On-Page SEO Process Guide
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is an optimization process you can use to rank higher in SERPs by tweaking the elements of your website that are within your control. This process plays an essential role when running successful SEO campaigns, helping you improve both your site’s rankings and user experience. Once you have all of the factors of on-site SEO covered, Google will better understand whether your page meets your target audience’s expectations.
This process can be time-consuming if done manually, but we’ve got you covered. In this guide, we’ll take you through the on-page SEO process step-by-step so you can easily perform it using a combination of simple online tools.
What are the most important on-page SEO elements?
Enhancing a website’s rankings has become more difficult and complex over the years because Google’s algorithms are constantly evolving. To keep up with these changes and drive more organic traffic, you’ll need to know the best on-site techniques.
Before we dive into any distinct features of the on-page SEO process, let’s first clarify what elements you’ll need to optimize. Tweaking these elements will boost your online presence and attract more Internet users.
Сontent
The first thing that usually comes to most SEO’s minds when thinking of on-page SEO is content. It’s no wonder Bill Gates once said, “Content is king.” Content plays a key role in any digital marketing campaign, and apart from text, SEO content also includes other elements like:
- Media (images, videos, infographics, presentations, etc)
- CTA buttons and links
- Supplementary content (supporting material that’s mainly used to enhance the user experience, e.g., header menu, sidebars, and navigational buttons)
Title tags
If you’re wondering how people decide which website on the SERP to go to during their Google search, they typically do it by clicking on the link with the most compelling title tag (HTML element that outlines the title of a web page). Title tags are among the most critical Google ranking factors, so optimizing them is a great starting point for any on-page SEO practice.
H1 tags
Unlike the title tag shown in the browser window and SERPs, the H1 tag is usually only found on the website itself. It indicates a website’s main topic, making it clear to both human visitors and bots what the content’s purpose is.
To segment content into a clear hierarchical structure, marketers often use different levels of heading tags, starting from <H1> to <H6>. This improves the navigation on the page for users and increases the speed with which Google can understand a page’s structure and purpose.
URL
Another crucial on-page SEO element is the URL address. Even though URLs themselves don’t have a major impact on a website’s rankings, you can improve the overall user experience by making this element SEO-friendly. Take a look at examples of good and bad URL structures:
Good: https://www.test.com/cabinetry/liquor-cabinet/
Bad: https://www.test.com/index.php?id_wca=926&dovp92mao
The first URL includes a focus keyword and clearly explains what the destination page is about. The second link is just a bunch of jumbled characters containing no useful info about that page. Users will almost always click on the first URL if given the option between the two, so don’t sleep on using a logical URL structure with page hierarchies.
Page experience
Google defines page experience as a combination of signals that measure the quality of users’ experience as they interact with a webpage. This SEO element has long been associated with ranking factors such as:
- Mobile-friendliness: how optimized is a website for mobile devices?
- HTTPS: does your website use a secure connection?
- Interstitial use: what is your website’s perception of nasty pop-ups?
- Safe browsing: is your website harmless for users?
In addition to these page experience metrics, Google announced its new Core Web Vitals in 2020. They are as follows:
LCP, or Largest Contentful Paint: This metric measures the time needed for the largest content element on a website to load.
FID, or First Input Delay: This ranking factor considers how long it takes for a user to be able to interact with a web page after loading.
CLS, or Cumulative Layout Shift: This parameter measures the total amount of layout shifts that occur on a website while it’s loading.
By optimizing a web page for the factors listed above, you can improve user experience by decreasing loading speeds, boosting interactivity, and increasing visual stability.
Usability
Website usability can be defined as a measure of the effectiveness and satisfaction that a human can experience while attempting to achieve their goals on a web page. To see if your website is easy for users to navigate through, the following factors should be considered:
- Adherence to WCAG standards
- Creation of responsive design and mobile friendliness
- Navigation simplicity
- Content legibility
A page can’t appear in the SERP if it’s blocked from crawling and indexing, so look out for these page issues before moving on to the on-page SEO process. Make sure your pages:
- don’t have the noindex tag.
- aren’t blocked by robots.txt.
- don’t have a canonical tag pointing to another page.
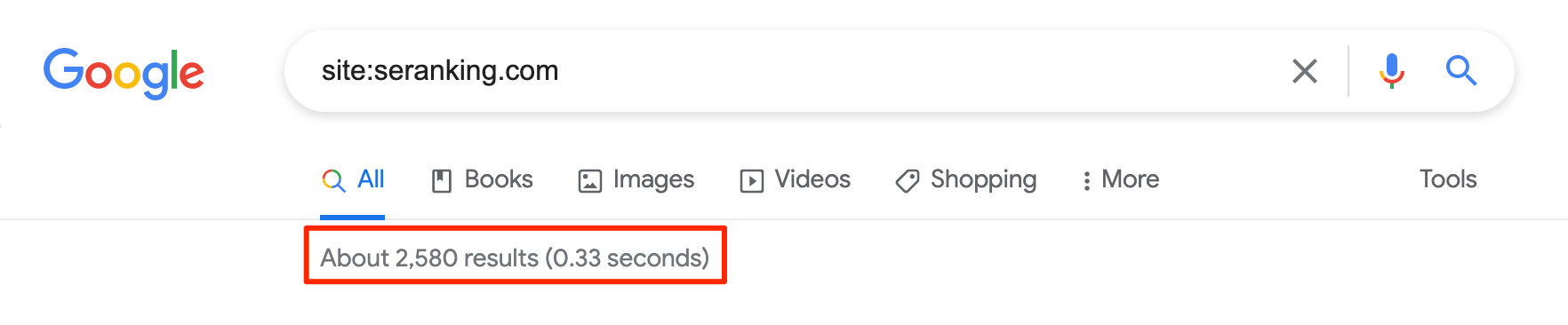
One of the most common ways to check whether your website pages are indexed is by typing “site:yourdomain.com” into the Google search box. Even though the number of results Google displays isn’t 100% exact, this technique can give you a solid understanding of which pages are indexed on your website.
The most compelling approaches to on-site optimization
Deciding which pages to optimize might seem like a simple task, but many people get lost during this step—optimizing nothing. Selecting pages suitable for on-page SEO depends on the type of business you run, including its goals and its vision.
There are different methods for identifying pages on your site that need to be optimized, but focus your approach on business priority and SEO potential.
Once you understand your website’s state using business and SEO metrics, then you can home in on your on-page optimization goals.
Optimization of pages based on business priority
Measuring your company’s business performance requires a comprehensive analysis of metrics. The only way not to get lost in a sea of key business metrics is to divide them by the roles they play:
- Sales metrics: net revenue, growth rate, lead response
- Product discovery metrics: impressions, reach, engagement
- Conversion metrics: sales conversion rates, average order value (AOV), shopping cart abandonment rate, checkout abandonment
- Retention metrics: customer retention rate, customer lifetime value (CLV), repeat customer rate, and refund and return rate
But how should these metrics affect which pages you choose to optimize?
There are two contrasting approaches. You can either keep track of metrics signaling good performance or track metrics signaling bad performance. For example, by optimizing high-converting pages, you can get more organic traffic and increase business profitability. On the other hand, you can identify pages with low engagement and develop an on-page strategy to improve them.
Optimization of pages based on SEO potential
To figure out which pages to optimize, consider these SEO metrics:
- Organic traffic
- Keyword rankings
- Organic click-through-rate (CTR)
- Average engagement time
- Page speed
There are several ways to put these metrics to action. One way is to optimize your meta tags to increase organic CTR. You can also increase the average time visitors spend on a page by improving your page’s structure and adding visual content. And the list goes on ad infinitum.
To learn more about SEO metrics that can be used to measure the performance of your website, make sure to read our complete guide on this topic.
The best ways to collect metrics
To collect analytical metrics like traffic or conversion rates, use Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or customizable dashboards generated in data visualization tools like Looker Studio. Start by estimating your website’s health score and spotting critical issues that SE Ranking’s Website Audit tool can help you fix.
In the Website Audit tool, you can head over to the Crawled Pages section to see every page of the website found during the audit. It can help you identify your website’s status on a page-by-page basis.
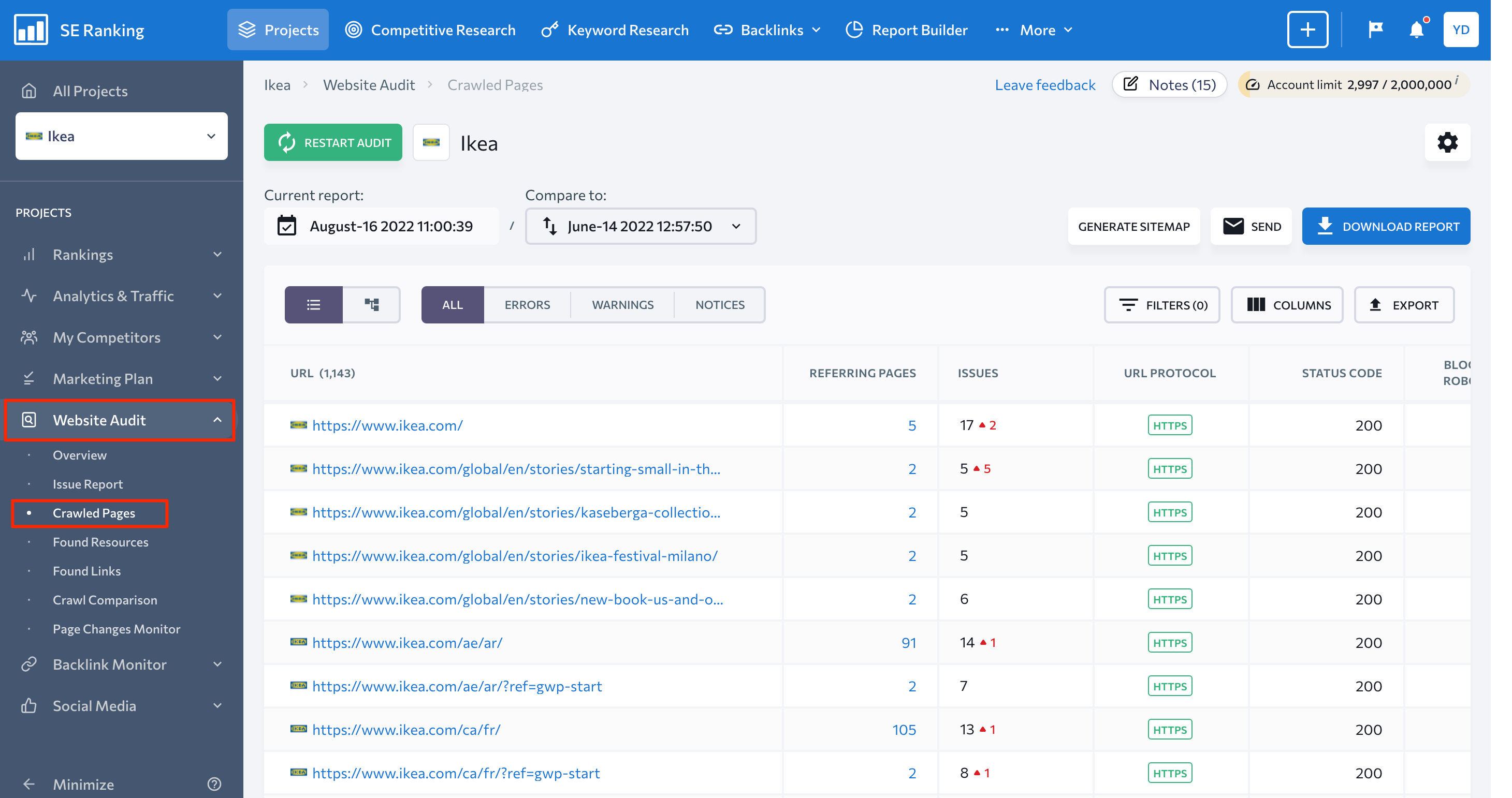
To get the most out of this report, filter pages by status code, referring pages, robots meta tag, their indexation status, link ratio, or by the type of issues detected on these pages:
- Errors ( severe issues that must be immediately addressed)
- Warnings (less critical issues that still need to be addressed)
- Notices (issues that may not be creating problems but need to be examined)
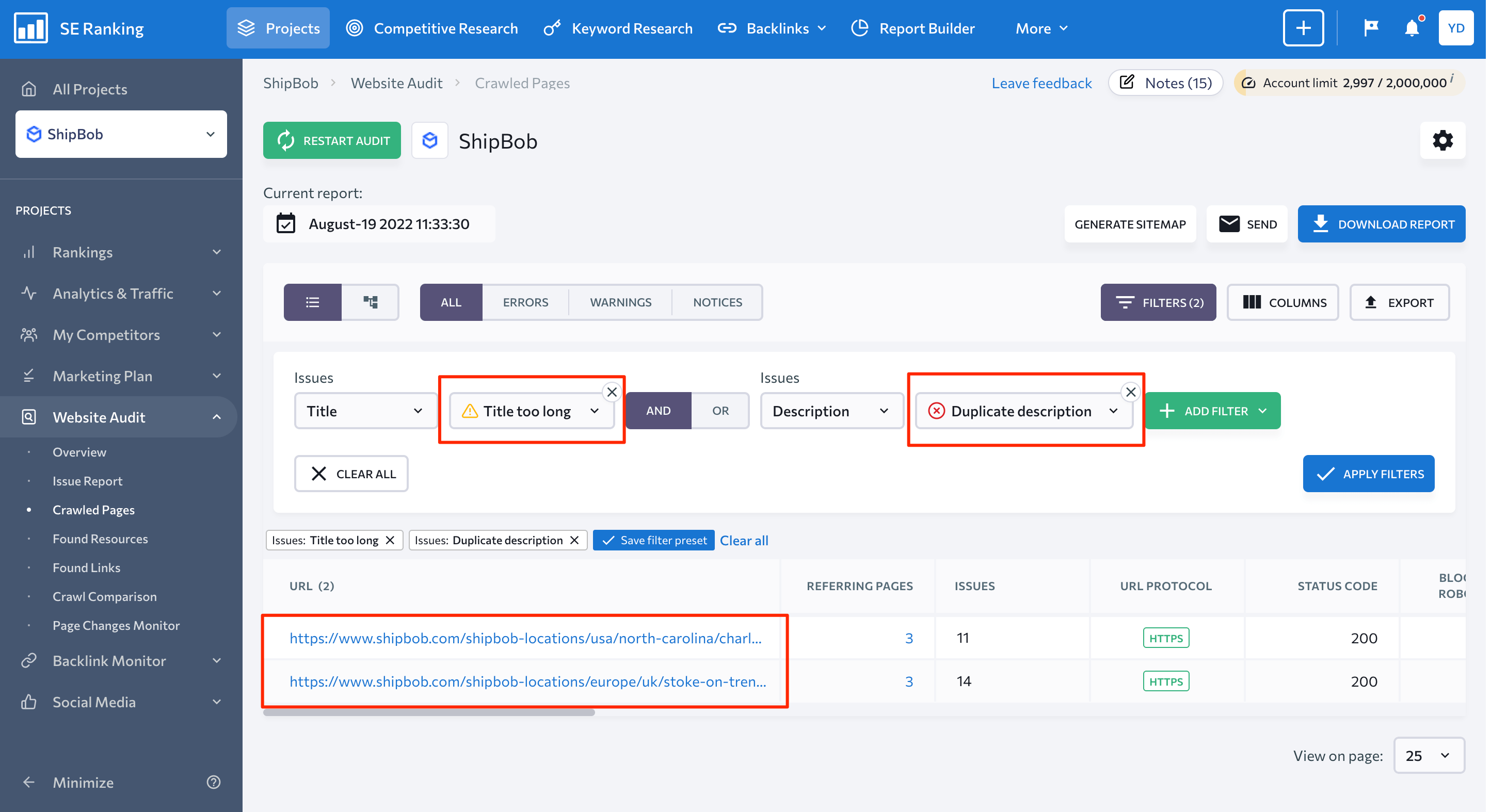
By combining multiple filters at once, you can get exact results. Let’s say you want to find all website URLs whose titles are too long or description issues so you can change them later in bulk. You can easily add these two filters to the report.
Consider leaning on user behavior metrics to create a fully functional dashboard report with information on the website’s overall state. To do this, go to the Looker Studio home page. Here, you can either create a blank report or use one of the offered visualization templates.
To simplify the process of gathering analytical data, go to the Template Gallery and choose the Google Analytics Behaviors Overview dashboard (or any other dashboard you want to use).
Then, click the Use My Own Data button, choose your account, and select the project you want to analyze from Google Analytics 4.
