How to optimize for ChatGPT: LLMs.txt doesn’t matter but brand mentions on Quora and Reddit do
When it comes to ChatGPT citations, the internet is full of bold claims. Some swear by LLMs.txt, others by domain authority, recency of content, and even structured metadata like schema markup. But which of these actually matter?
To separate facts from speculation, we ran a new research study analyzing 129,000 unique domains and 216,524 pages across 20 niches to identify citation patterns in ChatGPT’s AI responses.
Understanding the rules of AI citations, however, is one thing. Seeing how you’re doing under those rules is another. That’s where the ChatGPT Visibility Tracker comes in. It gives you a direct view into how ChatGPT treats your brand by allowing you to:
- Check how ChatGPT answers your target queries
- Monitor when and where your brand appears in ChatGPT responses
- Compare your brand’s presence to your competitors’
- Track your ChatGPT visibility changes over time
By combining ChatGPT research insights with ongoing visibility tracking, you’re not just learning why citations happen. You’re gaining the ability to observe, evaluate, and improve your presence in ChatGPT over time.
With that context in place, let’s look at what the data reveals about the signals that actually influence ChatGPT citations.
-
Strengthen your overall domain authority.
Sites with over 32K referring domains are 3.5x more likely to be cited by ChatGPT than those with up to 200 referring domains. This pattern also holds for Domain Trust (DT): high-trust domains (DT > 90) earn almost 4x more citations than low-trust sites (DT < 43).
-
Grow your visibility in traditional Google search (traffic + average ranking position).
Sites with over 190K monthly visitors receive nearly twice as many ChatGPT citations as domains with lower traffic (let’s say 20 or 20K visitors). Similarly, pages with average ranking position from 1 to 45 get around 60% more citations than pages ranked 64–75.
-
Ensure your homepage attracts high organic traffic.
It’s not traffic to random pages that matters: global traffic to the homepage drives the highest citations. Sites with at least 7.9K organic visitors to their main page have about twice the chance of being cited compared with sites receiving up to 400 visitors.
-
Build your presence on Quora and Reddit.
Domains with millions of brand mentions on Quora and Reddit have roughly 4x higher chances of being cited than those with minimal activity. For smaller, less-established websites, engaging on Quora and Reddit offers a way to build authority and earn trust from ChatGPT, similar to what larger domains achieve through backlinks and high traffic.
-
Produce comprehensive, in-depth content (at least 1,900 words for most topics).
Articles over 2,900 words average 5.1 citations, while those under 800 get 3.2. For smaller domains, content length has roughly 65% more impact on ChatGPT citations than it does for top domains.
-
Structure your content for readability and clarity.
Organize your content into sections of 120–180 words between headings. Pages with this structure receive, on average, 70% more ChatGPT citations than pages with sections under 50 words.
-
Keep your content fresh with regular updates.
Content updated in the past three months averages 6 citations versus 3.6 for outdated pages. So, by refreshing existing articles quarterly with new statistics, examples, or sections, you can nearly double your chances of being cited by ChatGPT.
-
Integrate question-based titles and H1s within your content.
This is especially important for smaller domains, where question-based titles have almost 7x more impact on citations compared to top domains. Plus, the presence of FAQ sections within the main content nearly doubles your chances of being cited by ChatGPT.
-
Yet, treat FAQ schema markup as optional, not essential.
Our data shows pages with FAQ schema average 3.6 citations, while those without reach 4.2. This means that schema alone does not significantly increase ChatGPT citation likelihood.
-
Use URLs and titles that convey the overall topic (rather than narrowly targeting a single keyword).
Broad titles and URLs that simply describe the main topic receive over 2x citations on average, compared to highly keyword-optimized ones. This shows that clarity and topic alignment matter more to AI models than strict keyword optimization.
-
Claim and maintain profiles on review platforms.
Domains with profiles on platforms like Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, Sitejabber, and Yelp have 3x higher chances to be chosen by ChatGPT as a source, compared to sites without such presence.
-
Optimize Core Web Vitals: INP, FCP, LCP, and Speed Index.
For example, pages with FCP under 0.4 seconds average 6.7 citations, while slower pages (over 1.13 seconds) drop to just 2.1. This means that fast-loading pages are 3 times more likely to be cited by ChatGPT compared to slower ones.
-
Don’t rely solely on LLMs.txt files.
Including LLMs.txt has shown negligible impact on ChatGPT citation likelihood. Our analysis even suggests that removing it improved predictive accuracy, so it shouldn’t be a focus for AI visibility.
Top 20 factors affecting ChatGPT citations
In our study of what drives ChatGPT to cite a website, we found a range of factors that impact citation likelihood (some familiar from SEO, others unique to AI systems).
