The Complete Canonical Tag Guide
-
Canonical tags help search engines identify the preferred version of a webpage among similar or duplicate ones.
-
You can specify the canonical URL in the HTTP response header, add a canonical tag to the HTML head section, or list the preferred URL in your website’s XML sitemap.
-
Google considers various factors when choosing the canonical URL, including the number and quality of links pointing to each page, the presence of a canonical tag & its specified URL, the use of HTTPS and HTTP, as well as mobile-friendliness (if a separate mobile version exists).
-
You can use tools like Google Search Console or SE Ranking to identify the URL Google has chosen as canonical.
-
Canonical tags offer many SEO benefits like preventing duplicate content issues, consolidating page authority, improving crawl budget efficiency, and ultimately increasing search rankings.
-
Canonical tags are particularly recommended in cases like faceted navigation, the same items listed under different categories, UTM tags & tracking parameters, and pagination.
What is a canonical tag in SEO?
Let’s start with the canonical tag definition.
A canonical tag is a method used to identify the preferred version of a page among duplicate or very similar pages on Google search results. In other words, search engines rely on canonical tags to determine which version of a URL to prioritize.
Canonical tags play an essential role in preventing duplicate content issues that may arise when the same content is accessible from multiple URLs.
What is a canonical URL?
Now that you have a clear understanding of the canonical tag SEO meaning, you might have the following questions: what is a canonical URL? How does it differ from the canonical tag?
Here’s the answer:
Google defines a canonical URL as the URL of a page chosen (by Google) as the most authoritative among a group of duplicate pages. Simply put, Google recognizes the canonical URL as the “master” version of all other pages displaying duplicate or similar content.
How to specify the canonical URL
When a site contains multiple pages with identical or very similar content, search engines may struggle to decide which page to display in SERPs. To tackle this problem, website owners can specify a canonical link element, indicating their preferred page for display.
In technical SEO, there are several methods for specifying the master page (with and without canonical tags), many of which are described in more detail in Google documentation. Here, we will go through the most commonly used methods for specifying canonicals.
Important! Canonical tags are suggestions that Google can easily ignore.
Tags within <head> of HTML
If you want to specify the canonical URL for your page, one common method is to include a canonical tag like <link rel=”canonical”> in the <head> section of its HTML code. This straightforward approach is the most widely used and tells search engines which version of your web page should be indexed and displayed when users type in the queries it targets.
For example, if two pages on your website contain identical content but have different URLs, adding the line of code with a rel canonical can indicate that it is the preferred page to display. Take a look at this canonical tag example:
<head> <link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page.html"> </head>
Canonical HTTP Response Header
For websites that display dynamic pages based on user input or other variables, adding a canonical URL in the HTTP response header is an effective approach. In this case, canonical tags can direct search engine crawlers and, therefore, ensure that your desired version of the webpage is indexed. For example, you can add canonical in HTTP headers in this way:
Link: <https://www.example.com/preferred-page.html>; rel="canonical"
XML Sitemaps
Another way to specify the canonical version of a web page is by including it in your website’s XML sitemap. This allows you to communicate to search engines which URL should be indexed for users’ queries.
While Google considers all sitemap entries as suggested canonicals, it’s not a definitive signal. Search bots may still analyze content and user signals to determine the most relevant version for a specific search query. However, adding canonicals in sitemaps can be especially beneficial for large or complex websites with many pages.
Absolute URLs
Google recommends using absolute URLs rather than relative URLs when setting up canonicals. Absolute URLs include the full web address, starting with the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) and ending with the specific page or post. This helps search engines understand which version of your content is the original and should be prioritized in SERPs.
How Google chooses the canonical URL
The precise factors and their weights affecting Google’s selection of a canonical URL are not fully disclosed. However, during a recent Search Off the Record podcast, Allan Scott from Google’s “Dups” team shed light on how the search engine handles duplicate content.
Google reportedly assesses around 40 distinct signals to determine which URL should serve as the primary, or canonical, version among duplicate pages.
Scott noted that when strong signals, such as rel=”canonical” tags or 301 redirects, conflict with one another, Google’s system may fall back on weaker signals to make a decision.