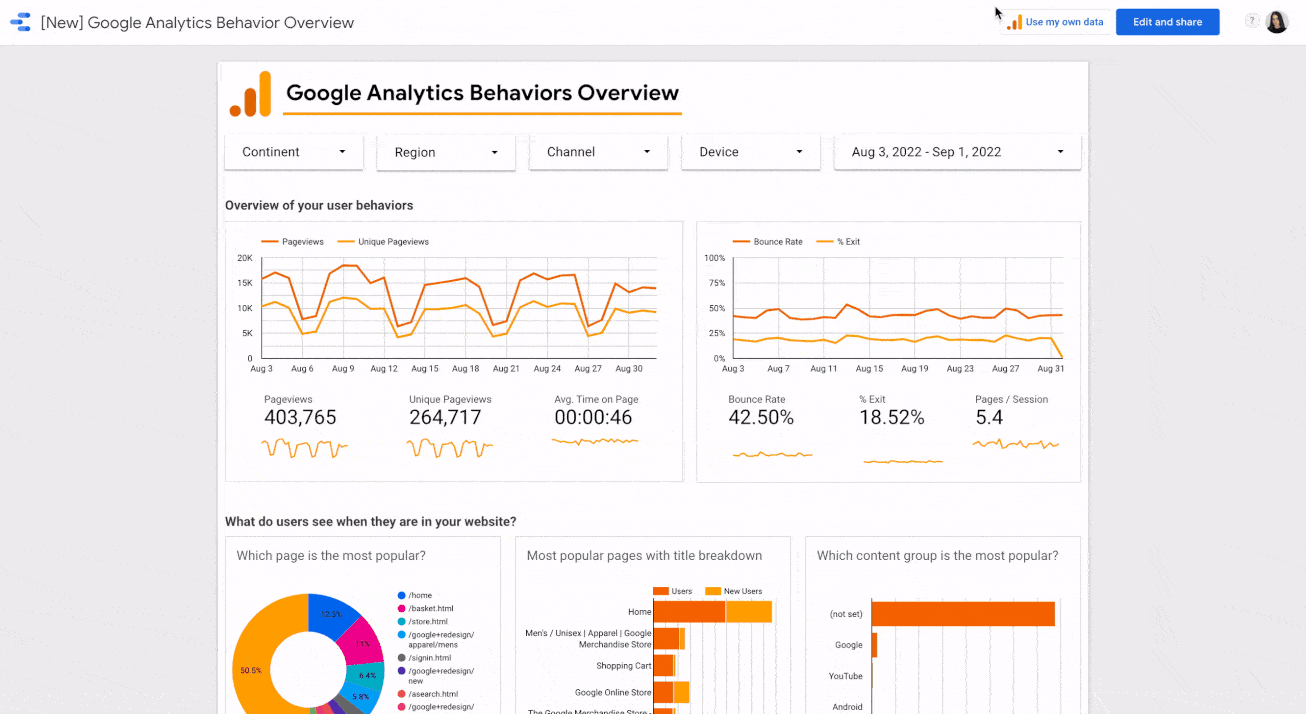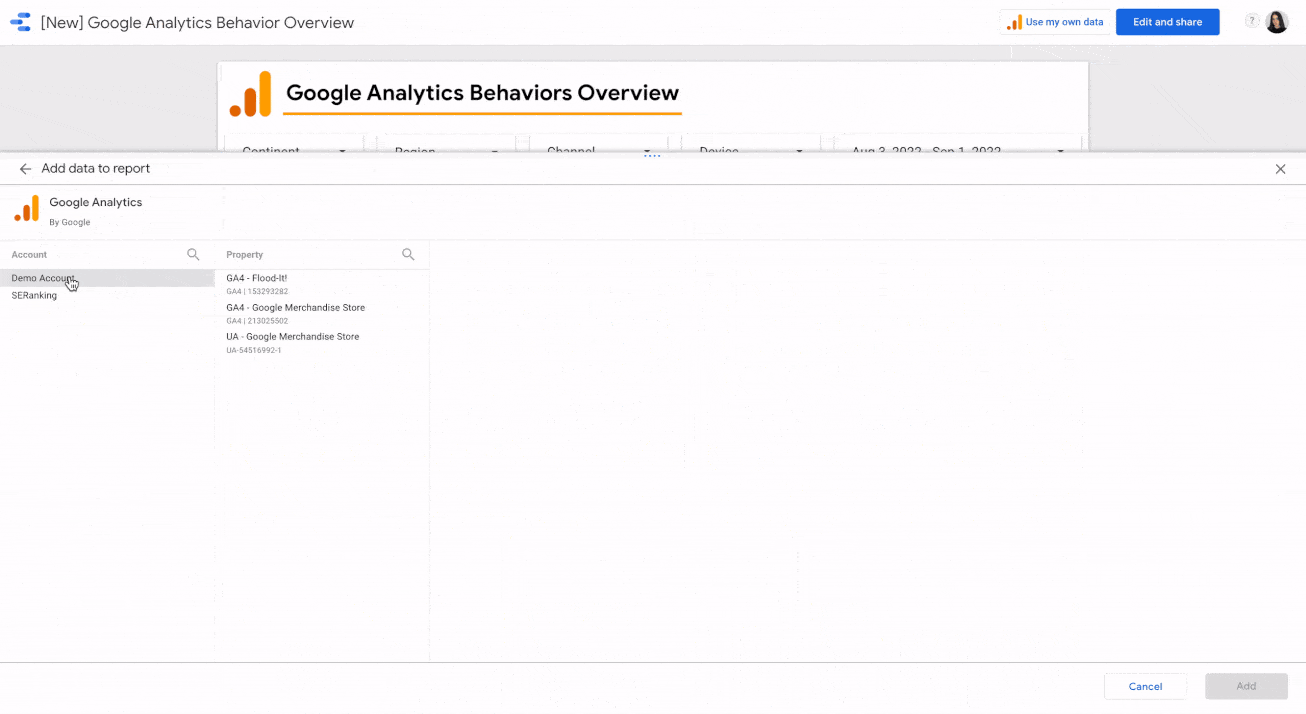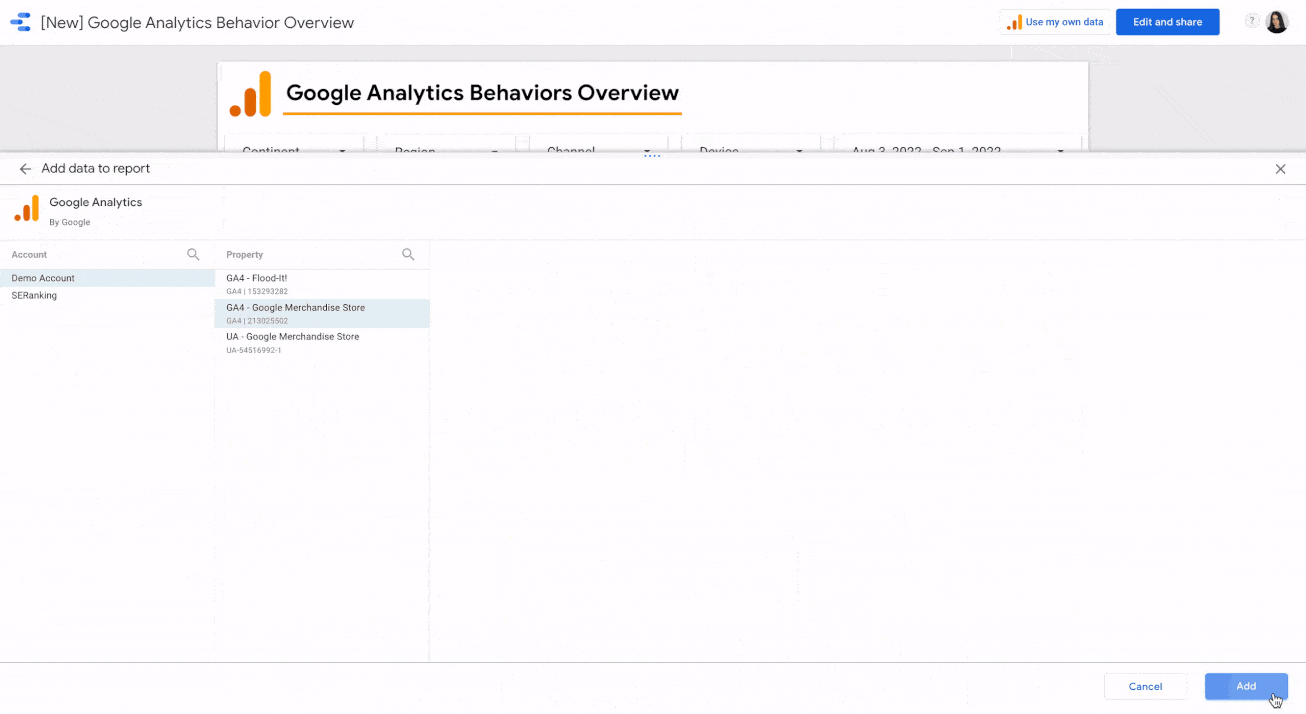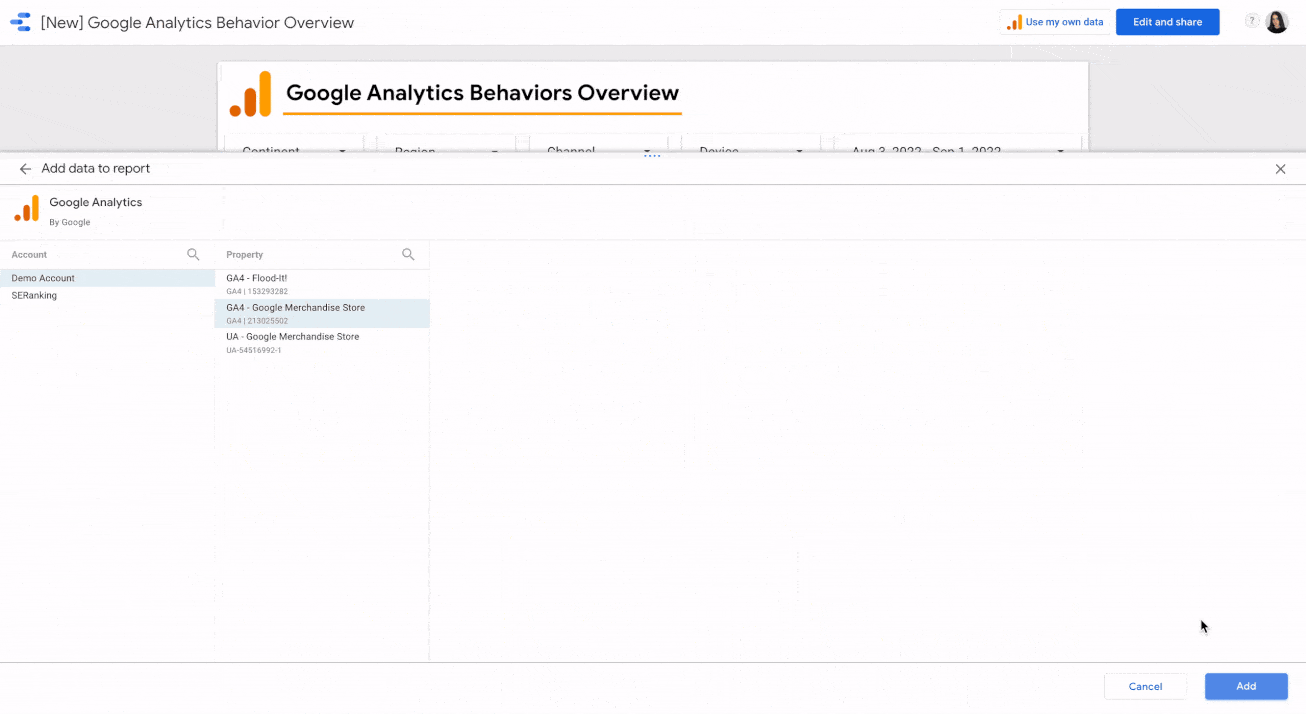
You will get a dashboard like this:
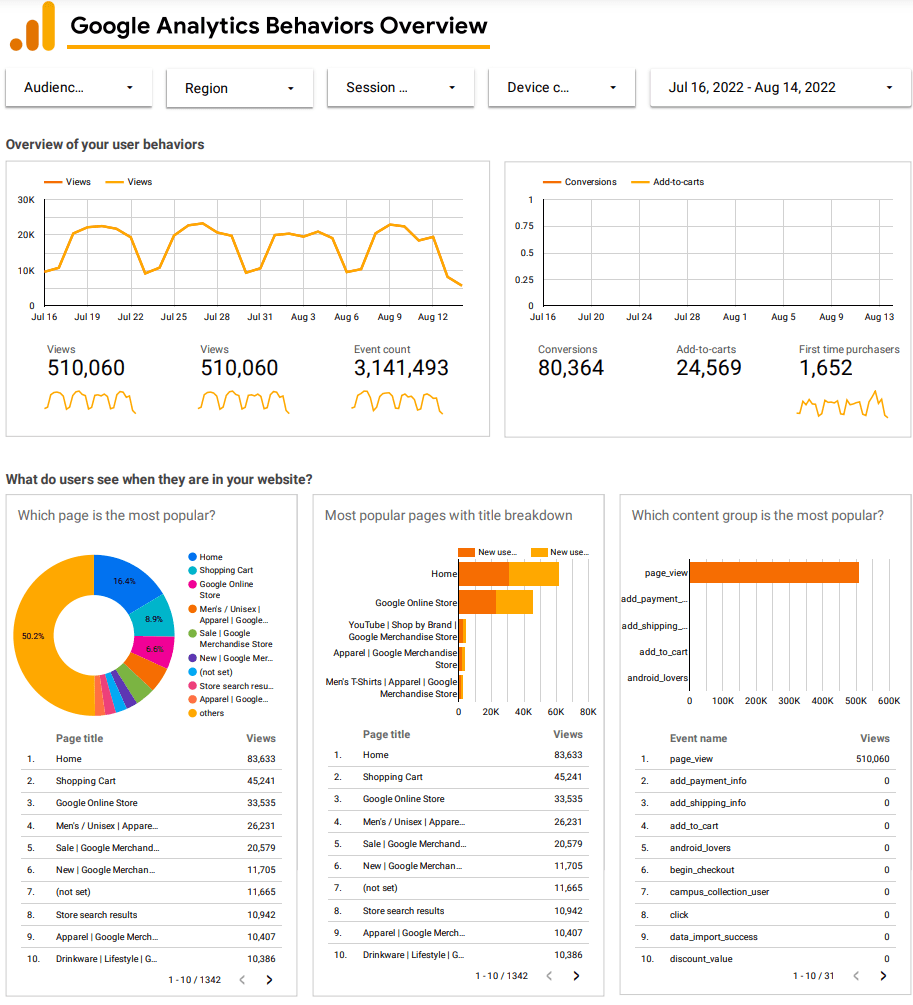
It provides comprehensive information about the most popular pages among your audience. For the analyzed merchandise store, these pages are:
- Home
- Shopping Cart
- Google Online Store
Since we need to pay attention to pages with high organic traffic and CTR first, the report outlined above can help us in determining these pages.
You can also generate dashboard reports based on the data from Google Search Console. Just go to Looker Studio, select any suitable template, and click Use My Own Data.
From here, you will be asked to sign in to your Google Search Console account. Once all the necessary data is downloaded and inserted into the report, you can use it for your on-page SEO purposes.
With Google Search Console, you can compare a certain period of time (e.g., month to month) and see pages where the clicks decreased. You can also use it to see pages whose number of impressions increased.
Since Looker Studio dashboards are absolutely customizable, you can include any data you want and display it in the form of tables, charts, or graphs. To create a dashboard, connect data from Google Ads, BigQuery, Google Sheets, Youtube, and so on.
You can also get this data in Google Search Console or Google Analytics directly but it will be in different places and without the added bonus of good visuals.
List of pages that require on-site optimization
To determine pages that require optimization, your attention should be dedicated to:
- Pages with moderate organic traffic but high impressions.
- Pages with high organic traffic but low CTR.
- Pages with declining or neutral organic traffic.
- Pages with above-average conversion rates.
- Pages with the highest traffic potential (you can calculate this metric by determining all keywords a specific page targets and their search volume).
- Pages with technical SEO issues.
You can track all metrics listed above in Google Search Console by going to Overview > Performance > Open report.