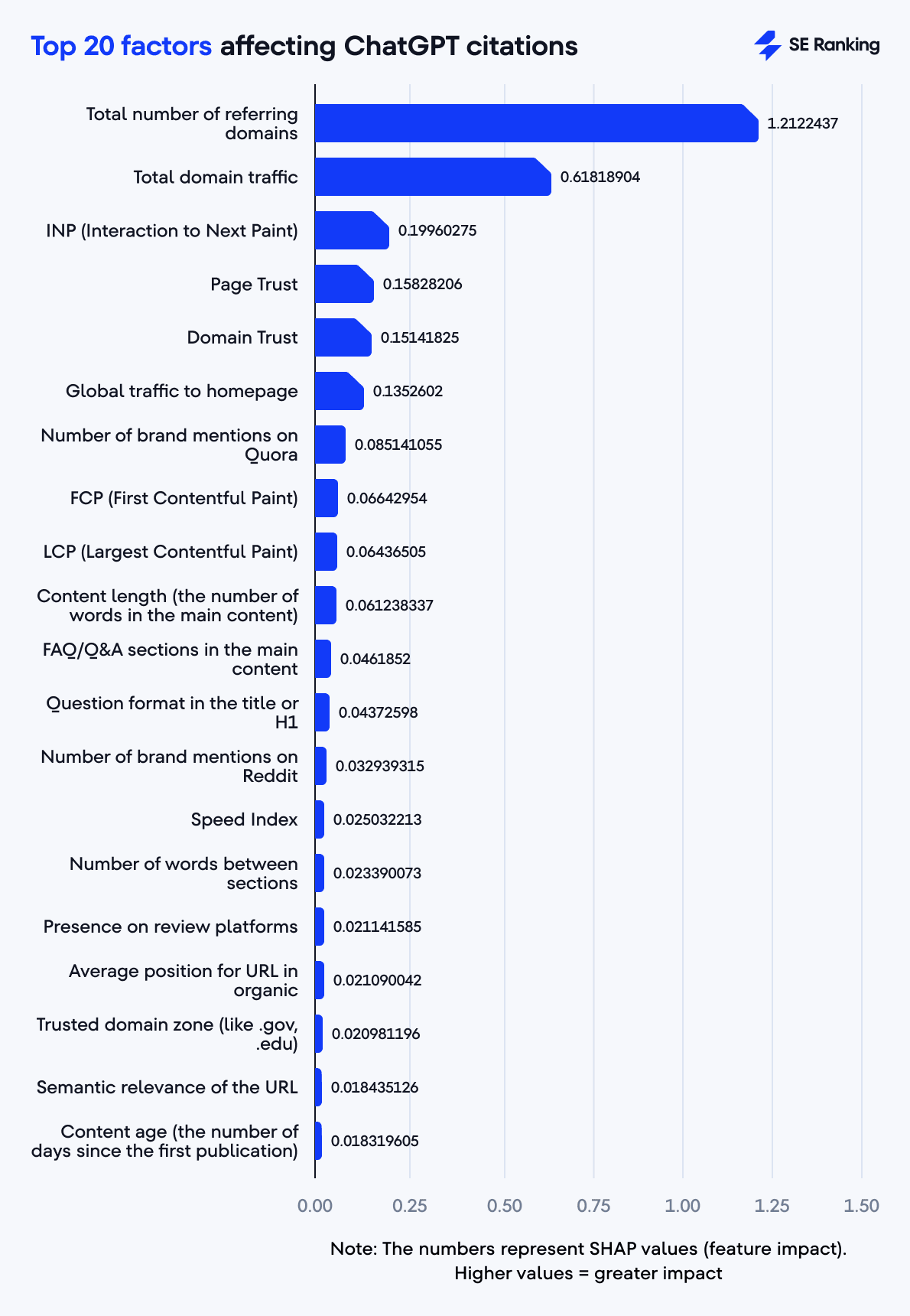
At the top of the list is the number of referring domains. The more diverse websites link to your content, the more likely ChatGPT is to treat it as credible. Right behind that is domain traffic: high visitor numbers signal authority, credibility, and broad relevance.
But authority isn’t just about links and visitors. Page and Domain Trust scores play a critical role by showing how reliable and reputable your site appears.
Technical performance also makes a difference. Pages that load quickly (as measured by INP, FCP, and LCP) are more likely to get attention.
Content structure and depth are equally important. Longer articles, FAQ or Q&A sections, and question-based titles and headers all correlate with higher citation likelihood. And while brand-new content isn’t always favored, keeping content fresh and regularly updated helps maintain relevance over time.
Even social signals matter. Sites that are actively mentioned or discussed on platforms like Quora and Reddit enjoy a higher chance of being cited on ChatGPT.
Taken together, these factors show that ChatGPT citations rely on a combination of technical optimization, authoritative content, social proof, and user-friendly experience.
Key tactics to improve your ChatGPT visibility
Now, let’s break down these ranking factors into actionable strategies so you can improve your chances of being cited by AI systems like ChatGPT.
Disclaimer: This research shows that multiple variables impact ChatGPT citations, yet their effects are interdependent. Over-optimizing one factor while ignoring others reduces overall effectiveness in optimization for ChatGPT. An effective strategy requires a balanced approach across authority, content quality, technical performance, and data structuring.
Boost your website’s authority
According to our analysis, building authority is key to getting cited by ChatGPT. Among all factors, backlinks remain the strongest signal of trust and credibility.
Specifically, sites with a higher number of referring domains consistently outperform weaker link profiles (and often by several multiples).
- Websites with up to 2,500 referring domains receive an average of 1.6-1.8 citations.
- Those with over 350,000 referring domains receive 8.4 citations on average.
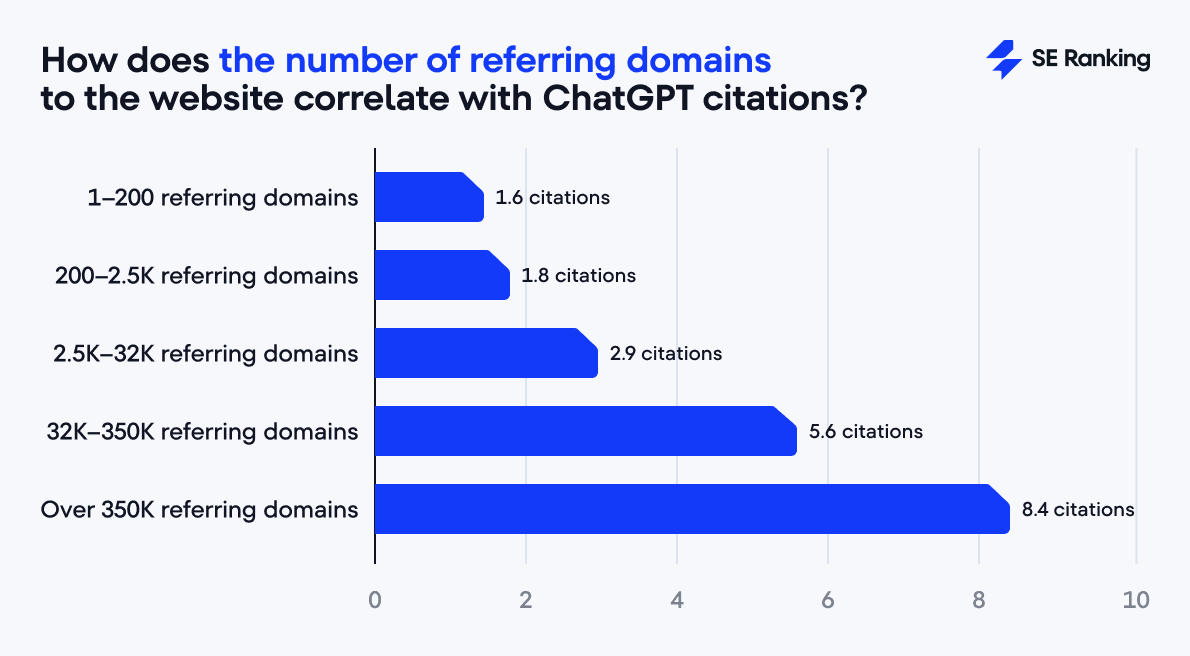
The biggest growth spike occurs when crossing the 32,000-link mark, where citations nearly double from 2.9 to 5.6. This clearly demonstrates that link authority compounds. Once a site reaches a critical number of backlinks, its perceived trustworthiness rises exponentially.
