidifies rankings and user trust.
Success still depends on human oversight, quality control, and following Google’s content standards. As long as you’re not using AI to game the system and you review everything carefully, you don’t need to worry about penalties.
Final thoughts
Programmatic SEO isn’t easy money. Handling large amounts of data and pages can be tricky. You need to provide useful information to rank high and ultimately help people. And make sure you don’t overlook the SEO fundamentals. Those are always crucial.
Use this guide to build programmatic SEO content that brings in qualified traffic and drives conversion.