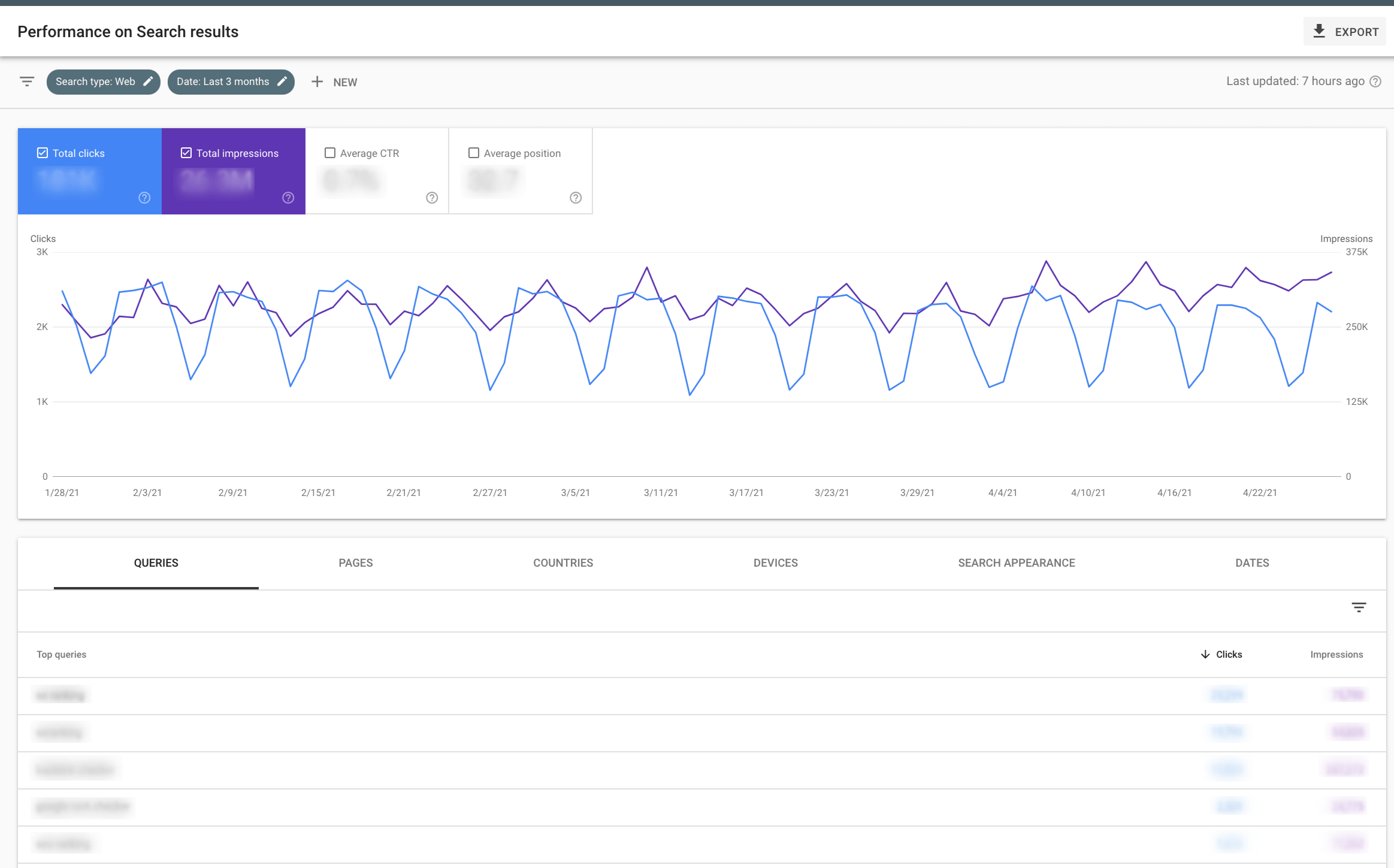
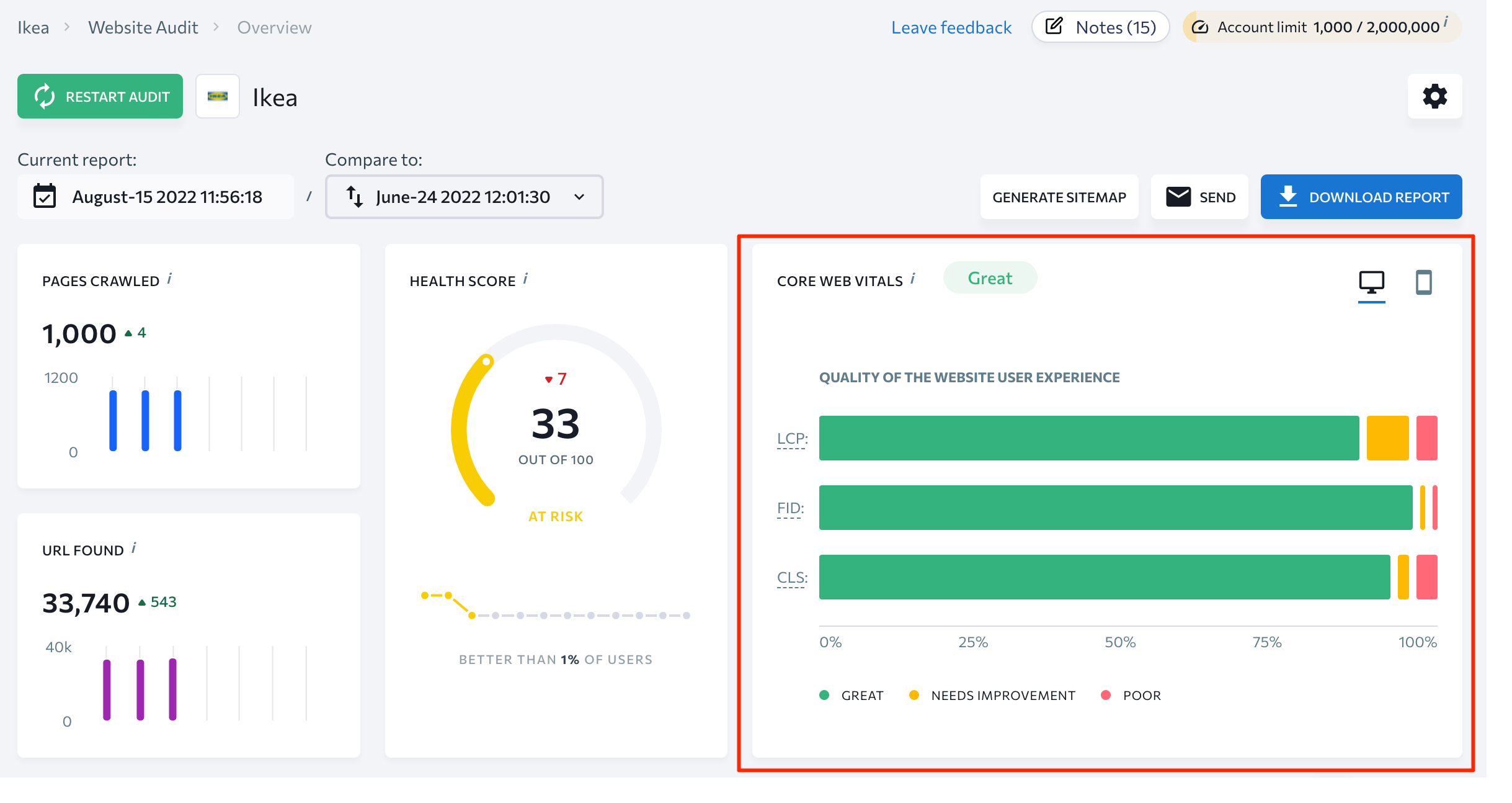
Pages with potentially overlooked page experience issues also require optimization. You can identify them through the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console or the Website Audit report in SE Ranking.
To get access to the report in Google Search Console, follow this algorithm: Overview > Experience > Core Web Vitals.
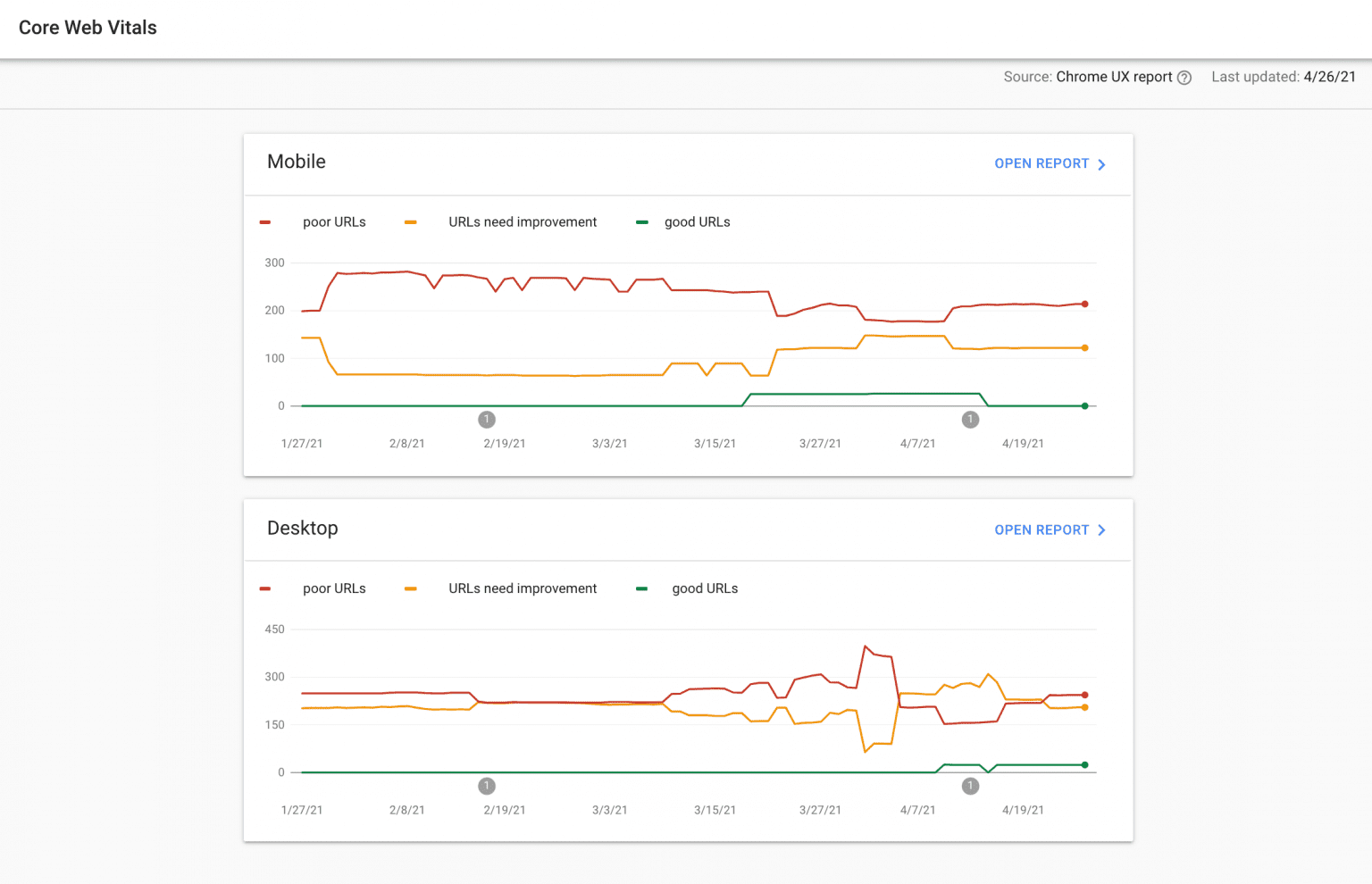
SE Ranking’s Website Audit tool is also useful in this case because it has a dedicated Core Web Vitals section.
Consider determining which pages require on-page SEO by combining information gathered from different metrics. For example, pages with the highest traffic potential and high current conversion rates are a perfect choice for on-site optimization.
On-page SEO process flow
After collecting all the necessary metrics, define your main goals for the on-page SEO process. These goals might differ from case to case, but most marketers usually strive to:
- Optimize one page per time.
- Optimize all pages in bulk.
- Optimize a group of pages – e.g. blog posts, clusters.
1. Optimizating one page at a time is the most straightforward and commonly used type of on-page SEO optimization. To do this, focus on one metric (e.g., the amount of potential traffic for a certain URL) and the intersection of metrics (e.g., potential keyword cannibalization and several ranking keywords).
2. Optimizating all pages in bulk can be a perfect fit for cases when certain page parameters require optimization across the whole website. For example, if your SEO metrics analysis demonstrates that images across your website are not optimized, the “all pages in bulk” approach will be hands-down one of the best solutions to this problem.
By finding a balance between good quality and file size, you can improve your pages’ loading speeds and enhance user experience.
3. Some marketers also find it convenient to optimize a group of pages based on their similarities. This approach is widely used in the e-commerce area.
Let’s say you work for Apple and you need to optimize the meta description on all of your pages that offer Apple products to increase the organic CTR. Instead of dedicating time to each page, you can combine them in clusters and apply changes to the whole group, saving you lots of time. If your site is powered by WordPress, for example, you can use Yoast SEO, one of the free SEO plugins it provides. Just enter a new meta description and assign it to a specific area on your site (e.g. categories).
This is the end of the preparation phase. You can now start the process of on-page SEO.
From here, we will review this process step by step from the perspective of the two most commonly used approaches:
- Optimization of all pages in bulk
- Optimization of one page per time
Optimization of one page per time
Optimizing one page at a time typically consists of five main steps. Let’s review them in detail.
Estimating current state
After identifying pages requiring on-page SEO optimization, you can estimate their state with the help of our On-Page SEO Analysis Tool. Not only does it measure every webpage against over 90 parameters that impact search rankings but also provides suggestions based on competitor performance in your niche. You can make a great to-do list with these insights.
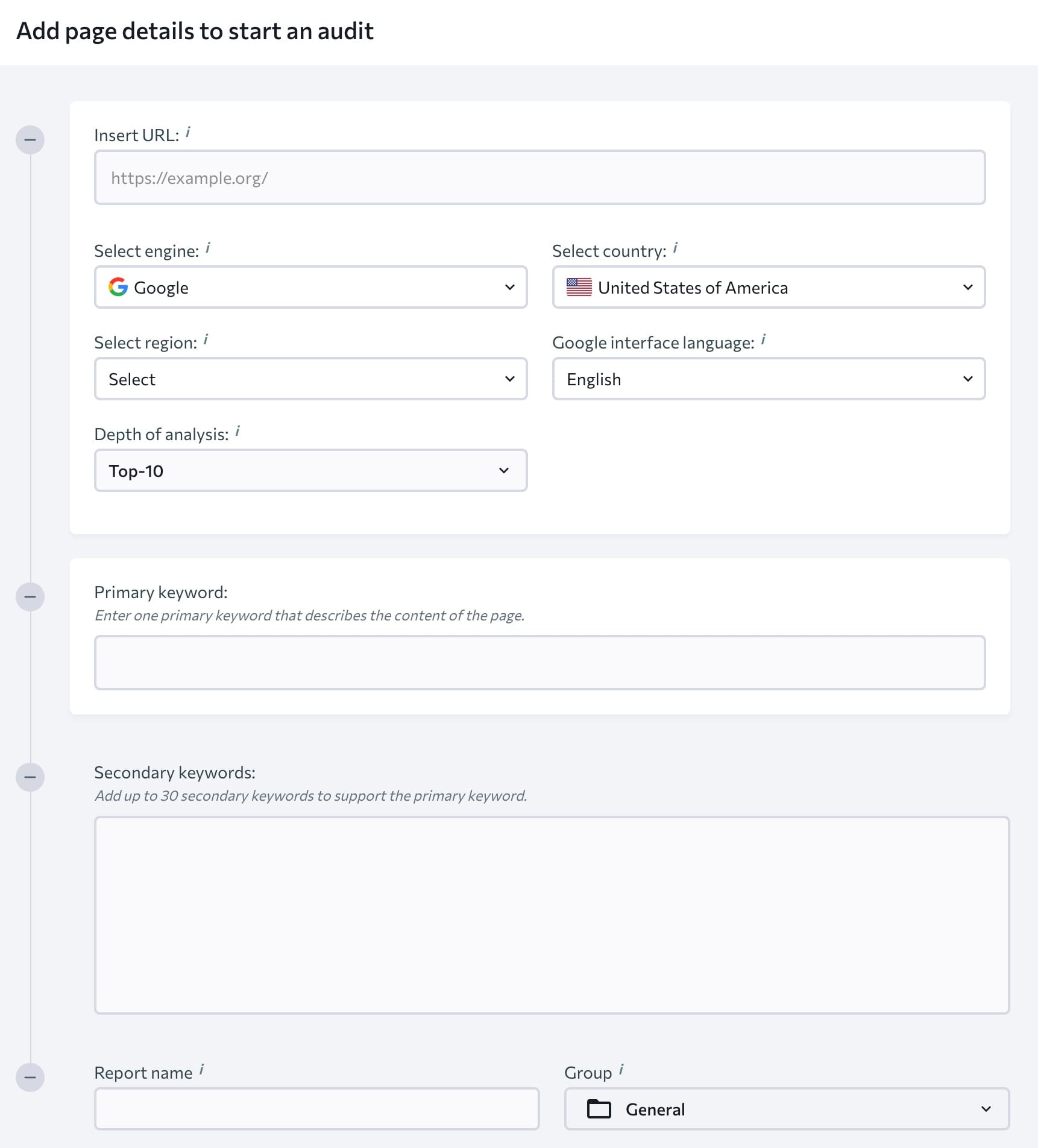
To start the on-page SEO audit, fill out all the fields with relevant information.