At the same time, our research shows that linking out from your website to other high-authority sites appears to have minimal effect. Whether you link to domains with Trust 70 or 100, the influence is almost zero compared to incoming backlinks.
This follows the same basic rule we’ve always seen in SEO: backlinks build trust. And ChatGPT seems to look at the variety of backlinks as signs that many people find a source reliable.
All of this ties directly into Domain Trust and Page Trust. Basically, the more high-quality backlinks your site has, the more “trust” it builds (both for the domain as a whole and for individual pages). So, strengthening these trust signals is another key step toward getting more AI citations.
- Domain trust
The trustworthiness of your domain has a major impact on citation growth. Sites with a Domain Trust below 43 struggle to gain traction, averaging only 1.6 citations. However, once your site’s DT hits 77, you begin to see noticeable benefits. The real acceleration happens once you cross 90, where citation growth becomes exponential and much more rapid.

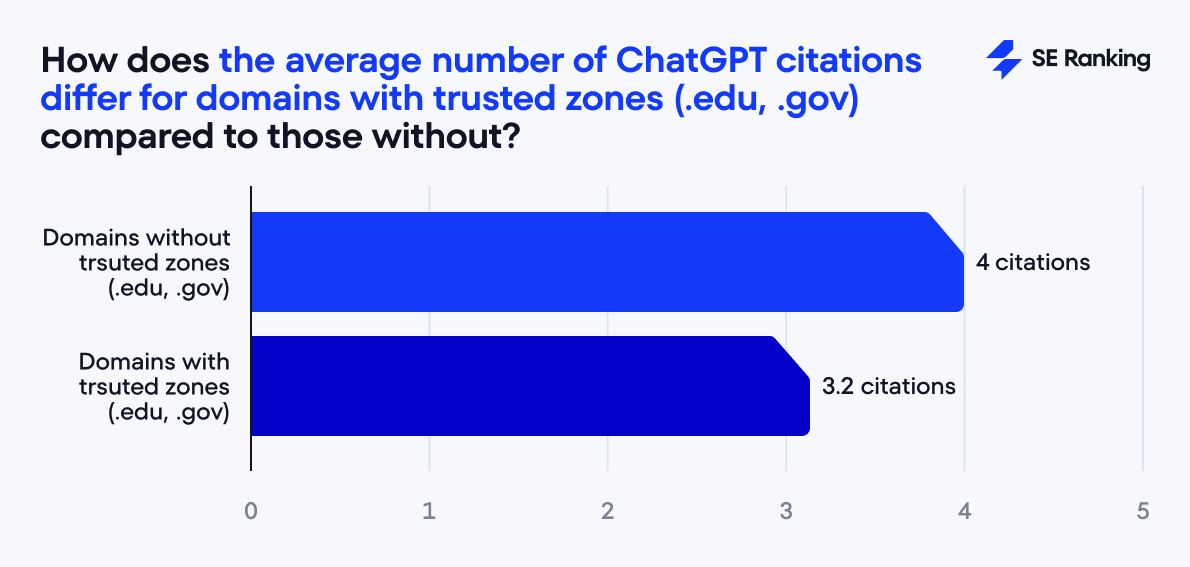
However, being in a “trusted” domain zone doesn’t automatically guarantee higher citations. For example, while one might expect domains ending in .gov or .edu to outperform others, our analysis shows they average around 3.2 citations (even lower than the 4 citations seen for sites outside these zones). So, what ultimately matters is not the domain name itself, but the quality of the content and the value it provides.
- Page trust
Similarly, trust at the page level is crucial. URLs with a Page Trust score above 23 start to see tangible results, and those that reach 28 or higher consistently average 8.2 citations.
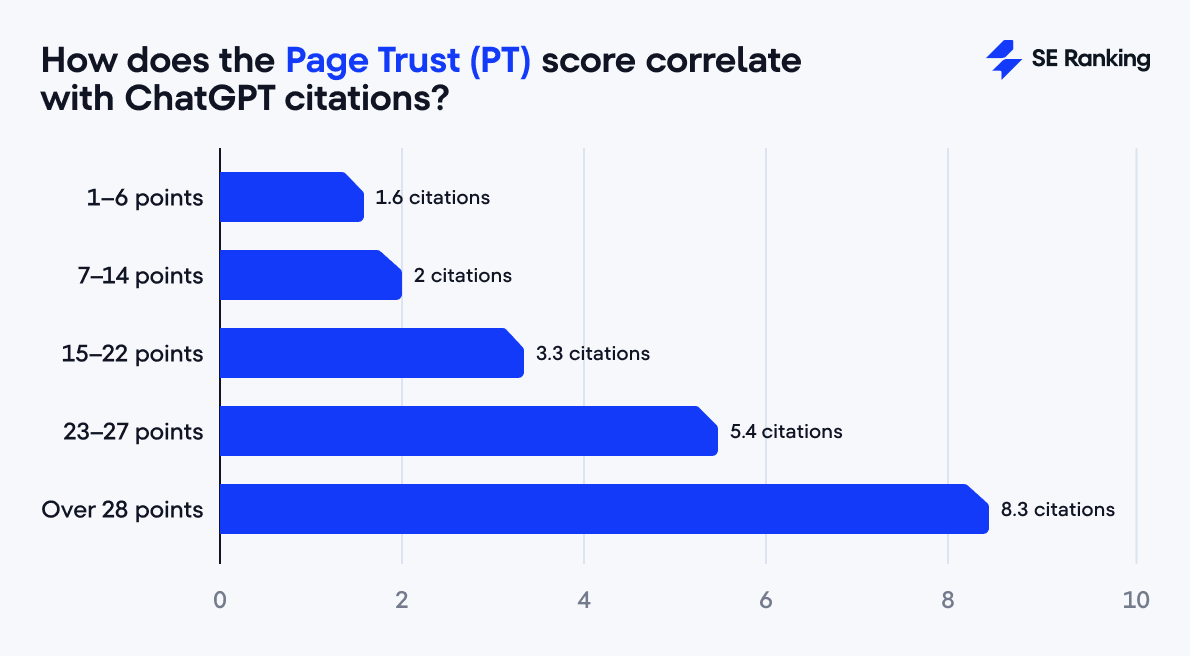
While a higher Page Trust score can boost a page’s chances of being cited by ChatGPT, it doesn’t have to be as high as the Domain Trust score. Surprisingly, any page with a score of 28 or above tends to get cited at about the same rate. This shows that ChatGPT is more interested in the overall authority of a domain than in the trustworthiness of individual pages.