This suggests that while implementing robust canonicalization techniques is vital, inconsistencies in these signals can lead to Google relying on less definitive criteria.
Here are some of the key factors that Google’s algorithm is believed to consider when determining the canonical URL:
1. Links pointing to the page: To evaluate a page’s relevance and importance, Google examines any internal and external links pointing to both pages and chooses the page with more links and better quality.
2. Canonical setup (tags, Response Header, sitemap): When determining the dominant version of a page, Google considers whether there is a canonical tag embedded in its HTML code, rel=”canonical” HTTP header, among other hints, such as URLs listed on the sitemap.
Additional factors that Google considers when choosing the canonical URL include:
3. HTTPS pages. Google prioritizes HTTPS pages over HTTP pages, except under the following conflict-creating conditions:
- An invalid SSL certificate is present on the secure page.
- There are insecure dependencies (aside from images) included in the protected page.
- Users are redirected to or through an unprotected webpage via its secured counterpart.
- The secure webpage has a rel=”canonical” link pointing to its unsecured version.
4. Hreflang clusters. To ensure that the sites’ localization efforts are successful, Google recommends grouping together URLs with hreflang tags into clusters for canonicalization.
Learn more about the differences between canonical and hreflang tags.
5. Mobile-friendliness. To ensure that the canonical version of a page is indexed correctly, include a rel=”alternate” link element, which references the mobile version of the page if it exists on a separate URL.