FYI, we will provide more information about keywords needed for this audit later in this article.
Once all details are specified and the audit is launched, you might have to wait several minutes before the data is gathered. You will be informed about this process’s completion via email.
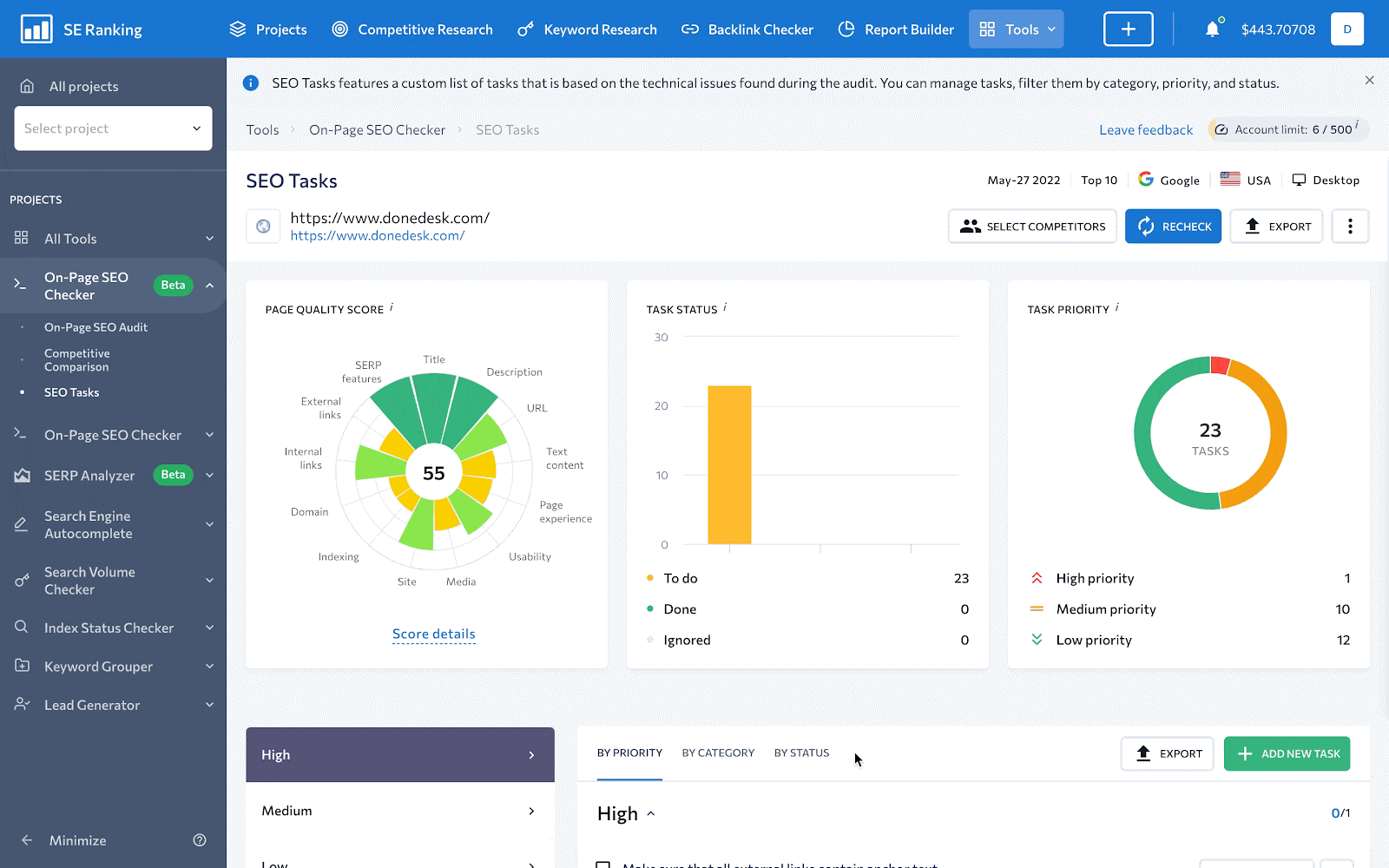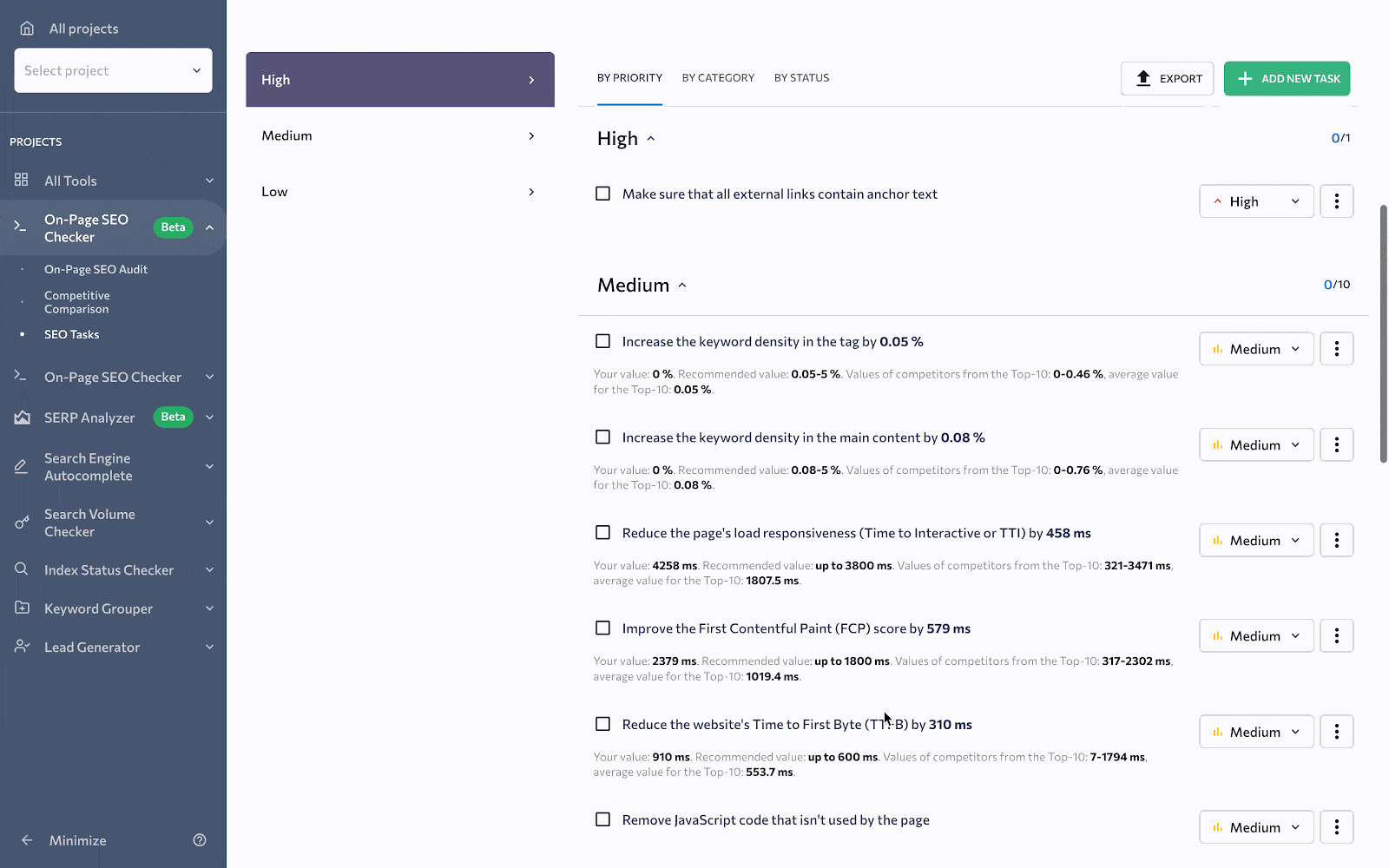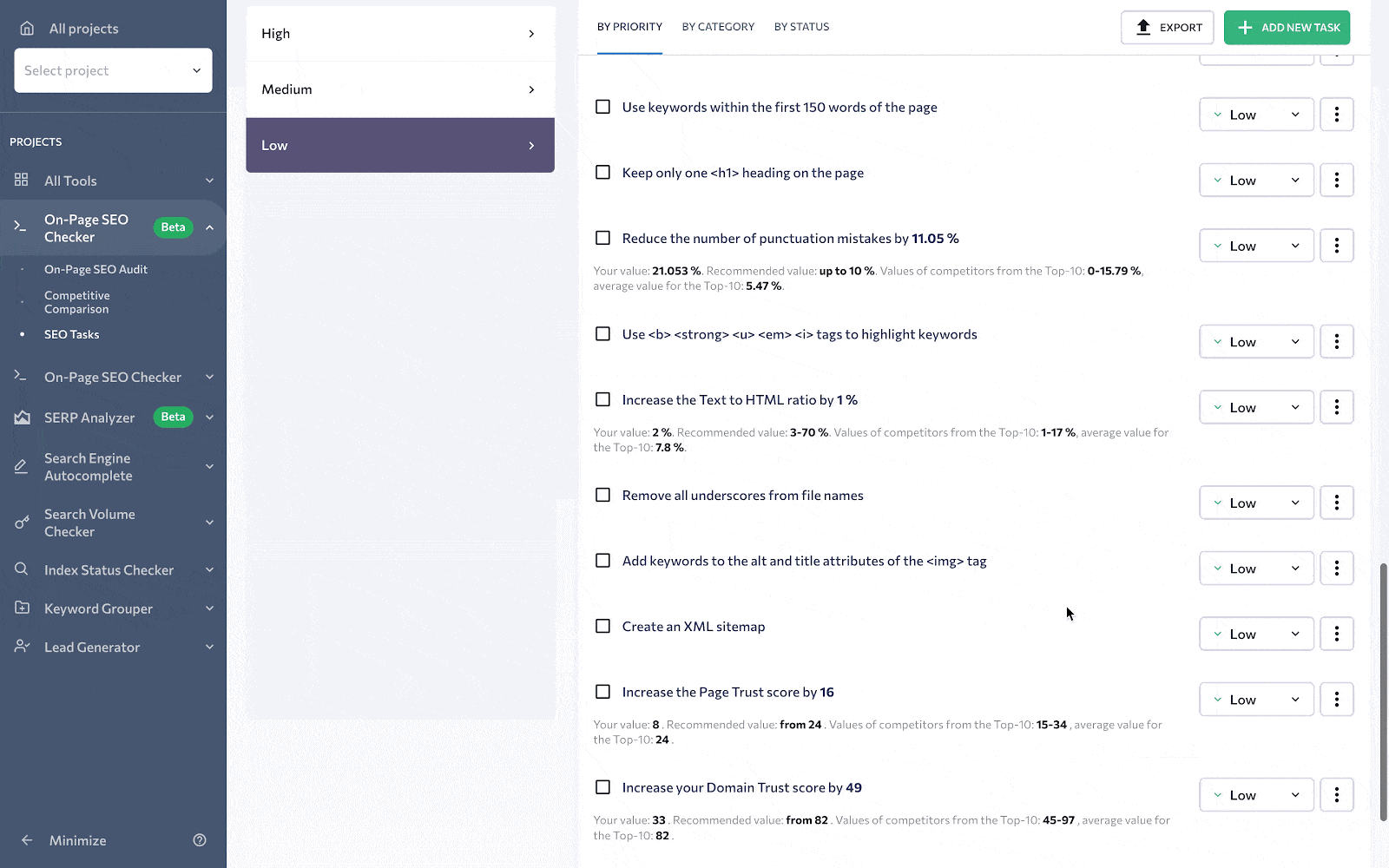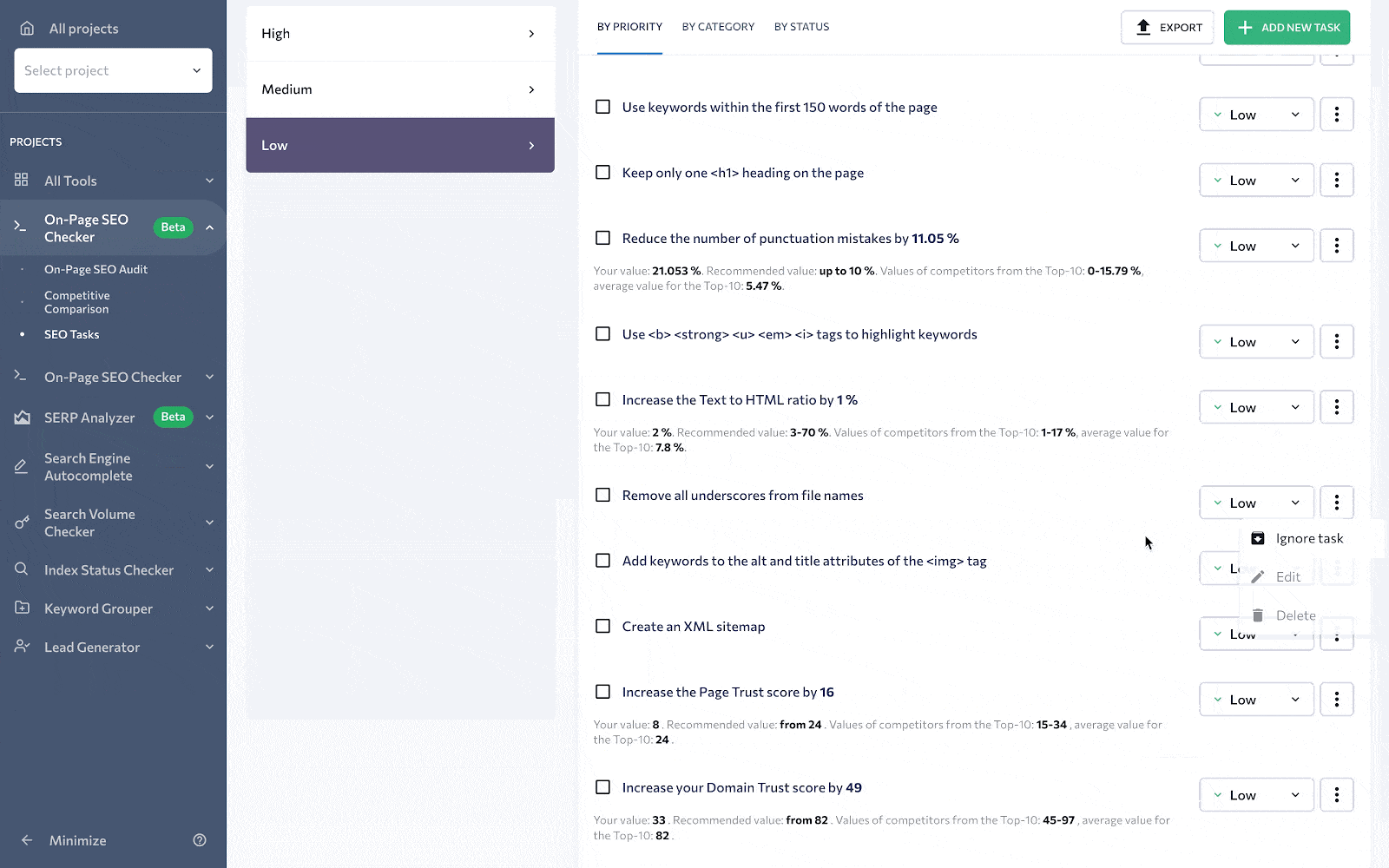
You’ll notice some key metrics on the main page of this report. These include:
- Page quality score.
- SEO tasks to improve your page.
- Top organic competitors based on the keywords you’ve added.
- A breakdown of all issues into 4 categories, such as Errors, Warnings, Notices, and Passed Checks.