Grow your overall visibility in Google
Beyond traditional authority factors, a site’s overall visibility on Google (measured by traffic and average ranking) also significantly affects its chances of being cited by ChatGPT.
To begin with, domain traffic ranks as the second most important factor for ChatGPT citation, but it remains less influential than backlinks.
- Sites under 190,000 monthly visitors average 2-2.9 citations.
- Only after passing 190,000 visitors does a notable correlation appear.
- Domains with 10M+ visitors average 8.5 citations.
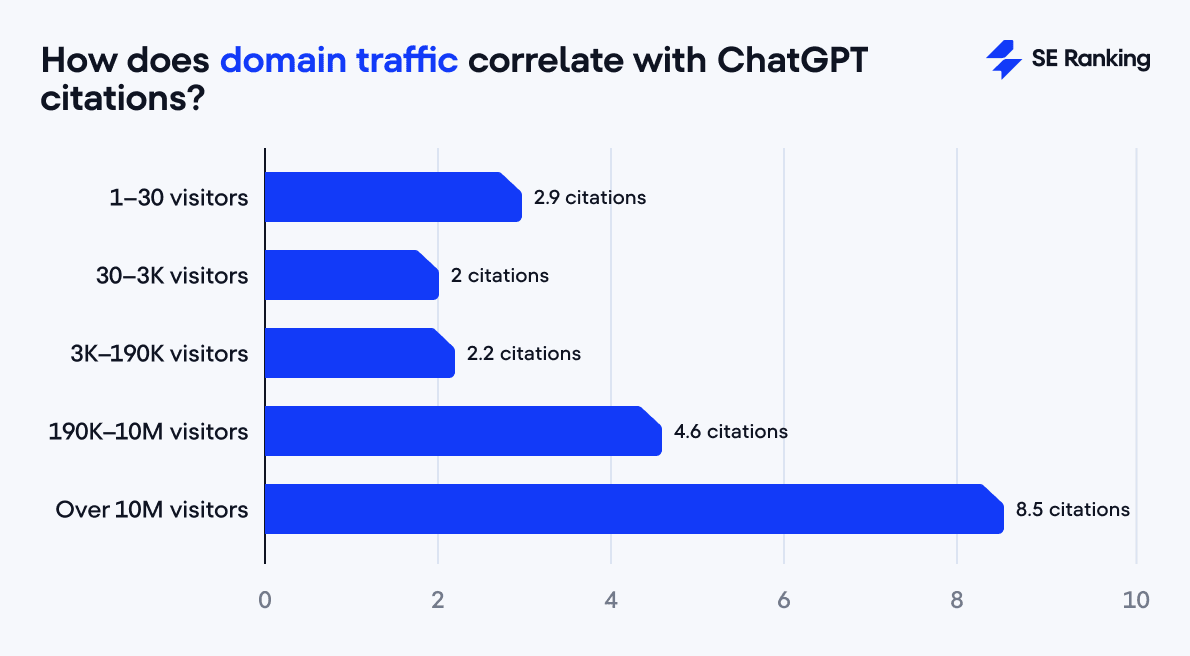
This pattern suggests that LLMs like ChatGPT seem to care less about popularity until it becomes undeniable.
Low- to medium-traffic websites don’t gain much advantage in ChatGPT citations. For example, a site receiving 20 organic visitors and another receiving 20,000 visitors tend to receive roughly the same “score” from ChatGPT. In such cases, other factors (like content quality, relevance, and authority, etc.) likely outweigh raw traffic numbers, so even smaller websites have a chance of being cited by ChatGPT.
And once a site achieves mass exposure, the likelihood of appearing in ChatGPT responses increases significantly.
But, it’s not just about attracting traffic to random pages of your website. Our analysis shows that it’s the global traffic to the main page that matters. And websites with at least 7,900 organic visitors to their main page have the highest chances of being cited by ChatGPT.