Google, as you can see, utilizes a variety of signals to decide which URLs should be selected as canonicals. Normally, if a canonical tag is available, it will use it, but not always. Google might occasionally choose a non-canonical option if it believes that another page better satisfies user preferences or offers more accurate information.
How to find out which page Google considers canonical
Although the rel=”canonical” element in the HTML code of your pages lets Google know which version has to be canonical, Google can ignore it and choose non-canonical pages instead.
Don’t worry, though! There are several simple methods to determine which page Google considers canonical, including:
- Using Google Search Console
- Using SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker
Let’s review both options on how to discover the Google-selected canonical in more detail.
Using Google Search Console
If you’ve already verified ownership of your website in GSC, use the Google Search Console’s Page Indexing report to identify the preferred page for search engines.
This report provides a list of all indexed and non-indexed site pages, allowing you to identify any discrepancies with alternate canonical tags or duplicate content lacking user-selected canonicals. If you see any pages without user-selected canonicals, you can fix this by including the canonical tag on your webpages.
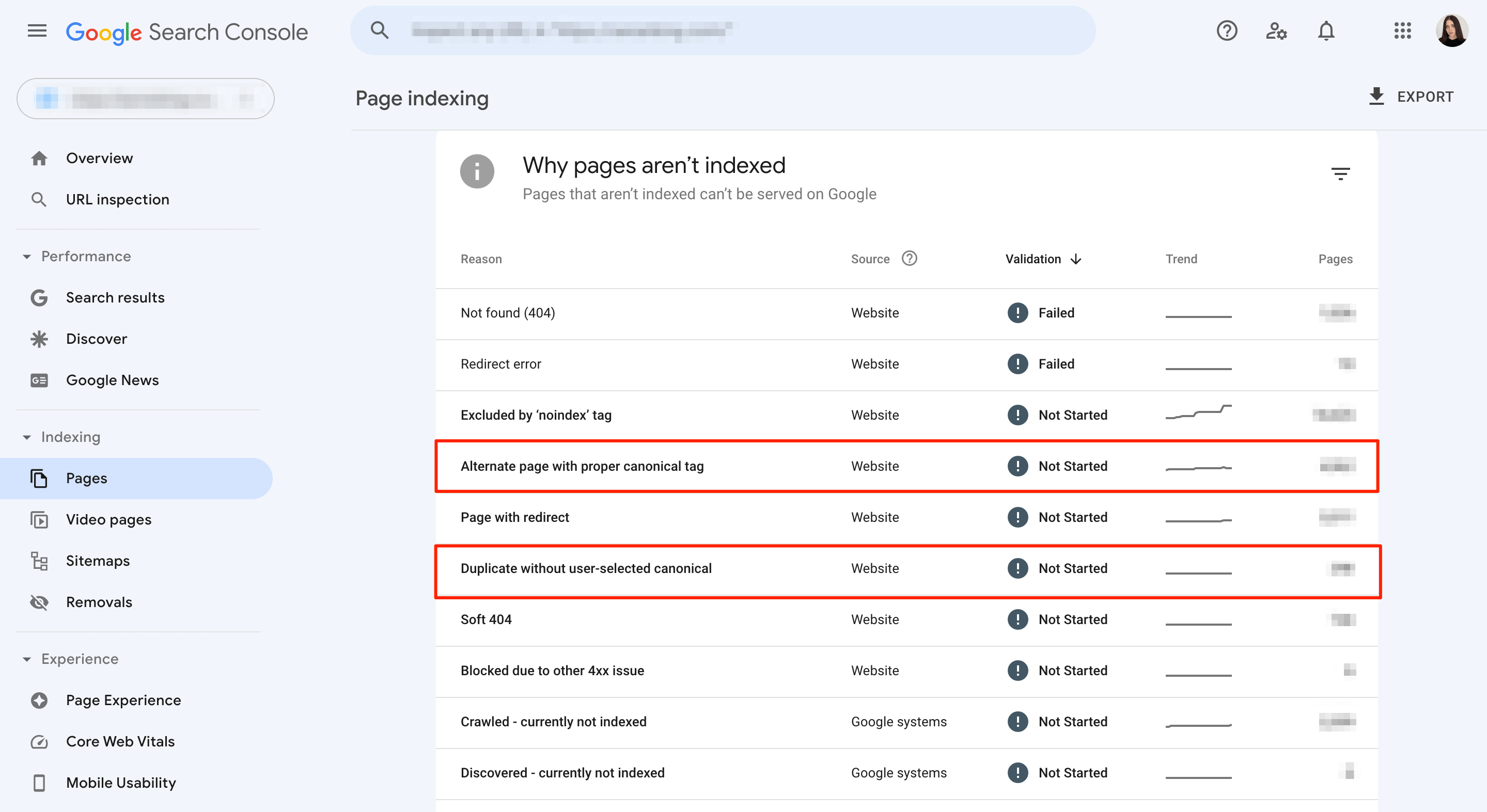
The Performance report provides an overview of your site’s performance in search, including the number of clicks and impressions on each page. If you notice that your non-canonical URLs are attracting attention and receiving impressions during the most recent period of time, it could indicate that Google is disregarding your canonical tags. This situation can even occur when your canonical tags are set up correctly. Sometimes, for example, non-canonical pages receive more backlinks or internal links without any clear reason.