Page quality score provides comprehensive data on the page’s on-site SEO state using a 100-point scale. Metrics playing a critical role in terms of on-page SEO have a greater impact on the page’s overall score, whereas less important factors are given less weight. The list of elements it analyzes includes but isn’t limited to:
- Title
- URL
- Text content
- Page experience
- Usability
- And much more
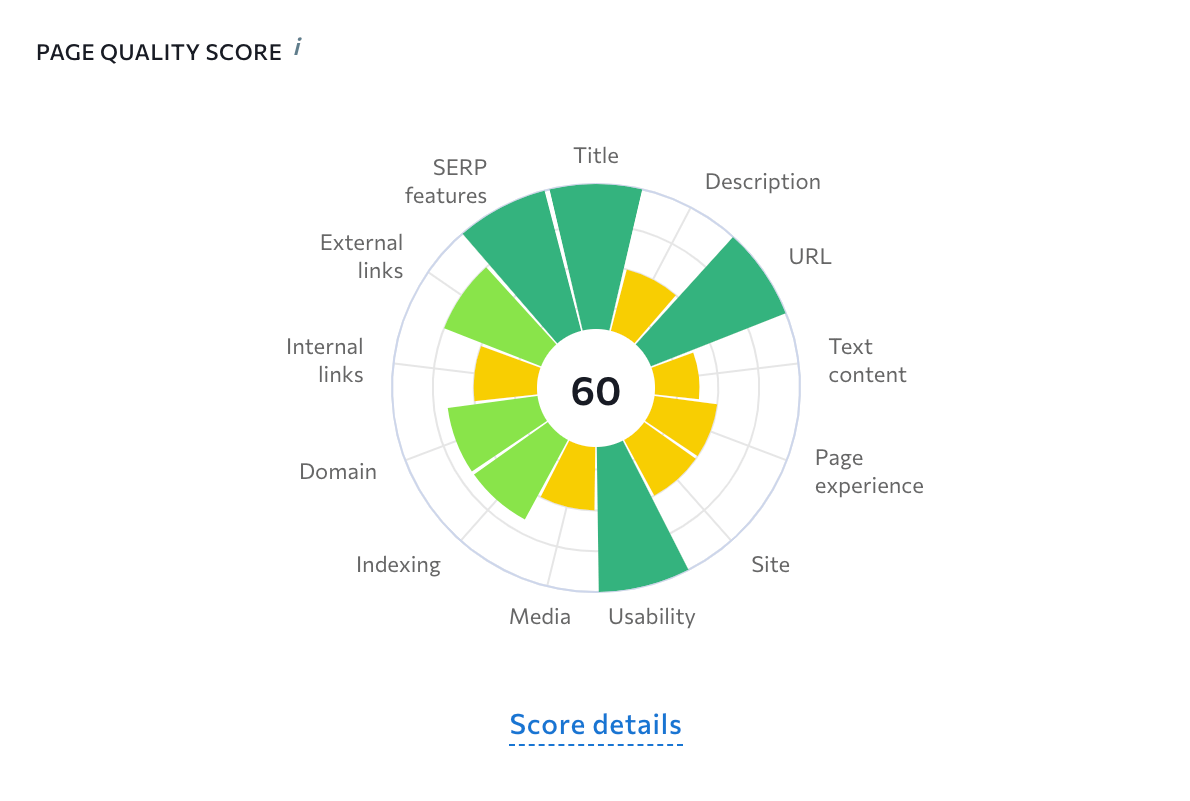
By the way, off-page parameters don’t affect the page quality score even though they are presented on this diagram.
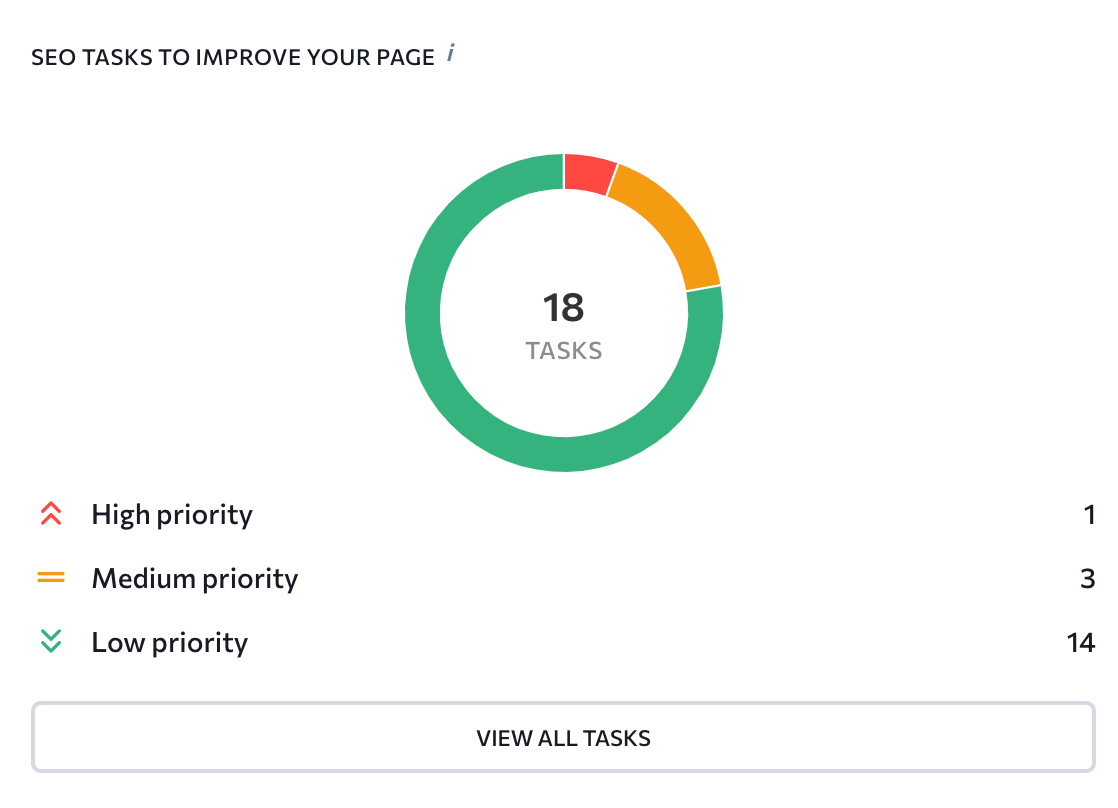
To the right of the page quality score diagram, you can find the SEO tasks feature that gives a brief description of the number of found issues. It also divides them based on priority. By clicking View All Tasks button, you will be redirected to the SEO Tasks section—which will be reviewed in this article later.
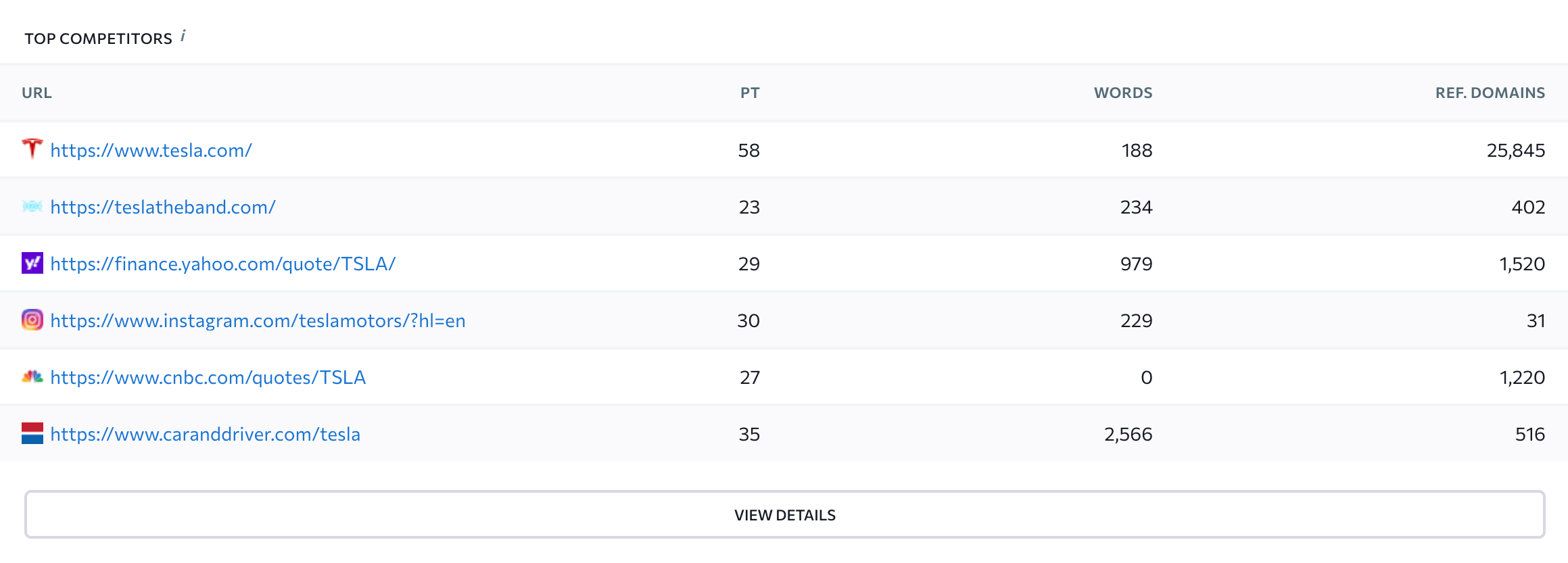
Below you can find the Top Competitors feature that provides detailed information on three to 50 SERP rivals. To conduct an analysis on each aspect of your competitor’s web page and to determine how each parameter should be optimized, click the View Details button. You will be redirected to the Competitive Comparison section—which we will also explore later.
To have all the data available at any moment, download the report in a PDF format by pressing the Export button at the top-right corner of the screen. Here, you can send the received report to anyone.
Building a strong semantic core
For the next step of the on-page SEO process, you’ll conduct a semantic analysis to target relevant keywords and integrate them into your page. The easiest way to accomplish this task is to use SE Ranking’s Competitor Analysis Tool in combination with a Keyword Research tool. Here’s a list of steps you’ll need to follow:
1. Go to the Competitive Research tool.
2. Enter your website or a specific URL, select the region you’d like to check the data for, and click Analyze.
3. The summary report will provide information on essential SEO data for both organic and paid search. It also offers a complete list of all targeted keywords.
4. To get a detailed report on all the keywords, hit the Keywords button under the Organic traffic research section.
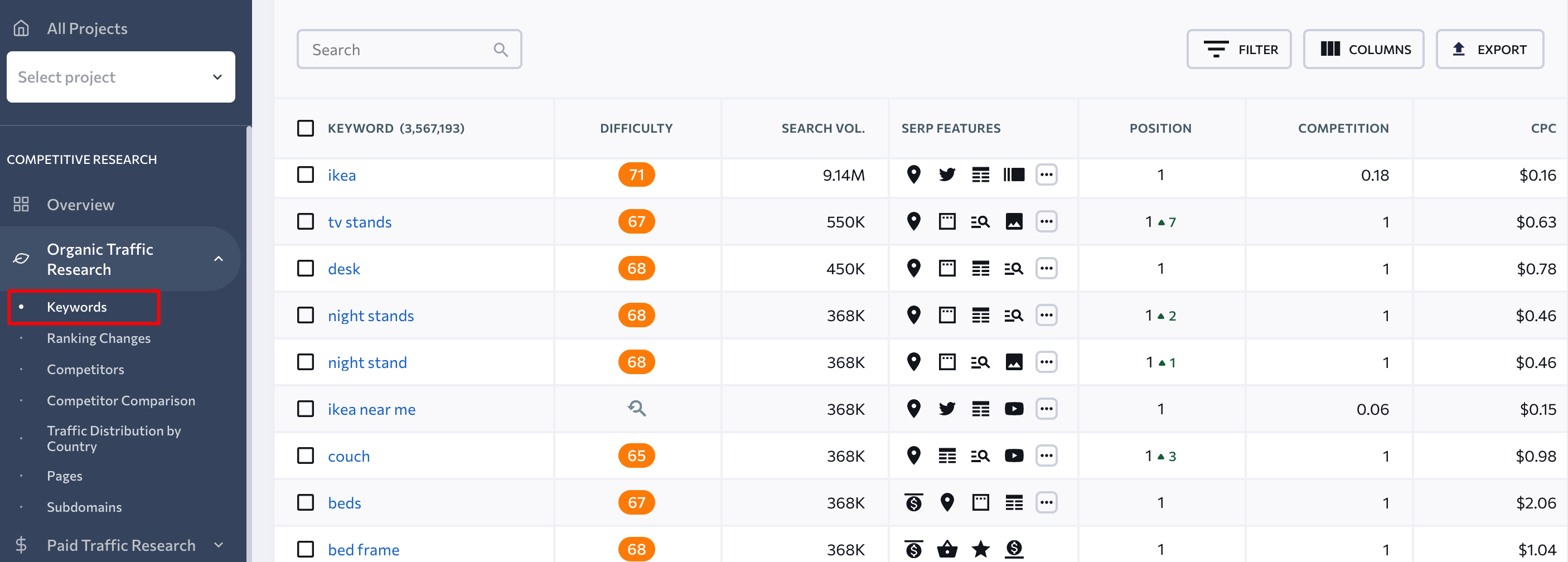
5. Once you know all the keywords your webpage already ranks for, pick keywords with the highest traffic potential (high search volume, position lower than 30) and optimize for them.
To add even more target keywords to your list, go to the Competitor Comparison tab under the Competitive Research section and add up to two competitors to line them up against your own site. The generated report will present a list of common, missing, and unique keywords for each page.
Let’s use Apple.com again as an example. To determine missing keywords for apple.com, you can add samsung.com and sony.com to the competitors’ list. Then access the Missing keywords tab and select apple.com in the dropdown list on the right. It is recommended to filter the results by a relatively high search volume and a low difficulty score.
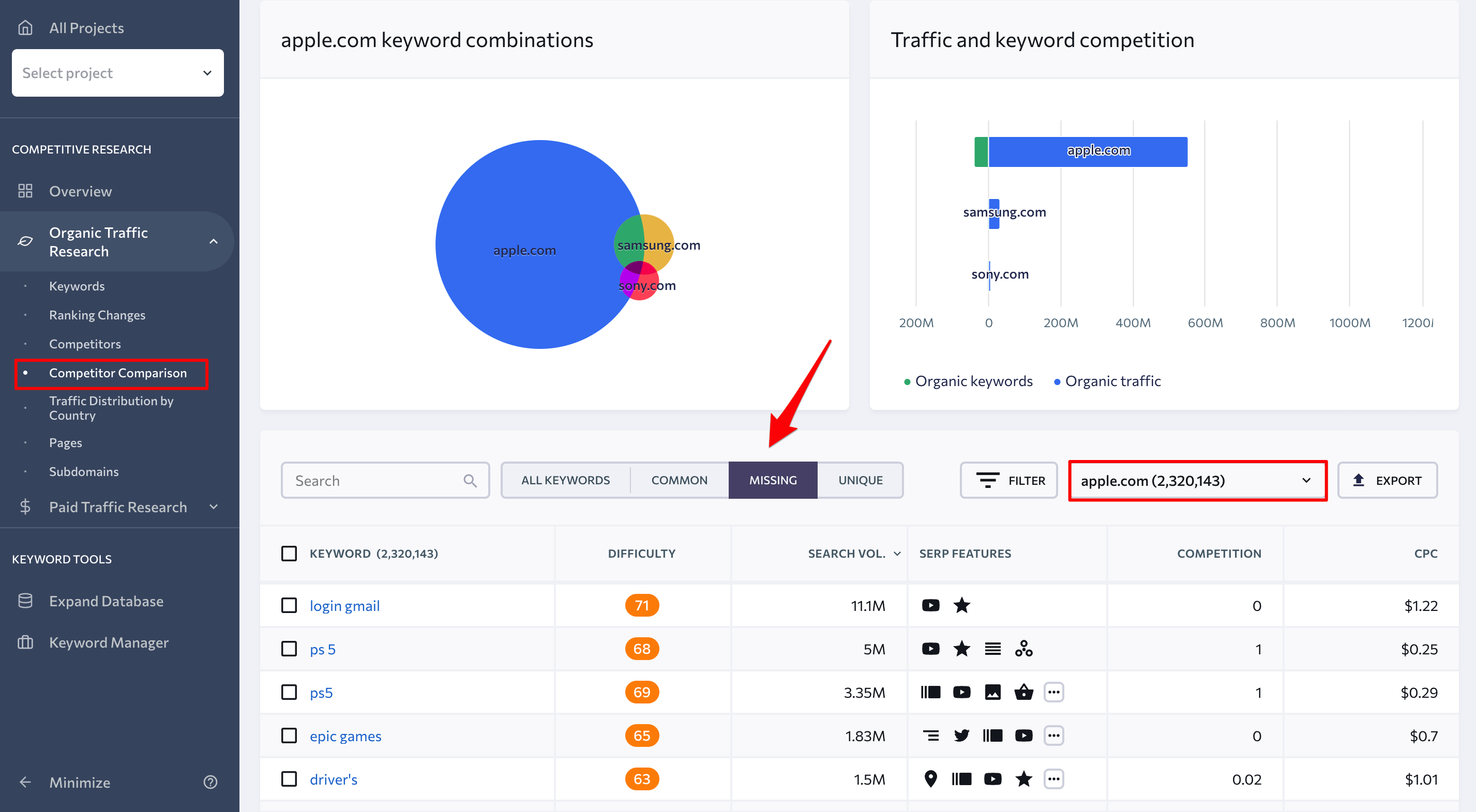
6. Alternatively, you can click on any keyword from the list to be redirected to the Keyword Research tool. Here you can find similar, related, and low search volume keyword suggestions that can be optimized to drive more traffic to your page. You can even use this tool to identify websites that are ranking for the selected keyword in organic search. To go even further, check the keywords of these top SERP players.