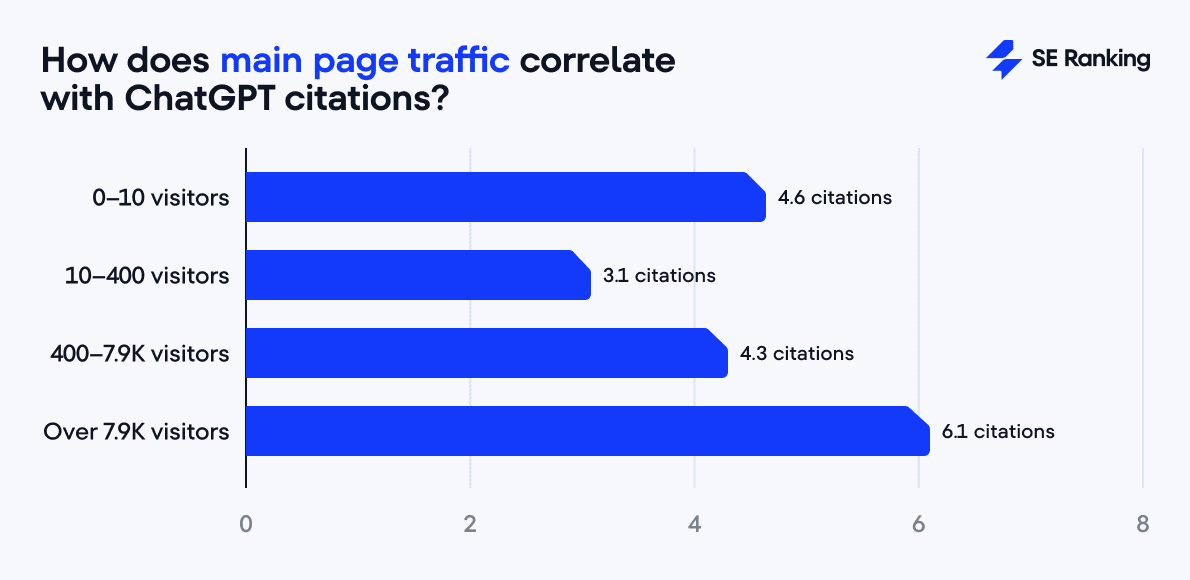
Still, getting lots of visitors is one thing, but does an average ranking position on Google affect how likely ChatGPT is to cite your page? Our analysis clearly shows that it does:
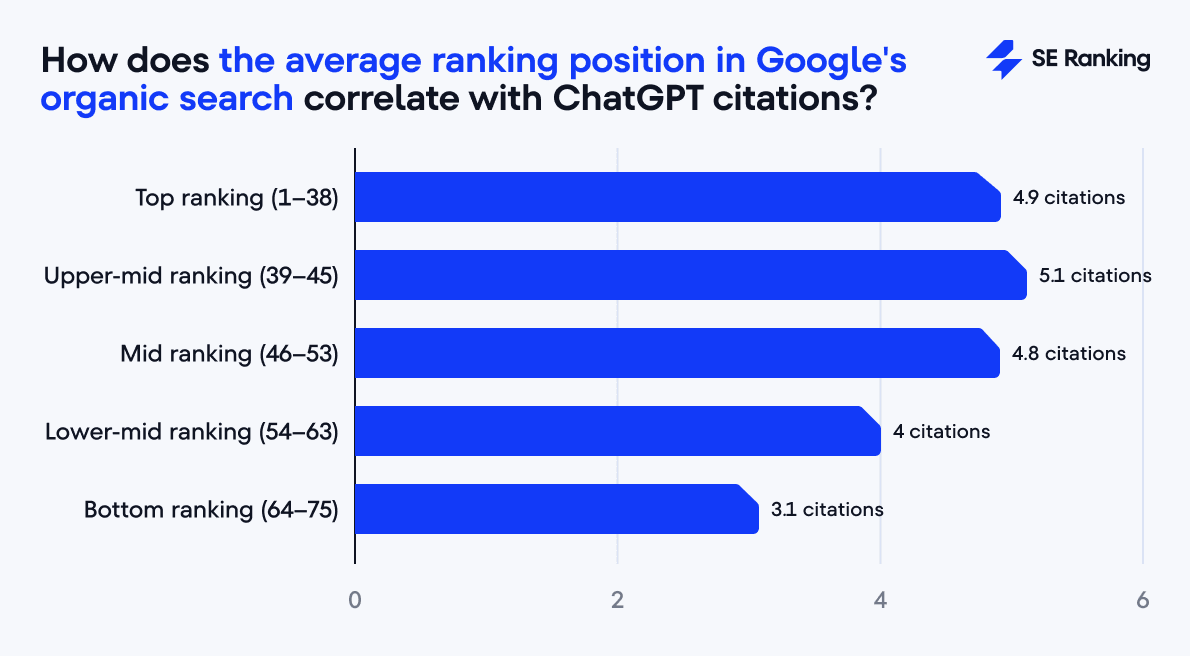
As you can see, the average position of a URL in Google’s organic search correlates with ChatGPT citations: pages with an average ranking between 1 and 45 receive 5 citations on average, while those with the ranking position 64 and 75 see only 3.1 citations.
While this doesn’t prove that ChatGPT relies on Google’s index, it suggests both systems evaluate authority and content quality similarly.
So, it makes sense to:
- Optimize your content for organic performance as well.
- Invest in technical SEO, link building, and high-quality writing.
- Treat Google rankings as a proxy for LLM visibility.
Produce comprehensive, in-depth content
Length and depth also directly correlate with higher ChatGPT citations.
- Short articles (under 800 words) average 3.2 citations,
- While long-form pieces (over 2,900 words) earn 5.1 citations.
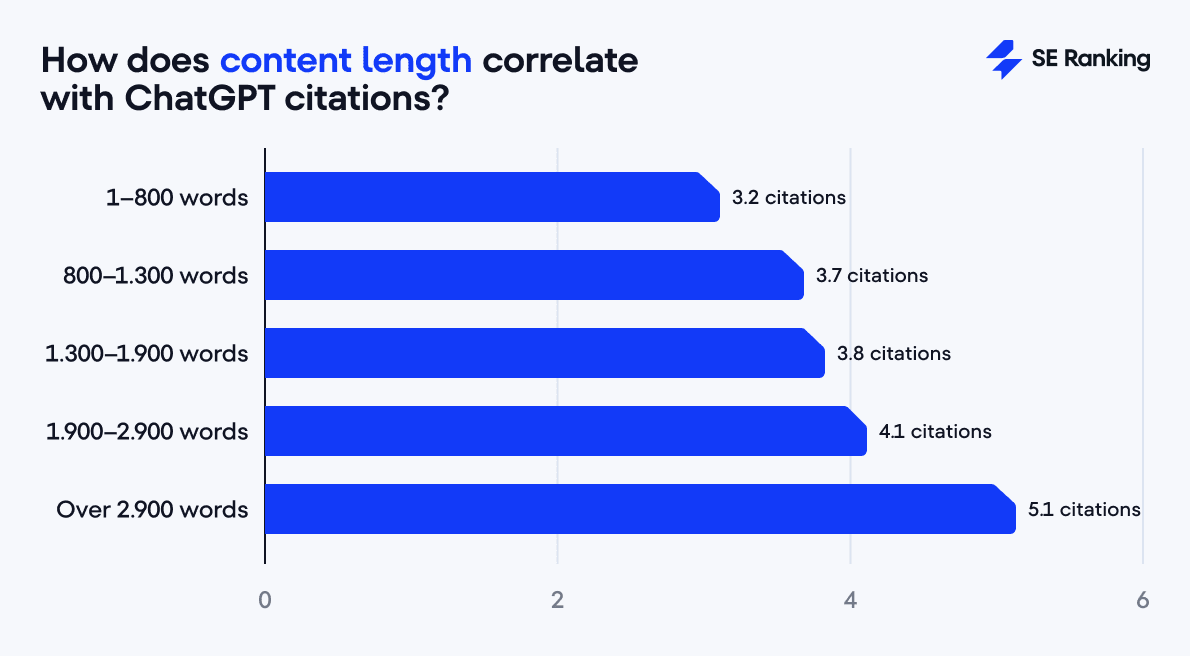
Still, the key isn’t length for its own sake, but it’s depth. ChatGPT favors pages that capture a topic’s full context, nuances, and subtopics.
To apply this:
- Aim for at least 1,900 words for most topics. Where necessary, increase the word count to at least 2,900 words.
- Cover related concepts, synonyms, and examples to enhance semantic variety.