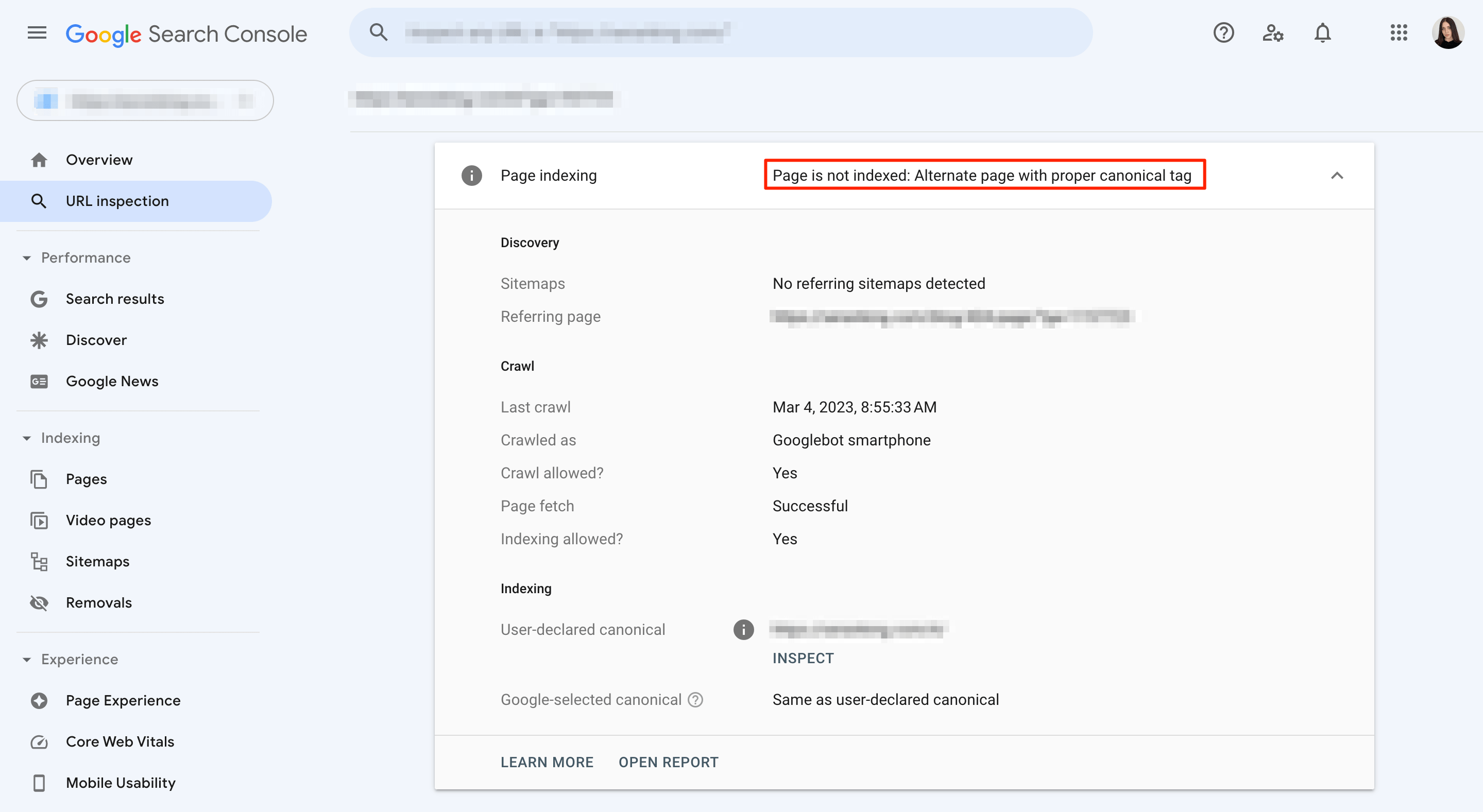
On top of that, Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool offers real-time updates regarding the indexing and crawling status of any page on your site. With this feature, you can easily identify and address cannibalization issues, such as duplicate titles and meta descriptions, as well as indexing problems and other issues related to a specific URL.
Using SE Ranking’s Rank Tracker
With the help of SE Ranking’s ranking tracking tool, you can get information on the page that Google is paying the most attention to. Check this by going to the Detailed report and hovering over the URL next to your keyword.
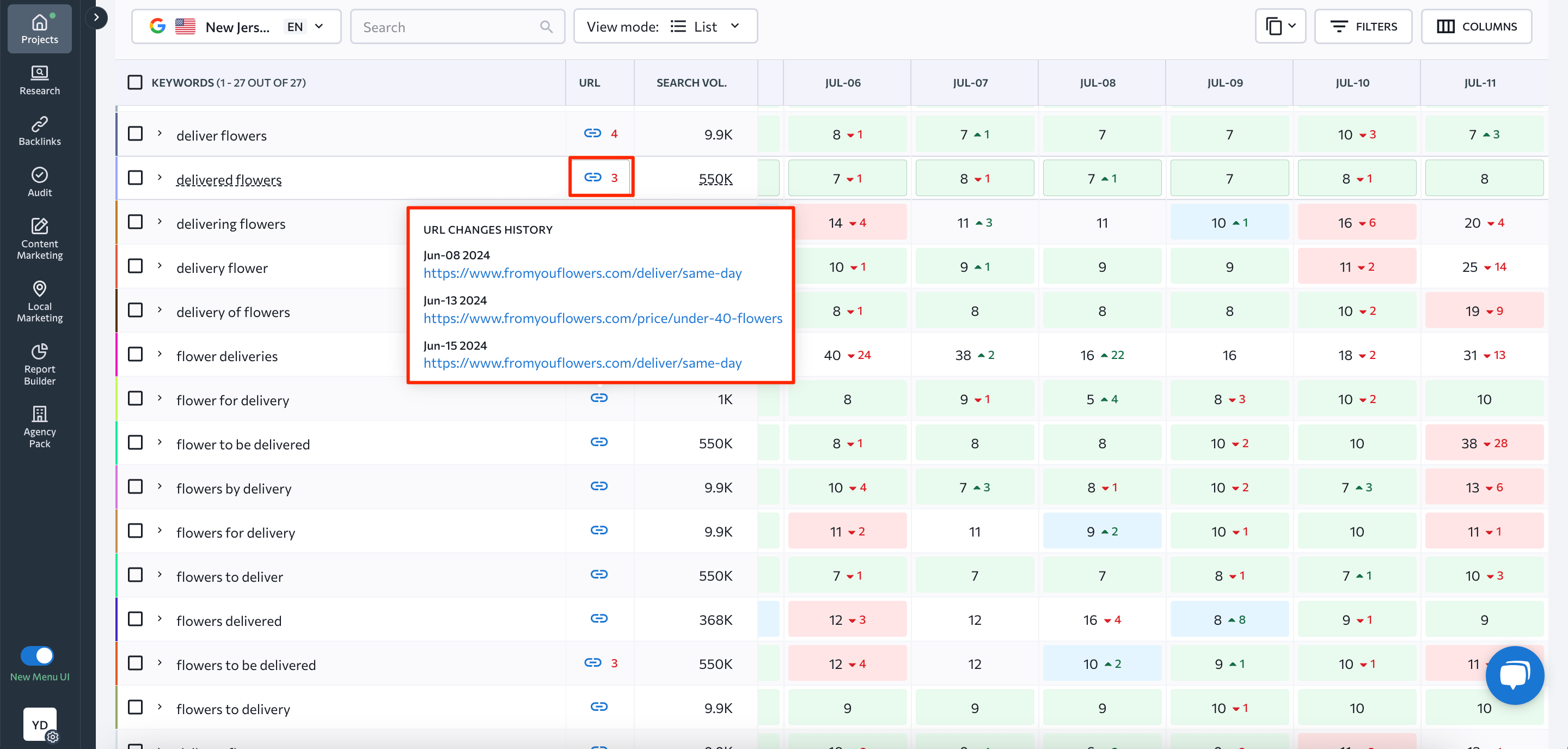
- The number on the right represents how many pages are competing for the particular keyword.
- A blue icon indicates that the URL was successfully found on SERP for a given keyword.
- A gray icon indicates that the URL wasn’t found on SERP for a given keyword.
- A red icon indicates a mismatch between the website’s actual URL and the target URL you set for the keyword.
Why are canonical tags important for SEO?
Canonical tags offer several key benefits for SEO. Here’s a closer look at how they can improve your website’s performance:
Save crawl budget
Search engines have a limited budget for crawling and indexing websites. If you have multiple versions of the same content on different URLs, search engines may waste resources indexing all of them. Canonical tags help you avoid this by specifying the preferred version so that search engines can focus on crawling and indexing the most valuable pages.
Prevent duplicate content issues
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and make it difficult for them to determine which version of your content to rank. This can lead to lower rankings and missed traffic opportunities. By using canonical tags, you can clearly tell search engines which page is the original and most valuable.
Fixing duplicate content isn’t just about using canonical tags—it’s also about making your content clear. Using heading tags the right way helps Google understand which page is most important. Check out our guide to HTML heading tags to make sure your content and SEO work together.
Improve search rankings by consolidating link equity
Links from other websites are a major ranking factor for search engines. When you have multiple pages with similar content, the link equity (ranking power) from those links gets divided. Canonical tags allow you to consolidate this link equity to the preferred URL, which can potentially lead to higher rankings in SERPs.
Avoid penalties associated with duplicate content
In some cases, search engines may penalize websites with a significant amount of duplicate content. By properly implementing canonical tags, you can avoid these penalties and ensure your website remains in good standing with search engines.
When should we use the canonical tag for SEO purposes?
Canonicalization maximizes website performance and can assist you in avoiding duplicate content issues that negatively impact SEO. Following the recommendations provided in this section can help Google index your content in the right way.