7. Once you have a list of relevant keywords, add them to the analyzed page. It is usually recommended to put your keywords not only in the content itself but also in:
- Title tags
- Description tags
- Alt image tags
- H1 (heading 1) tags
But don’t overuse target keywords. This can lead to keyword stuffing and, as a result, a negative user experience in combination with a decline in your site’s rankings.
Analyzing market and competitors
Expanding your semantic core and just adding more keywords to your existing page isn’t enough to outrank your competitors. You also need to outshine them by publishing high-quality content. To compare your on-page SEO with competitors and gain crucial insights, take advantage of the Competitive Comparison module offered by the On-Page SEO Checker.
To get started, go to the Competitive Comparison section and take a look at the three tabs at the top of the page. These are Terms, On-Page Metrics, and Content.
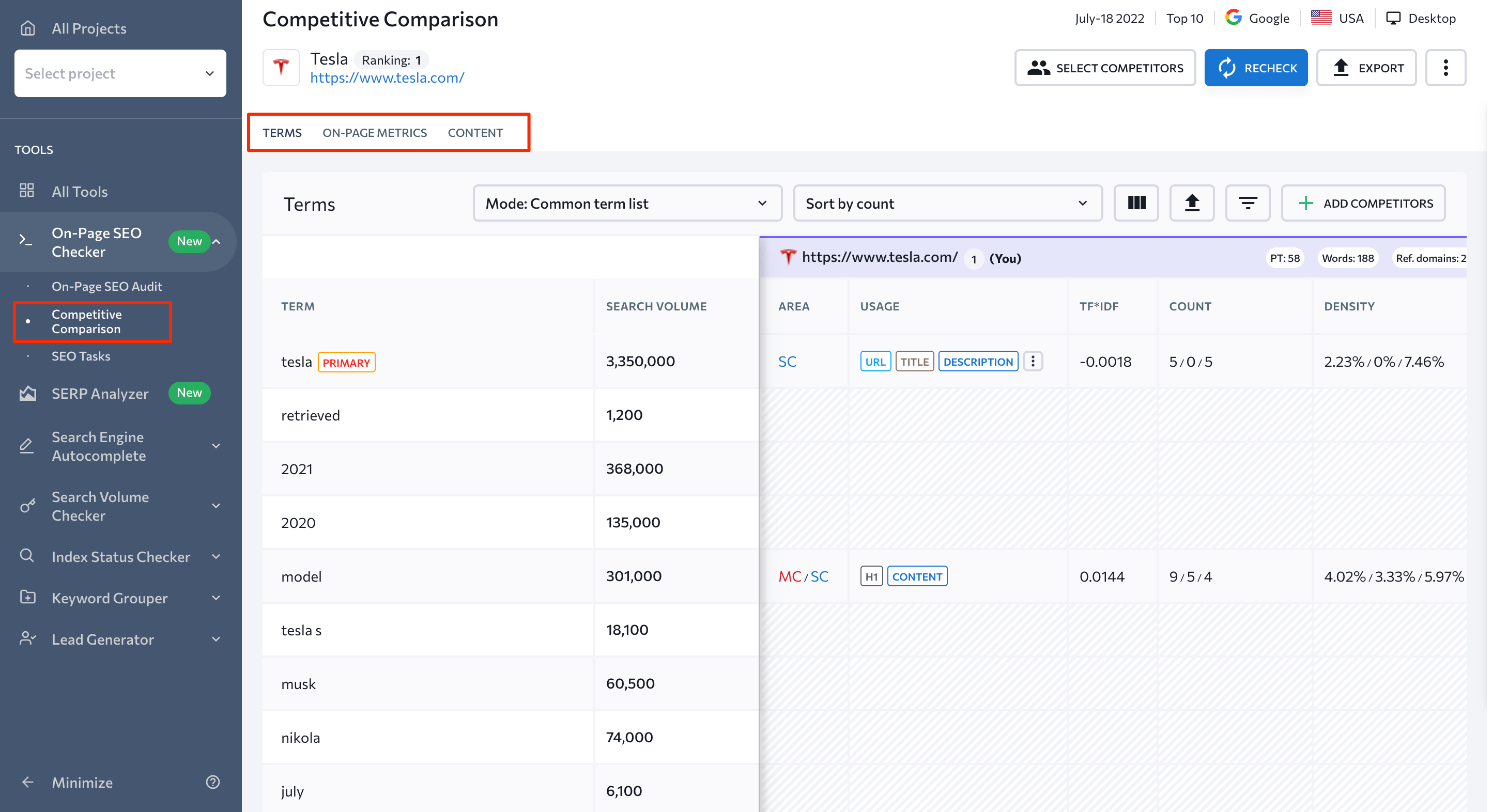
The Terms tab helps you check what keywords your competitors are using, how often they use them, and where these words/phrases are featured in their content.
The first table contains all keywords targeted by your rivals and their search volume. There’s a filter on it you can use to single out a full list of keywords missing on your page. You can also separate the keywords your rivals used in their main content from keywords used in their supplementary content.
In the second table, you can find information about the type of content where every keyword was found (title, H1, URL, etc) and a TF*IDF score that evaluates how relevant a word is in the context of a page.
This table also shows how many times a particular term is mentioned on the page in the primary and secondary content (Count column). It also shows the ratio of keyword usage regarding the page’s word count (Density column).
The On-Page Metrics tab lets you check the parameters of your and your competitors’ pages side by side. The table contains measurements of 30+ parameters, including title tag length, the Core Web Vitals, the number of backlinks, and so on.
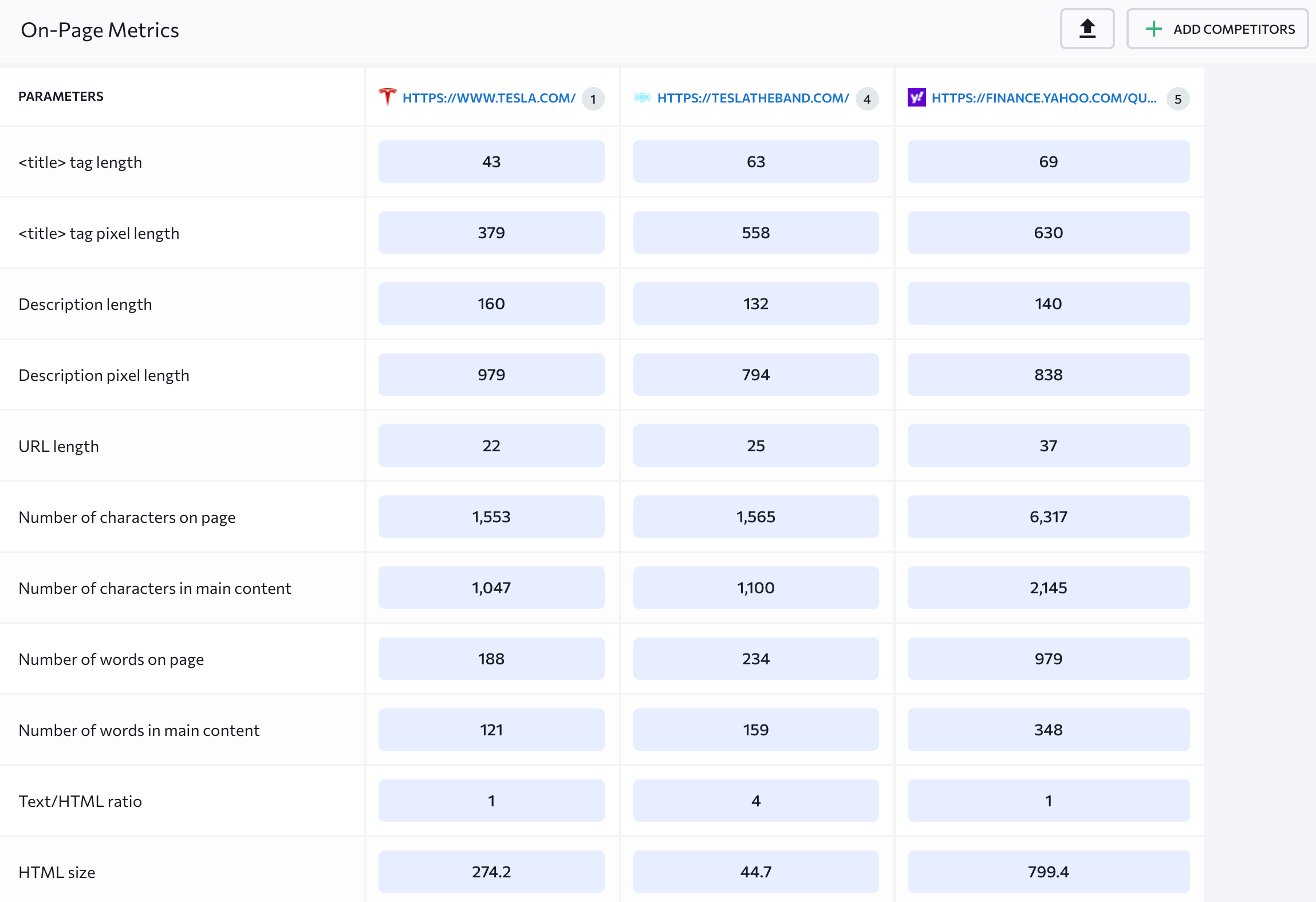
By the way, there’s a Select Competitors button at the top of the page. This is where you can choose the competing pages you want to analyze and compare. If some of the detected competitors are big players like Amazon or Wikipedia, you can remove them from the list.

The Content tab can be used to review content parameters separately from others. For example, by reviewing the H1 title used on each page, you can compare it with your own and get ideas on how to improve your main heading.
Creating a to-do list and prioritization
Once all of the necessary information for the on-page SEO is gathered, it’s time to put it into practice. This is where the SEO Tasks feature comes into play.
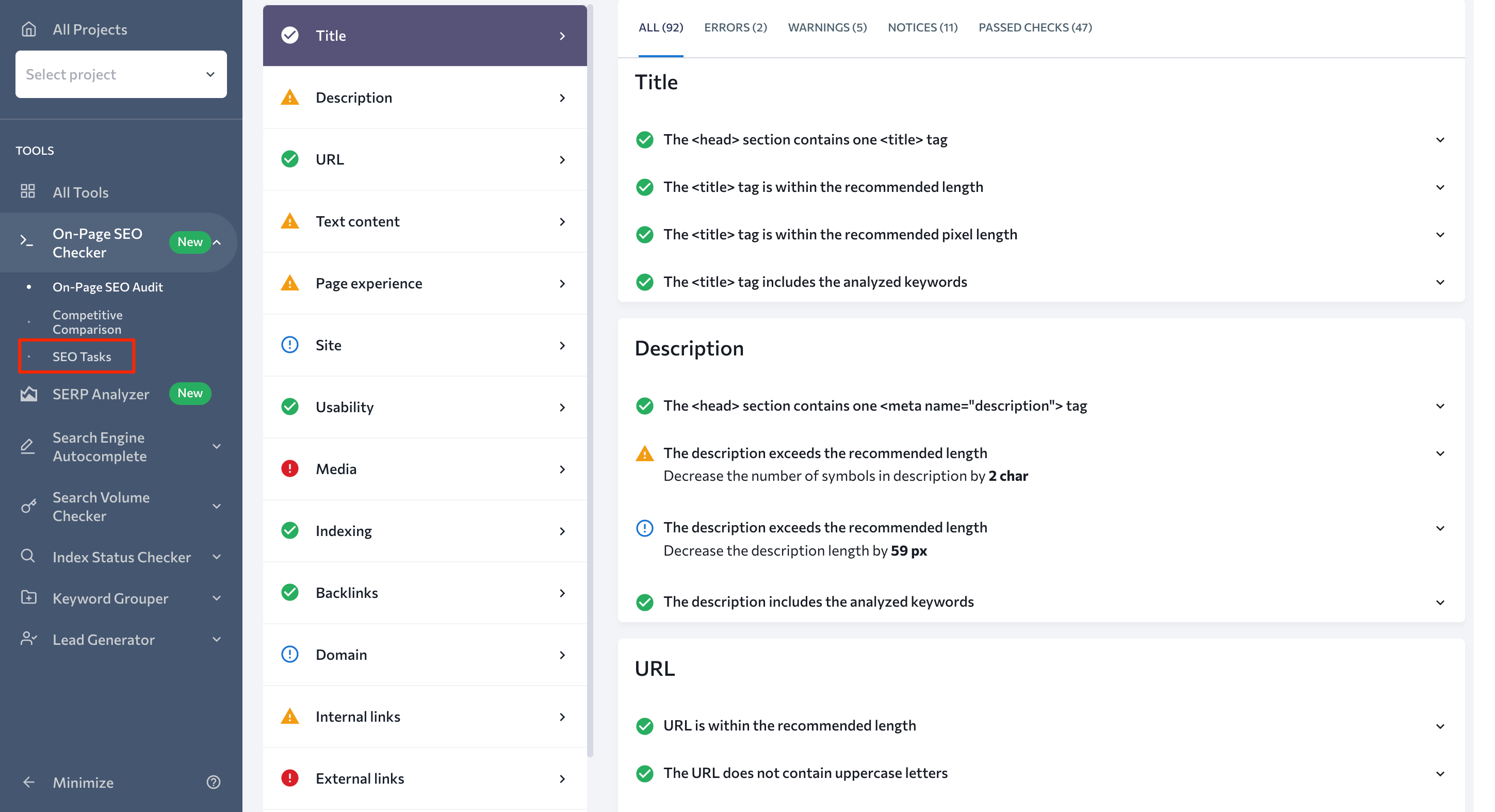
By going to this section, you can access a to-do list with all the issues (which are divided by priority, category, and status) found on your page. For instance, issues related to duplicate content and broken links are usually included in the list of tasks with a high priority. Problems regarding description length and the number of headings typically have low priority.
Since the whole report is fully customizable, you can manually change the priority of each issue. If you believe that the On-Page Checker reports an issue for something that’s not a problem for your page, you can always remove this suggestion from the list.
You can share this report with anyone you want in PDF format. This is a convenient option if you’ve got a webmaster to take care of all the work for you.
Optimization itself
The list of tasks that need to be done should determine how you optimize a specific page. For instance, after downloading our SEO Tasks report, you will see a table similar to the one listed below (but with actions specific to your page).
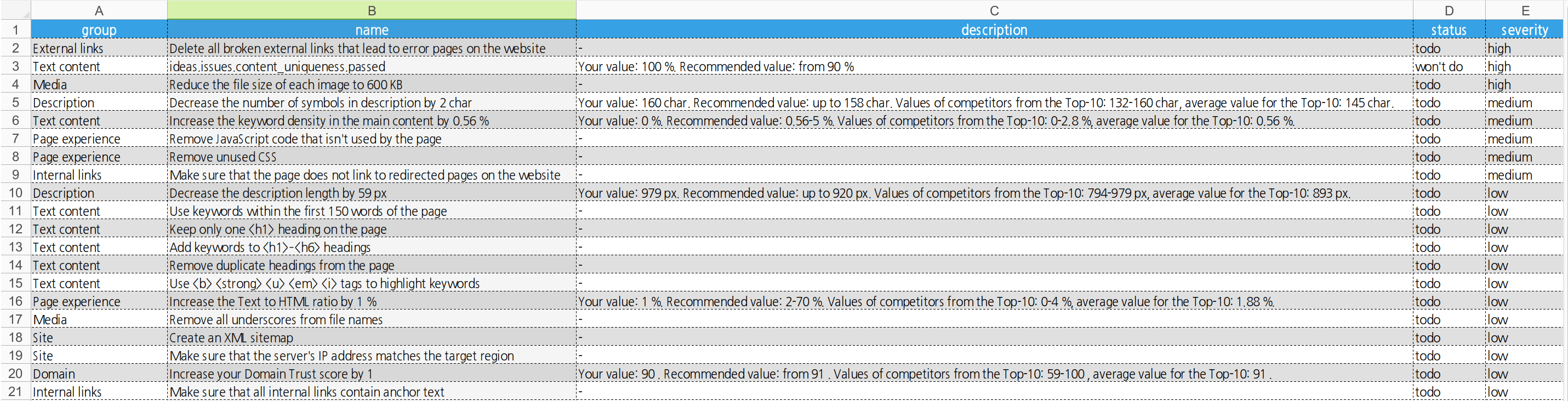
Go through each task step by step, starting with recommendations with high priority. Mark each completed action with the “done” status. This will give you a clearer vision of completed tasks versus tasks that still need your involvement.
Optimization of all pages in bulk
Even though it only takes two steps to optimize all pages in bulk, it requires no less effort than optimizing one page at a time. Let’s dig deeper into it.