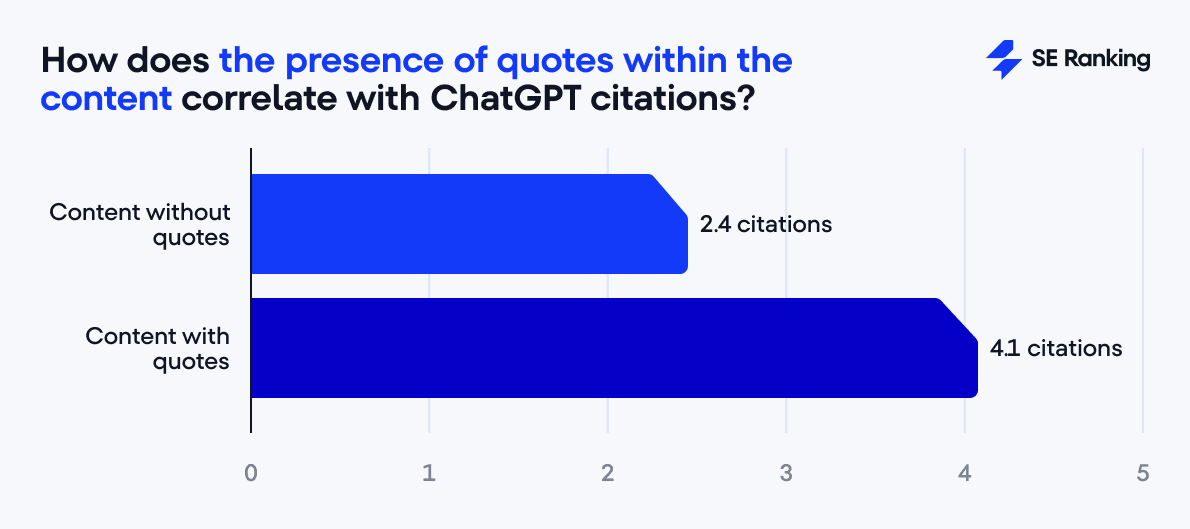
- Include supporting data, such as experts’ quotes and statistics.
In fact, our analysis shows that pages with expert quotes average 4.1 citations versus 2.4 without.
Those rich in statistics (19+ data points) average 5.4 citations, compared to 2.8 for minimal data.
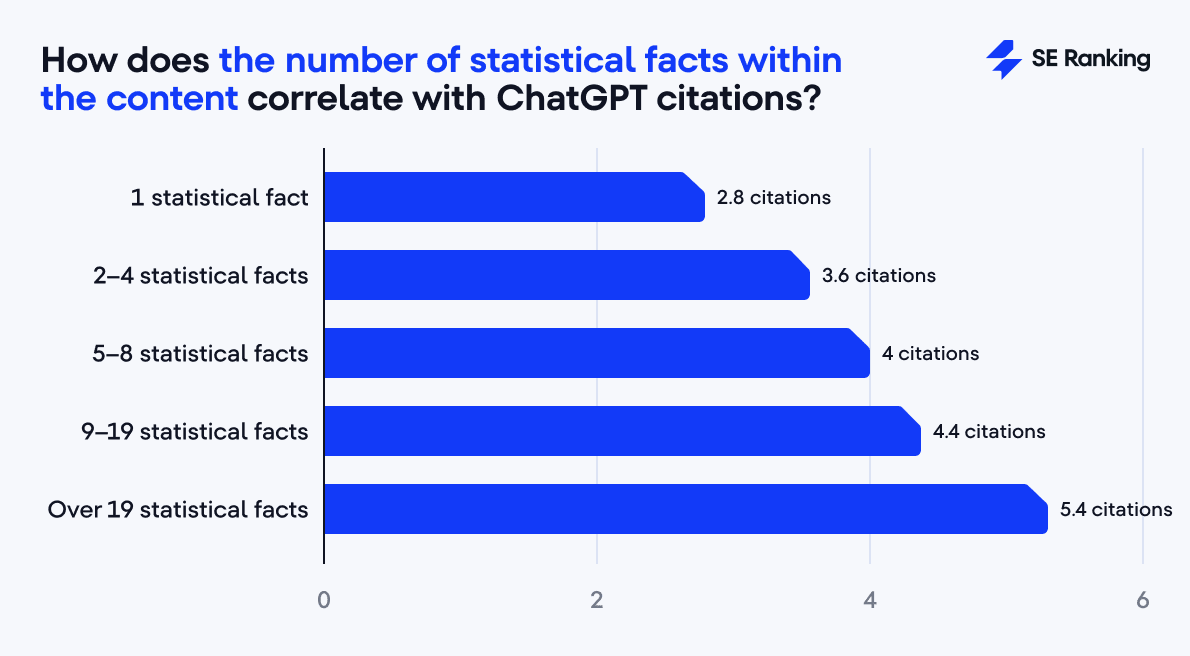
However, the impact of these factors is relatively minor compared to others, and they should be viewed as supporting indicators of high-quality content.
So, use data and quotes not as gimmicks, but as evidence of depth and professionalism.
Structure content for topical clarity
Even the best content can underperform if it’s structurally opaque. ChatGPT performs better with content that’s clearly segmented and logically layered.
Pages with an average section length of 120–180 words (words between headings) perform best, with 4.6 citations on average. Extremely short sections (under 50 words) usually result in 2.7 citations.
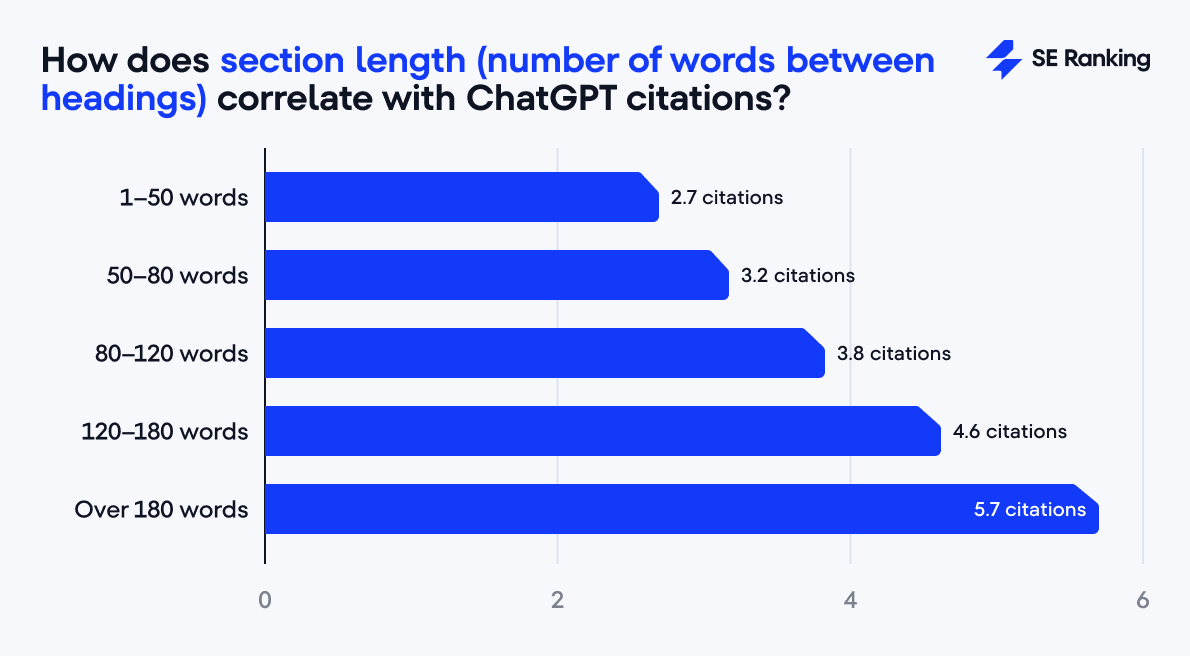
Interestingly, articles with long sections (over 180 words) perform slightly better (5.7 citations), but this likely correlates with comprehensive coverage rather than readability itself.