Faceted navigation
While faceted navigation (product sorting and filtering based on various attributes) brings lots of benefits to the table in terms of user experience, it might be a considerable issue for SEO.
Let’s say your potential client wants to buy black jeans size 10. All they need to do is filter your catalog by these attributes, and within several clicks, they can find clothing items of their interest.
Here’s how the link for this product might look:
https://yourwebsite.com/women-jeans/black/size=10
Yet, if they selected a size filtering first and then the color, the URL for the same item would look like this:
https://yourwebsite.com/women-jeans/size=10/black
The same applies to sorting options available within a website.
To better understand the connection between canonical tags and URLs with different sorting options, let’s take the laptop category on eBay as an example, which contains laptops for work and is optimized for this keyword cluster: https://www.ebay.com/b/Workstation-Laptops-Netbooks/175672/bn_7116632031?_dmd=2&mag=1&rt=nc
The canonical tag for this page looks like this:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.ebay.com/b/Workstation-Laptops-Netbooks/175672/bn_7116632031" />
As you can see, the page is referencing itself.
The navigational features this page offers include:
- Best match (time/price/shipping/distance)
- View type (gallery/list)
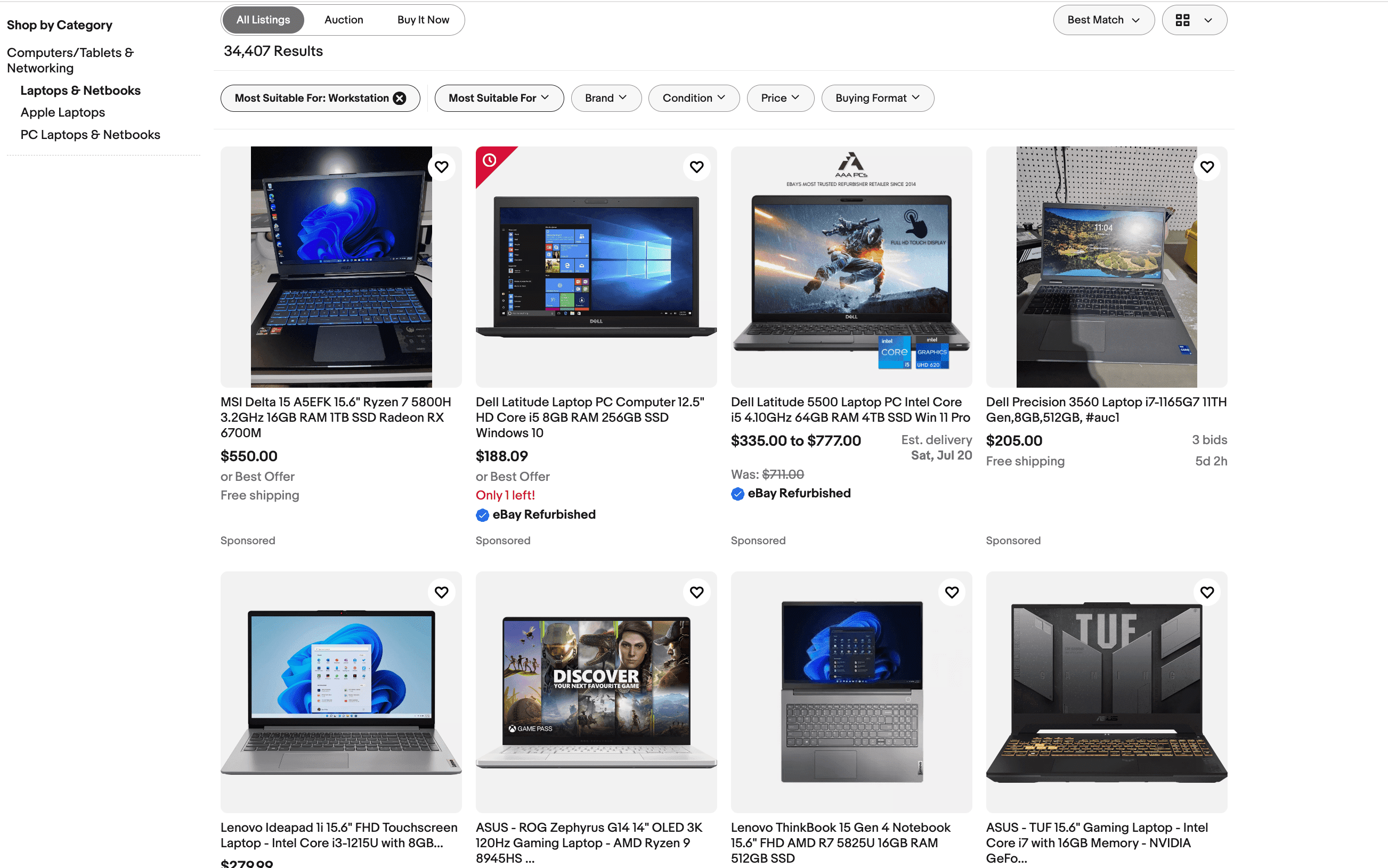
Let’s change the view type. The products should now be shown in a list format, and the URL changes to https://www.ebay.com/b/Workstation-Laptops-Netbooks/175672/bn_7116632031?rt=nc&_dmd=1.