Conducting a website audit
The automated website audit is arguably the best tool for making big changes because it reveals same-pattern issues across a whole site. To estimate the state of the entire website, you can take advantage of SE Ranking’s Website Audit tool. Use it to analyze a website (yours, a competitor’s, or a client’s) against over 120 parameters, including:
- Domain metrics
- HTTP status codes and redirects
- Meta robots tags influencing page indexation
- Page breakdown (textual content, titles and meta description, and so on)
- Page resources (images, CSS, JavaScript)
- Internal and external links
- Website security
In addition to providing clear and actionable recommendations on how to fix both on-page and off-page issues, the Website Audit tool also provides health score information on each of a website’s pages, including the website speed.
To start the audit process, select a project at the top left corner of the screen and go to Website Audit.
You can also access Website Audit by selecting a project on the main dashboard and clicking the three dots menu.
In the Overview Section, you will get a summary of the website’s technical SEO health. It can help you determine which issues should be your top priority during the on-page optimization process.
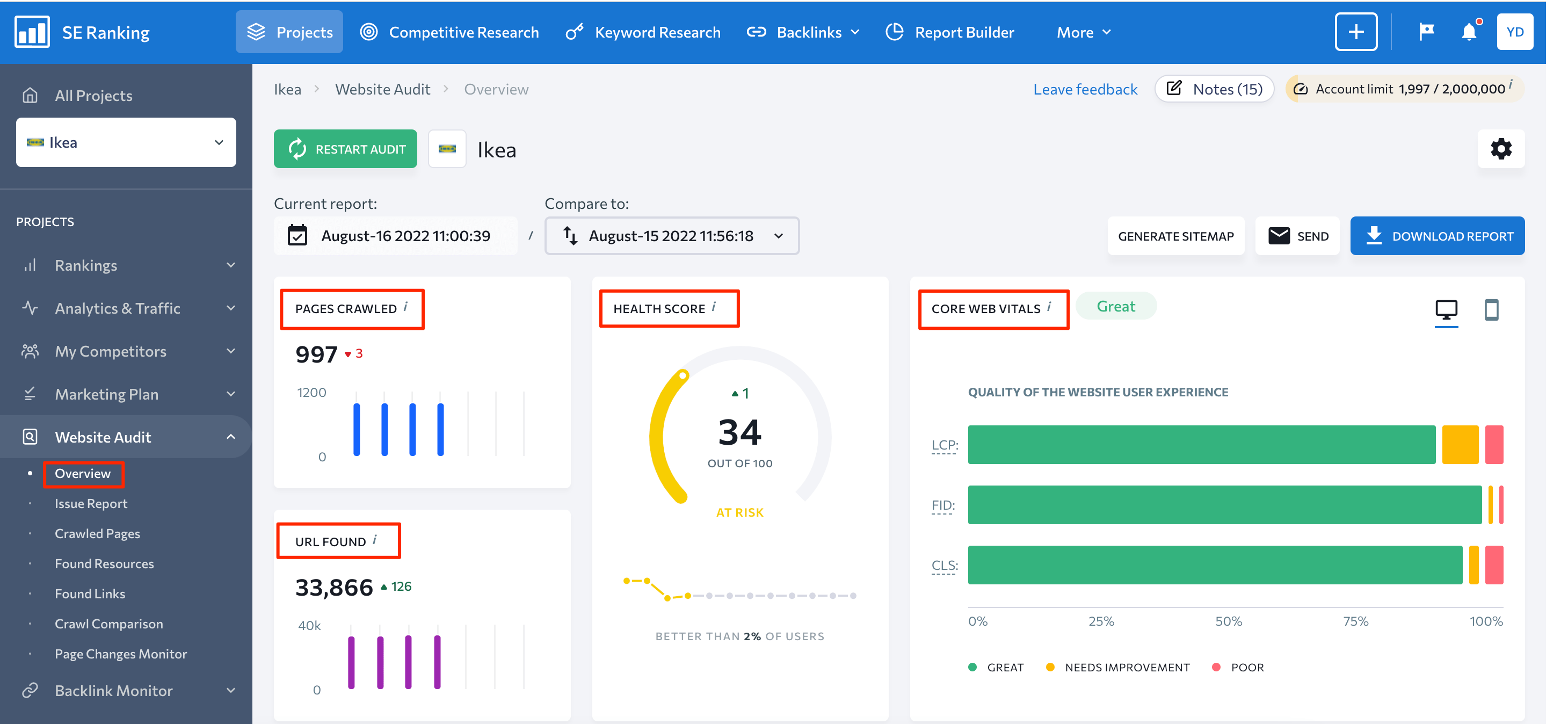
As you can see on the screenshot above, you can find (at the top of the page) brief information about the website. This includes the number of crawled pages and found URLs, the overall health score, and Core Web Vitals.
Under these blocks, you can access the Top Issues section demonstrating the top five critical issues to be addressed. You can also find the Distribution by Category graph. It shows from each category the number of pages of the analyzed website which have issues. Below, there is also a Domain Metrics section that shows your domain’s expiration date, the total number of backlinks, referring domains, and the domain trust score.
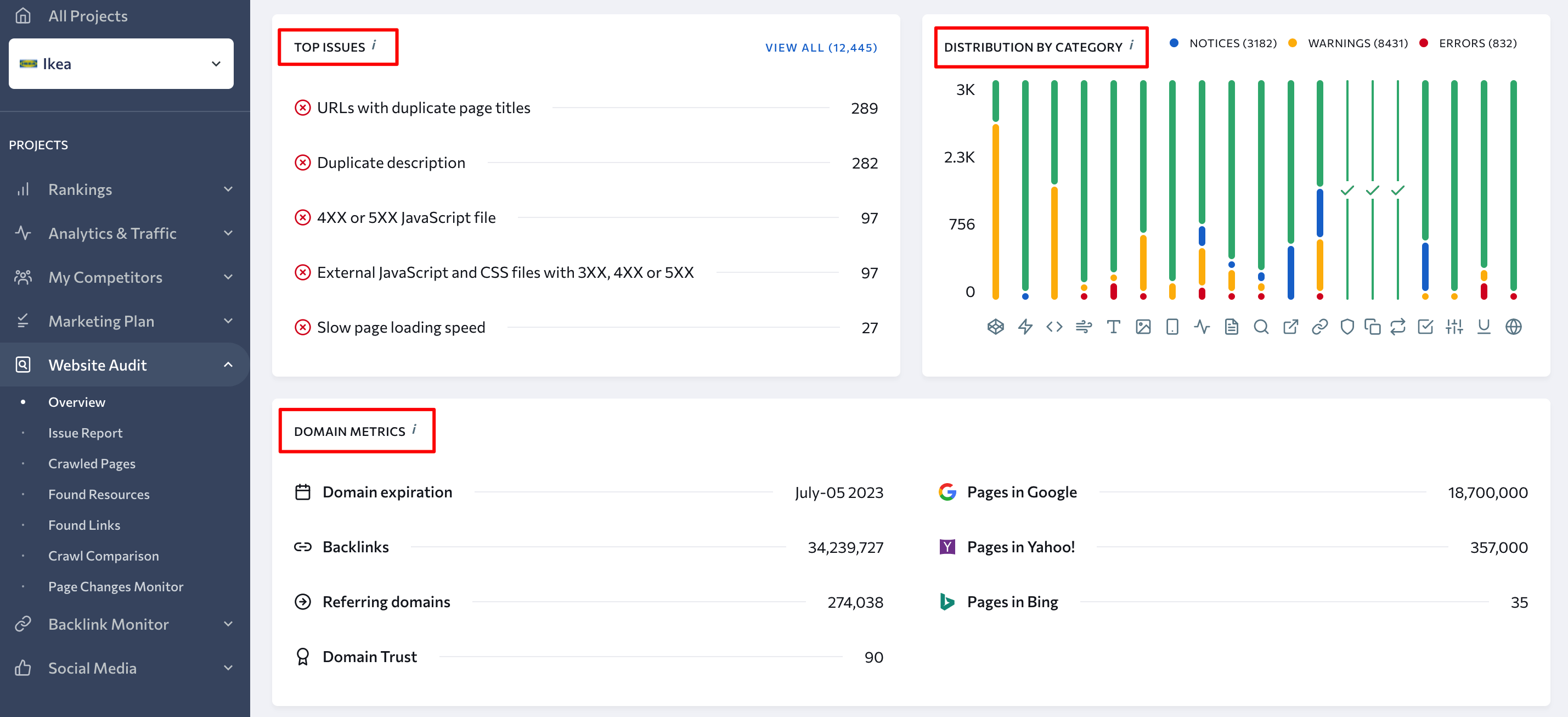
After reviewing the overall information on your website, go to the Issue Report section. In this block, you can see all detected issues grouped into nine categories, such as:
- Crawling
- HTTP Status Code
- Title
- Description
- Website Speed
- Textual Content
- Internal Links
- Localization
- Images
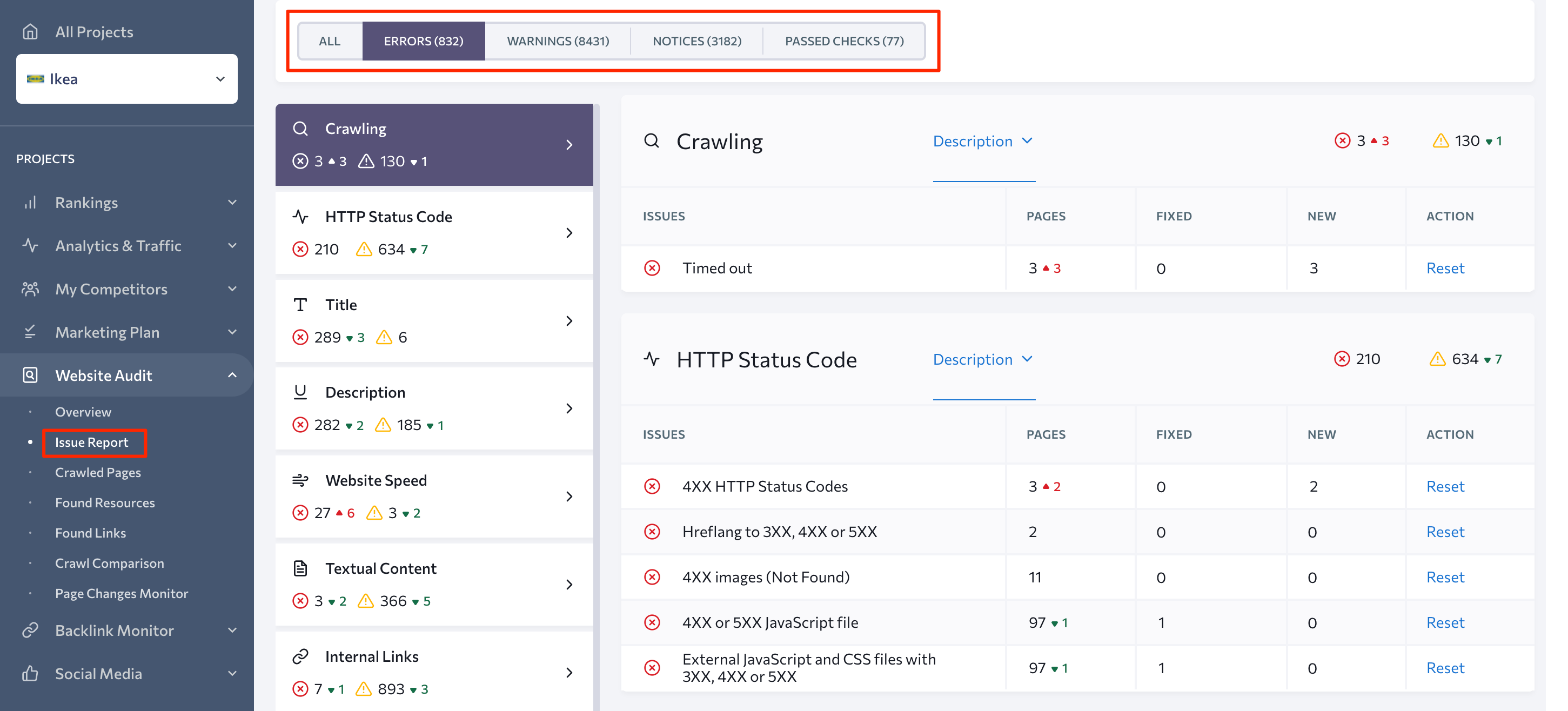
As you can see, all found issues are divided into three main blocks based on their significance:
- Errors
- Warnings
- Notices
To identify all pages that need their on-page elements to be optimized, click on the Errors button and select a specified category of issues. You will then get a list of pages requiring optimization.
For instance, if you select the Website Speed group of issues, you will get the URLs of all 27 pages that require on-site optimization in terms of loading speed:
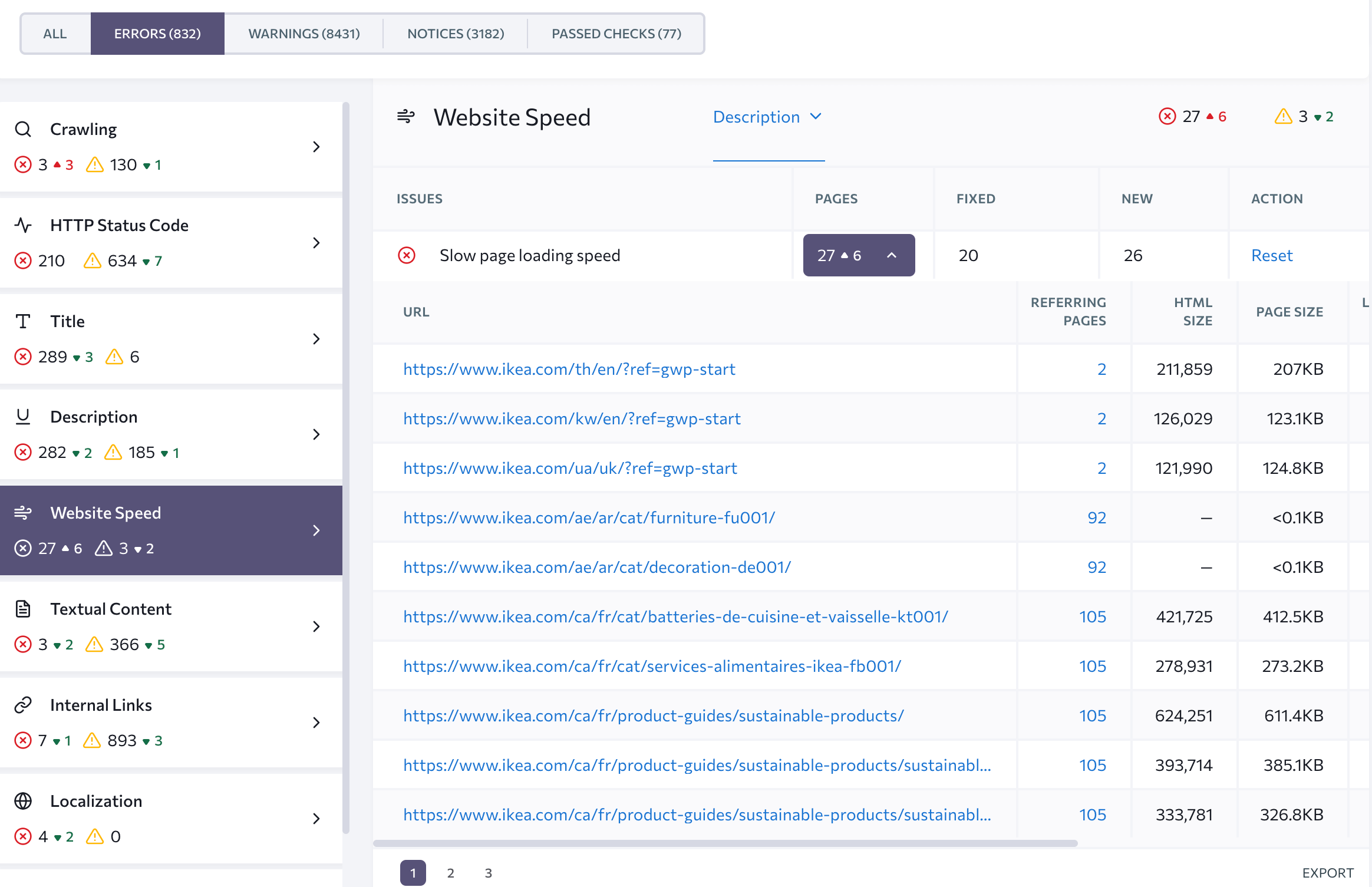
To get tips on how to fix a specific problem, click on the name of the issue you need to inspect. In this case, clicking on the Slow page loading speed button will open the issue description highlighted in red and the how to fix suggestion highlighted in green.