So, to make your structure work for you:
- Use subheadings to guide topic flow and clarify relationships.
- Break content into sections of 120–180 words.
- Maintain hierarchy (H2 for themes, H3 for specifics, bullets for clarity).
And keep in mind that structured clarity helps LLMs interpret your content better.
Embed FAQ sections and question-styled headings within your content
Many in the industry believe that including FAQ-like sections in your content helps ChatGPT find direct answers and increases your chances of being featured in AI responses.
To test this, we analyzed the text for patterns that indicate these sections. Examples include headings such as “FAQ,” “Frequently Asked Questions,” “Q&A,” “Questions and Answers,” “Common Questions,” and “Popular Questions.”
In addition to FAQs, we also looked at pages with question-style titles or headings. These pages often contain clear, concise answers that both users and AI are looking for, which could provide an advantage. For this analysis, we examined both the title and H1 headings.
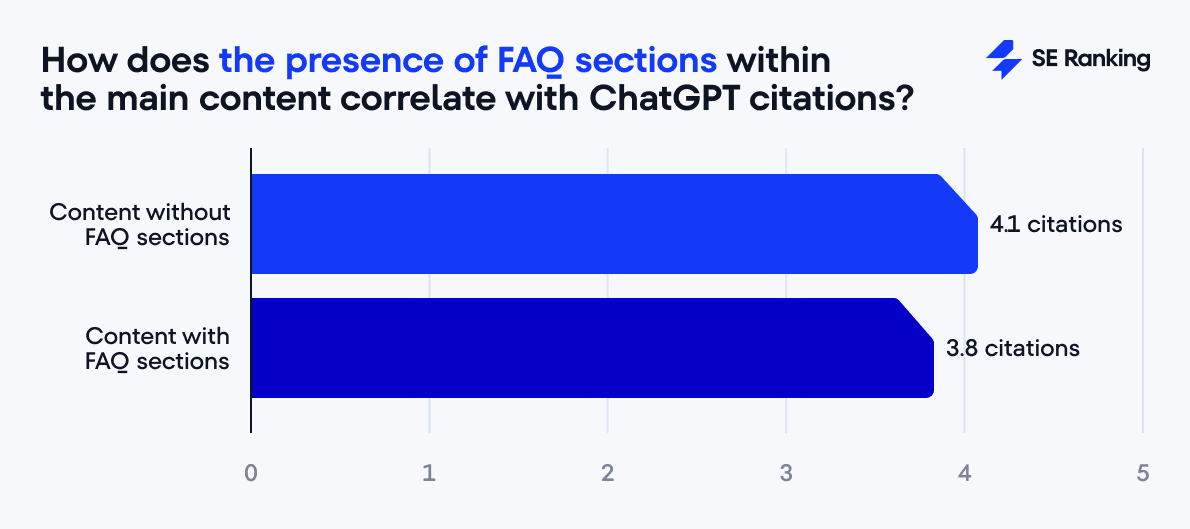
And at first glance, pages with FAQs and question-based titles seem to perform worse.
FAQ pages average 3.8 citations, compared to 4.1 for those without.
Question-style headings show 3.4 citations versus 4.3 for straightforward headings.
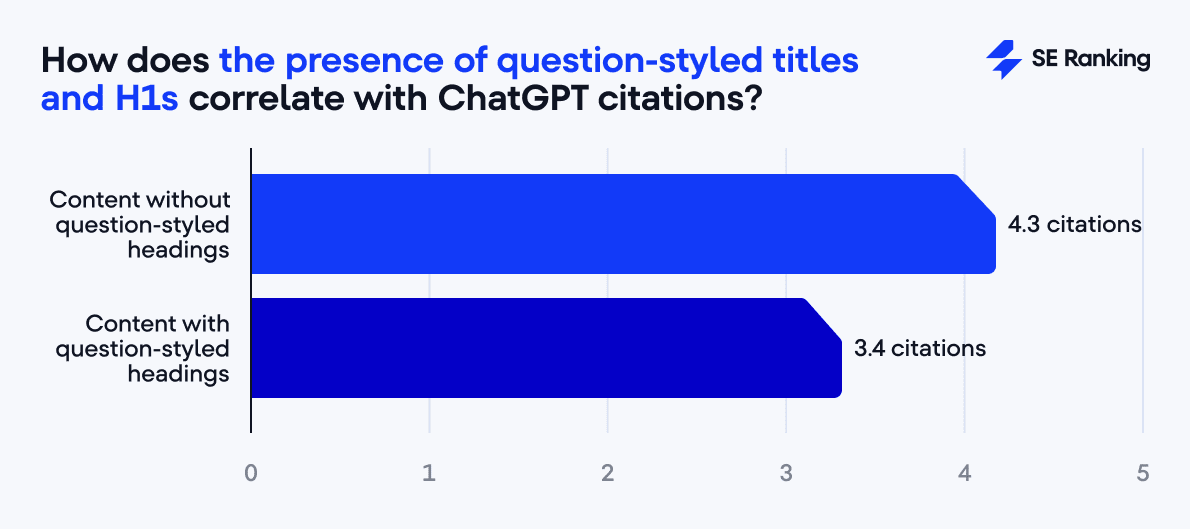
But the deeper insight is that, according to SHAP values, the model views the absence of FAQ sections as a negative signal. This means these formats aren’t inherently bad. They’re just context-dependent. FAQ sections often appear on smaller or simpler pages (like support docs or product info pages), which naturally earn fewer citations overall.
Still, adding a FAQ section alone won’t dramatically increase citations. Its true benefit comes when other factors (high-quality content, strong authority, and structure) are already optimized. This is when a FAQ section provides an extra boost in citations.