Notice how URL parameters appear at the end of the link. These parameters are used to perform sorting options and other operations.
Now, you can only imagine how many different URL variations (parameterized URLs) can be created for the same product. From a search engine’s point of view, all variations with a new parameter are unique pages.
Some SEOs use the noindex tag or robots.txt directives to address this issue although using a canonical tag is most often a better choice. Why? Because it allows you to:
- Retain link equity and page authority. At the same time, noindex and robots.txt prohibit indexing altogether, which discards any accumulated link equity or authority associated with those pages.
- Preserve page discoverability, as even non-canonical pages can still be discovered through internal links and sitemaps.
- Utilize the crawling budget efficiently. Robots.txt, in contrast, might block crawling and negatively affect the discovery of valuable content.
The same items under different categories
Some websites, especially those used for ecommerce purposes, might offer the same products but under different categories. For instance, if you sell Christmas sweaters for women, these products might be placed under two website categories: women’s clothing and winter collection. As a result, the same sweater will be accessible from two different URLs like:
https://www.yourwebsite.com/women-clothing/your-product/
https://www.yourwebsite.com/winter-collection/your-product/
While we can see that it’s the same product, Google is likely to consider these URLs as two individual pages with duplicate content.
Using the canonical tag, you can tell search bots which of these product pages is the “official” one and avoid duplicate issues.
Avoid duplicating URLs whenever possible. From an SEO perspective, it is more effective to link categories directly to the main version of the product as opposed to using canonical tags. This both prevents you from having redirects and optimizes search engine indexing.
UTM tags and tracking parameters
When utilizing UTM tags and tracking parameters, it’s important to be aware that this can create URLs that search engines may misinterpret as duplicate content. To counter this, apply canonical tags to your preferred version of the content, which should not include any UTM tags or tracking parameters. By doing so, you can ensure that your website is indexed correctly.
For example, a URL like https://site.com/page/ may have a version with parameters like https://site.com/page/?fbclid=IwAR3cnDV4ERw24pQNVLTFlwKzchPDA1. A similar link can also be generated in the case of a redirect from Facebook. Canonical would be a great solution in this scenario.
Pagination canonicalization
Choosing the most suitable approach to adding a canonical tag to your paginated pages can be a complicated task, as opinions on the best method vary greatly.
Option 1: You can take the traditional route and apply self-referencing canonical tags on all pagination pages, which is what Google recommends. This ensures that each page in the series contains a canonical tag that directs back to itself, like in the example below:
https://site.com/catalog/page/2/ contains <link rel="canonical" href="https://site.com/catalog/page/2/" />.
This canonicalization approach is generally considered safe because it enables web crawlers to reach all pages in the pagination set and correctly index the content. Additionally, by using canonical tags on all pagination pages, you can consolidate link equity across all pages in the series.
Option 2: If you’d prefer to inhibit the indexation of paginated pages, it’s not recommended to use canonicals because search engines may not respond to your directives. It’s better to use <meta name=“robots” content=“noindex, follow” /> tag instead. This will enable search engines to crawl and follow links on your website but prevent the indexing of any paginated sections.