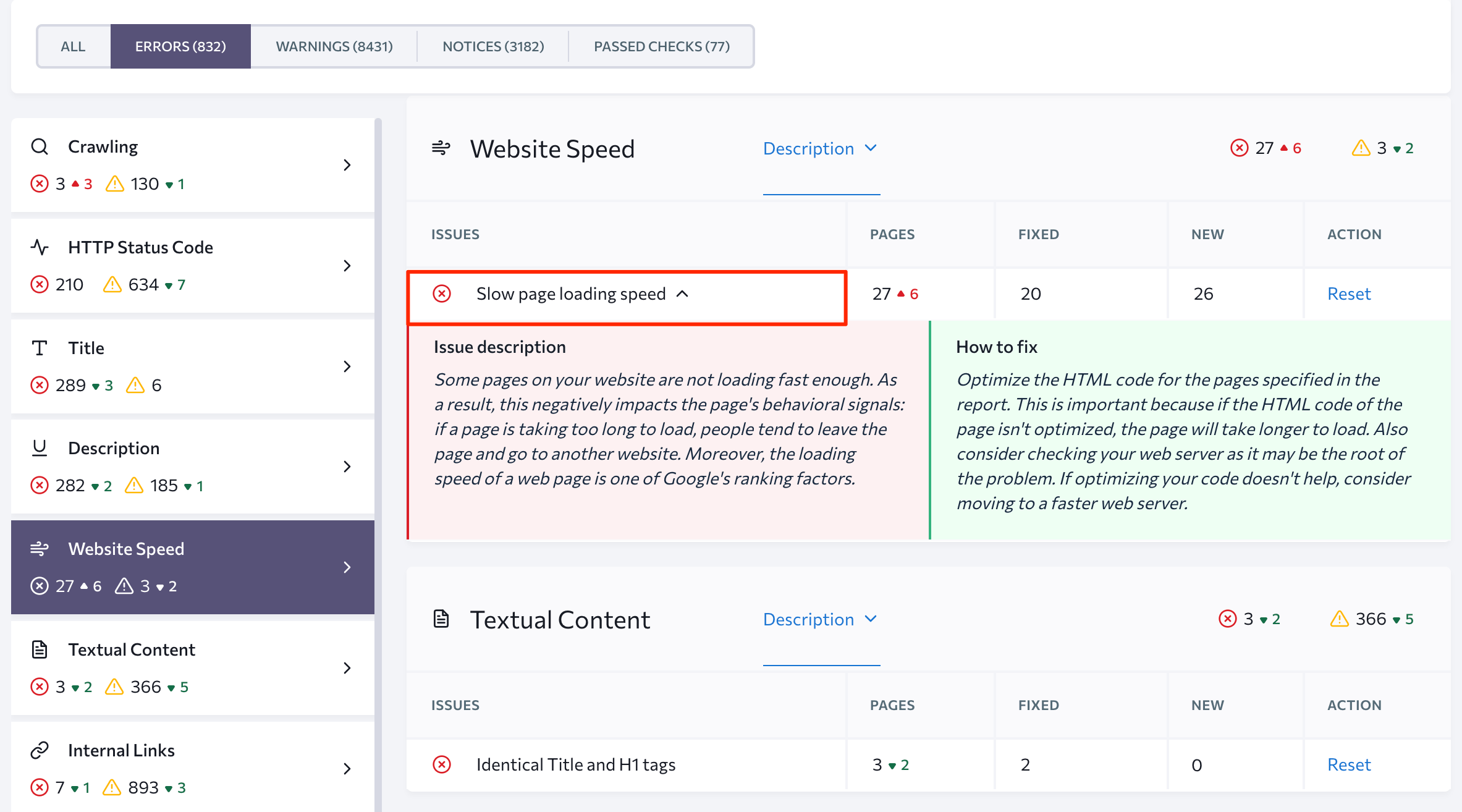
You can find groups of pages requiring the same type of on-page SEO and optimize them together instead of going through each page separately. For instance, you might discover that all of your category page headings and titles are the same. Fixing them individually could take up too much time when you could come up with some kind of automated solution instead.
Optimization itself
Optimization of all pages in bulk might be a perfect solution for situations where creating coordinated experiences across multiple web pages is needed. This approach is typically used for e-commerce websites, but it can also be used for larger websites.
The logic is simple: you select a group of pages based on their type and organizational structure, then make changes to a certain SEO element (whether it is a meta description, image, or video) that is repeated across all of the selected pages.
For instance, most e-commerce websites have hundreds, if not thousands, of product pages. It could be time-consuming to optimize each of them separately, so consider using templates that let you apply the same SEO settings to many pages at the same time.
Let’s say you need to optimize the title tag on all of the product pages of your e-commerce website to increase the organic CTR. You can do it manually, but WordPress SEO plugins make performing this task easier.
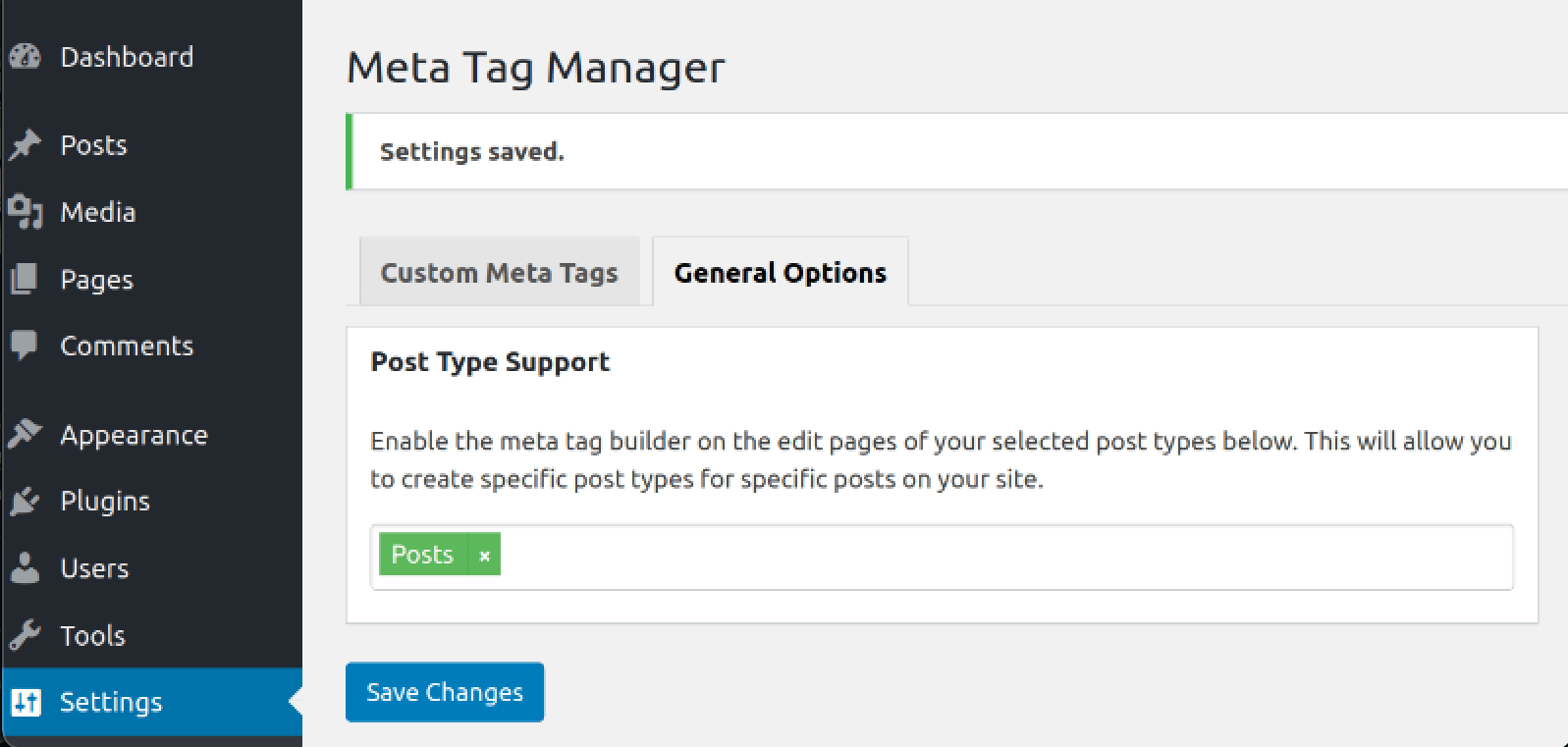
Begin by installing any third-party plugin. It could be the Meta Tag Manager, the All in One SEO Pack, or Yoast SEO. These tools offer both free and premium versions, but you can easily optimize meta tags without any subscriptions.
If you use the Meta Tag Manager, access this plugin at Settings > Meta Tag Manager. Then, go to the Custom Meta Tags tab and click on the + Add Meta Tag button. After adding your meta tags and assigning them to specific areas on your site (e.g. certain products or product categories), press the Save Changes button.
Consider the “all pages in bulk” approach if you run news or blog websites. So if you want to get more page views and keep users engaged, insert the Related Posts section on your website. Not only can this content element help your audience discover related content, but it can also improve your internal links and decrease your bounce rate.
You can also add related posts to your website with the help of Yet Another Related Posts Plugin (YARPP). This free feature creates lists of related posts based on the titles, content, categories, and tags of your pages. Don’t be afraid, however, to select other plugins if you find them more convenient to use.
After installing and activating YARPP, set it up according to your SEO goals. Like other plugins, YARPP can be accessed by going to Settings > YARPP. Here, you can determine post types and the number of related posts you want to display on your blog. With YARPP, you can also select the style of display (e.g. list style, posts with thumbnails, or custom code) and customize the order of display.
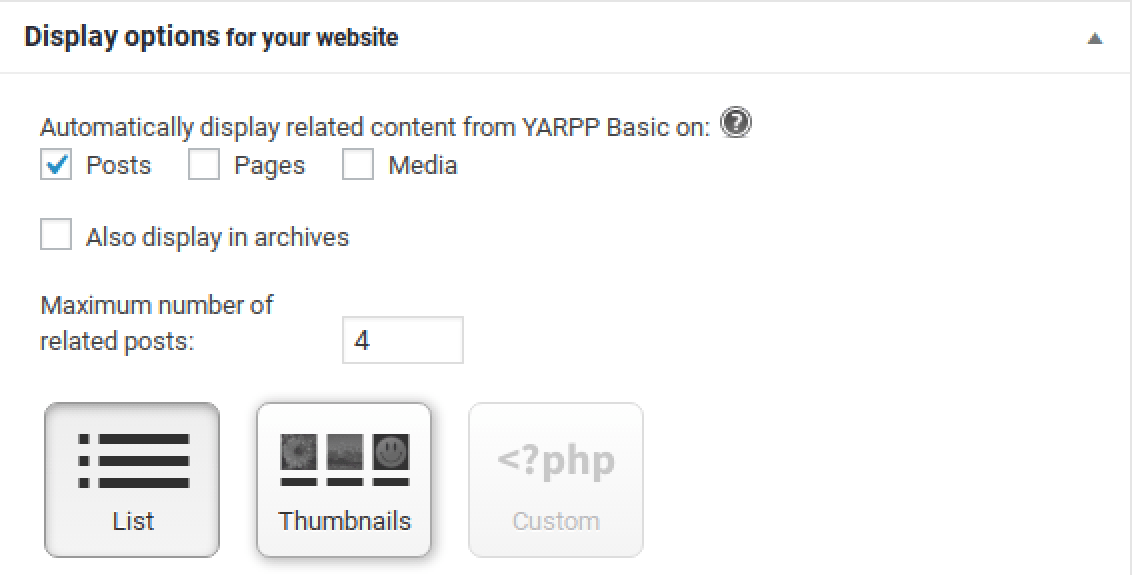
If you want to ban some pages from the list of related posts, mark disallowed content in the settings.
Optimization of all pages in bulk is also great for search results enhanced with visual or interactive data—also known as rich snippets. Since rich snippets improve the whole website’s appearance in SERPs, they can significantly increase CTR and drive more traffic.
To get rich snippets, add structured data to your web pages in one of the following formats:
- JSON-LD
- Microdata
- RDFa
You will either need to use your coding skills or hire a developer to add schema markup to your site. If your website is powered by WordPress, however, you can use plugins that assist you in customizing rich snippet code.
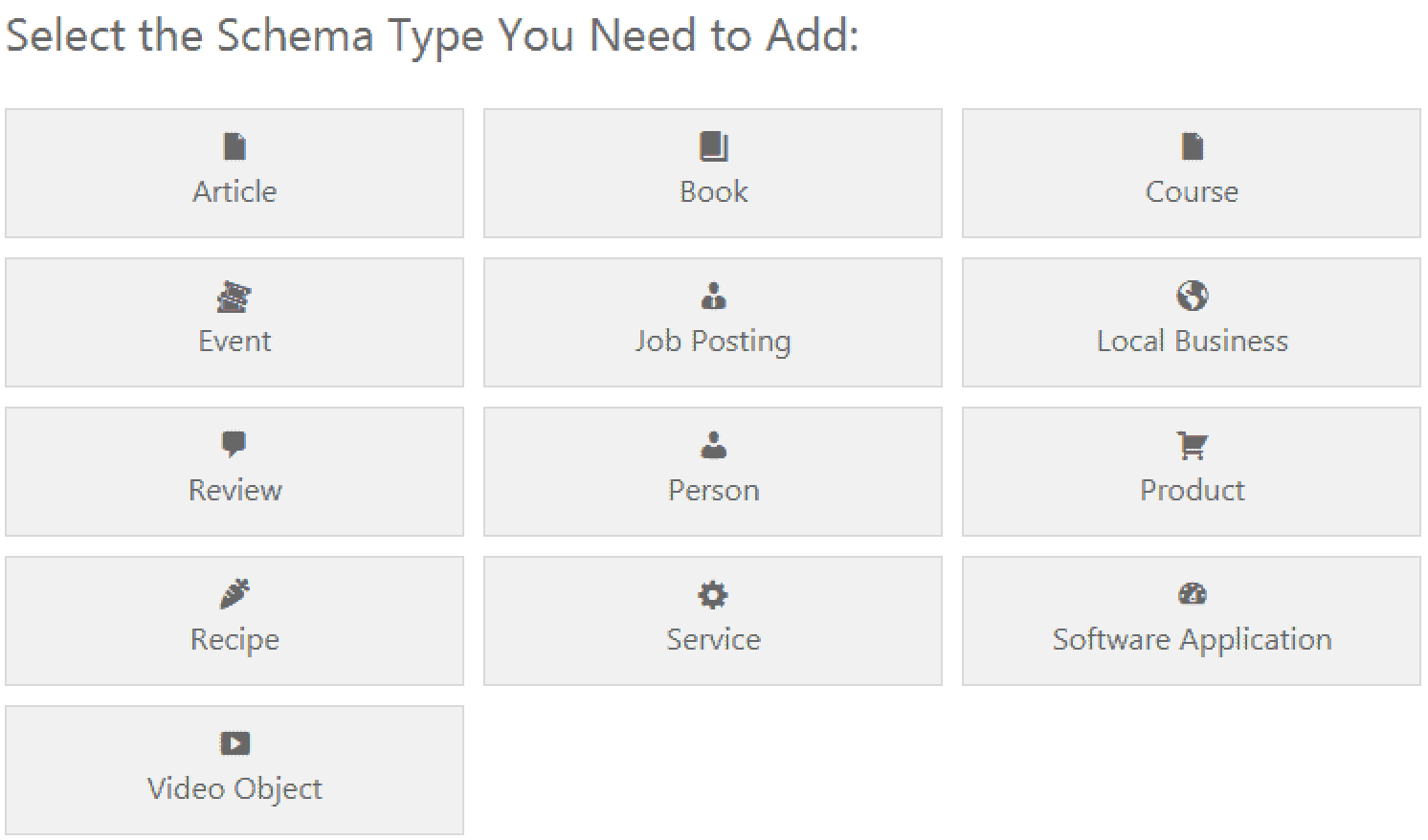
In this case, Schema Pro might be a perfect fit. With this plugin, you can manage your rich snippets in bulk instead of editing hundreds of posts or pages one by one. Once it is installed and activated, start configuring its settings.
To start, select one of the offered schema types, including review, book, product, article, recipe, event, local business, etc. Next, choose the page or group of pages where schema will be used. Then, you’ll see a prompt to complete the setup.
There are many other alternatives you can use to optimize all pages at once but the ones listed above can be used by almost any person, regardless of their experience in on-page SEO.
Final Thoughts
On-site optimization isn’t a one-time task. You can’t just boost rankings once and then call it a day. It requires time, effort, grit, and patience to reach the top positions in the SERPs. If you make it a habit to improve user experience by using the on-page SEO best practices we discussed in this post, you’ll be well on your way to becoming one of the major players in your industry.
Remember, when doing on-page SEO of one page at a time::
- Estimate its current state.
- Build a strong semantic core to optimize for.
- Analyze market and competitors.
- Create a to-do list.
- Optimize the page according to your plan.
When optimizing all pages in bulk:
- Analyze the whole website and find pages with the same type of problem or optimization opportunities.
- Apply changes to all pages in bulk.
Long story short, on-page SEO can help you boost organic traffic, improve user experience, and increase your conversion rate.