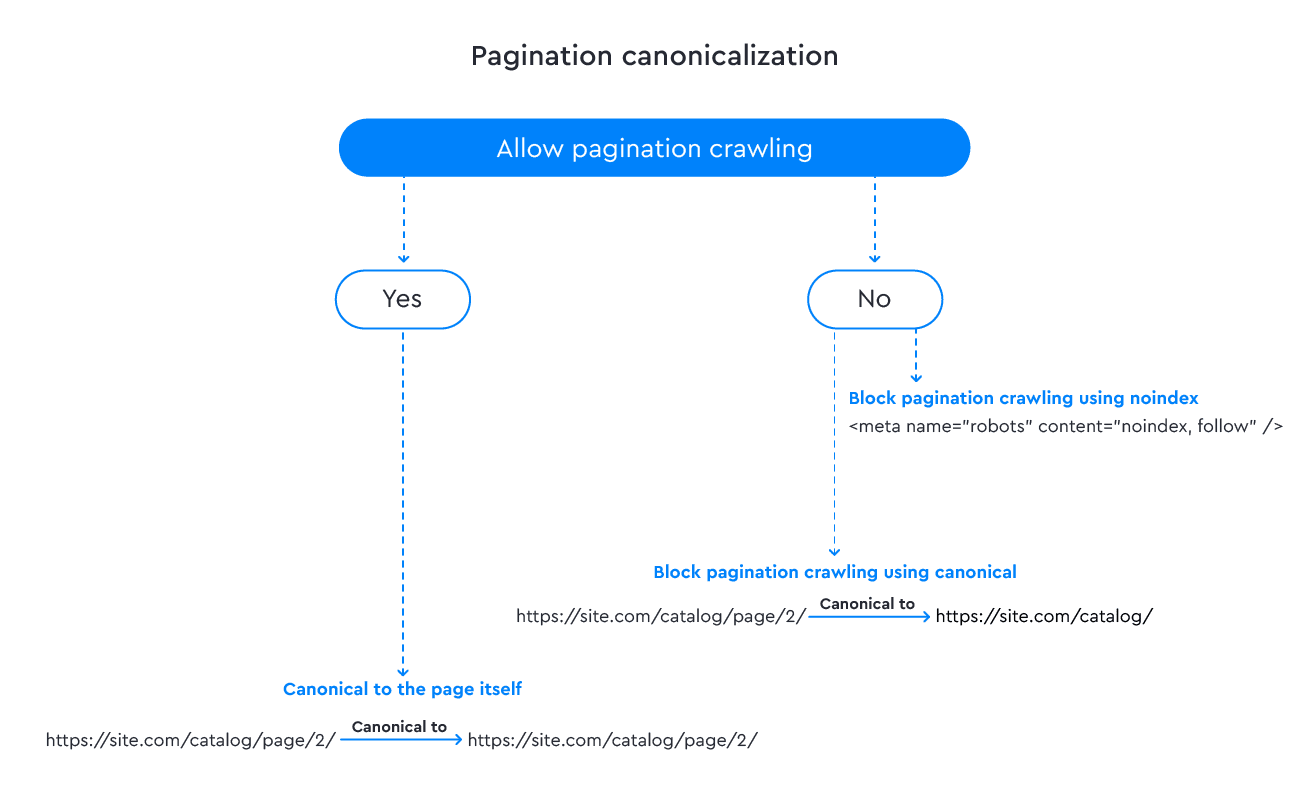
No matter which solution you go with, it is crucial to ensure that the paginated pages are linked properly to their corresponding main content, and that canonical tags are configured correctly to avoid any potential duplicate content issues.
The last word on canonical tags
Correctly using canonical tags is fundamental to SEO because it prevents duplicate pages and indexing issues from happening. If it’s set incorrectly, however, canonicalization may not bring the desired result and can even lead to lower rankings due to duplicate content. Explore the most common canonical tag issues and discover proven tips to fix them quickly and easily in this guide.
Follow best practices from this complete guide on canonical tags, but always evaluate each situation individually.