So rather than avoiding FAQ sections, make sure to:
- Focus first on creating high-quality, well-structured content.
- Build strong authority and credibility for your site.
- Add “FAQ” or “Common Questions” sections at the end of major articles.
- Use question-style subheadings naturally within the text.
- Keep answers concise, factual, and contextually rich.
Keep content fresh and regularly updated
Content freshness isn’t about being new. It’s about staying relevant.
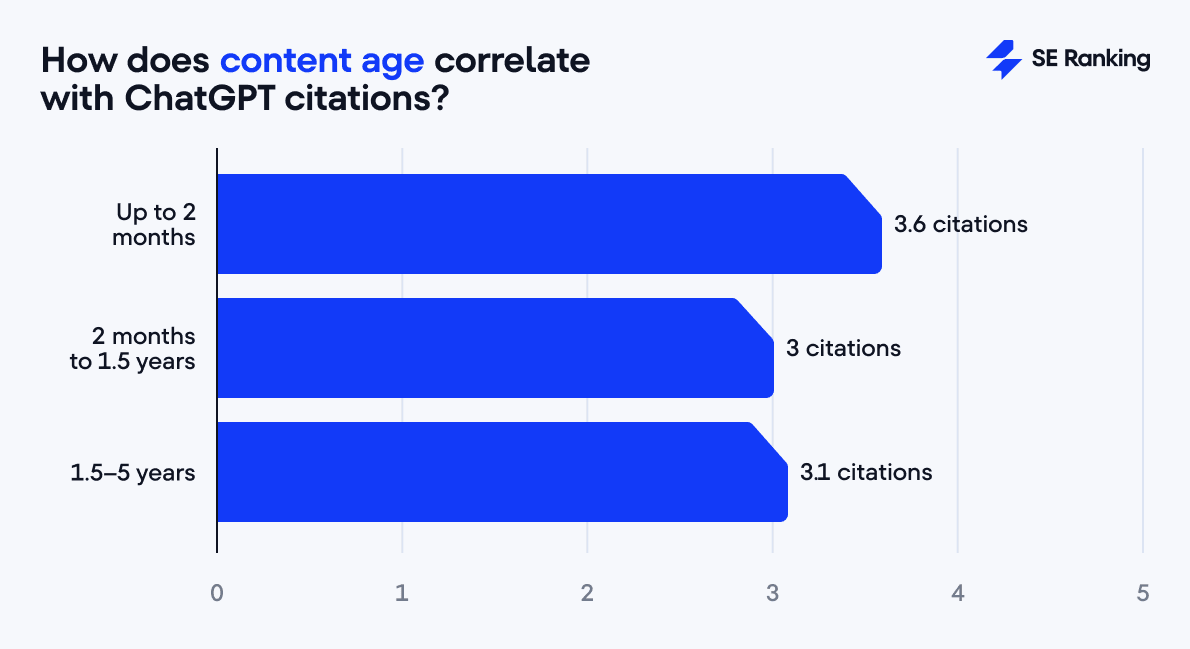
Our data shows that brand-new content performs only slightly better than older material.
- Very new content (up to 2 months old) averages 3.6 citations,
- While content aged 1.5–5 years performs similarly at 3.1 citations.
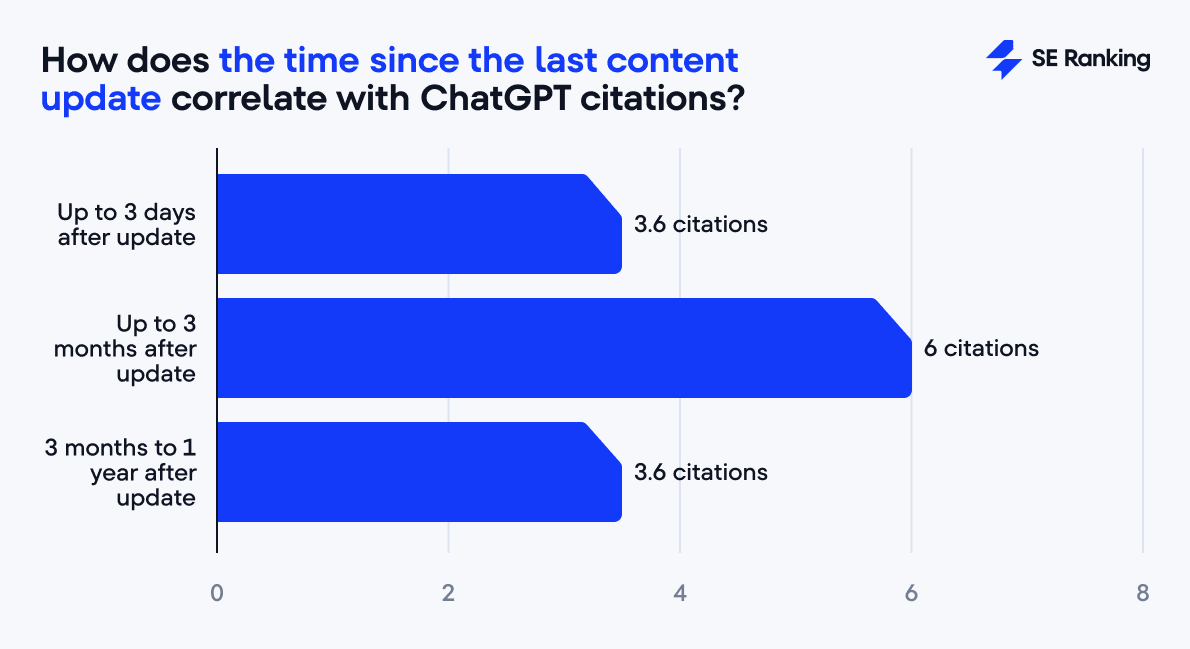
But content updated within the past three months averages nearly double the citations (6.0 vs. 3.6).
To use this to your advantage:
- Update existing articles quarterly with new stats, examples, and insights.
- Add recent trends or revised sections rather than republishing entirely.
- Track your most linked and cited pages and keep them fresh.
Don’t over-optimize your URLs and titles
For this part of the analysis, we checked whether the keyword’s similarity to the page’s target topic mattered. And our analysis shows that it mostly didn’t.
The effect was so tiny that it confirms what many already suspect: overoptimizing your content with keywords doesn’t help AI models understand it any better.
For URLs, our analysis shows a fairly linear pattern:
- Pages with low semantic relevance (0.00–0.57) average 6.4 citations,
- mid-range relevance (0.58–0.76) sees 3.4–4.5,
- and the highest relevance (0.84–1.00) drops to 2.7.
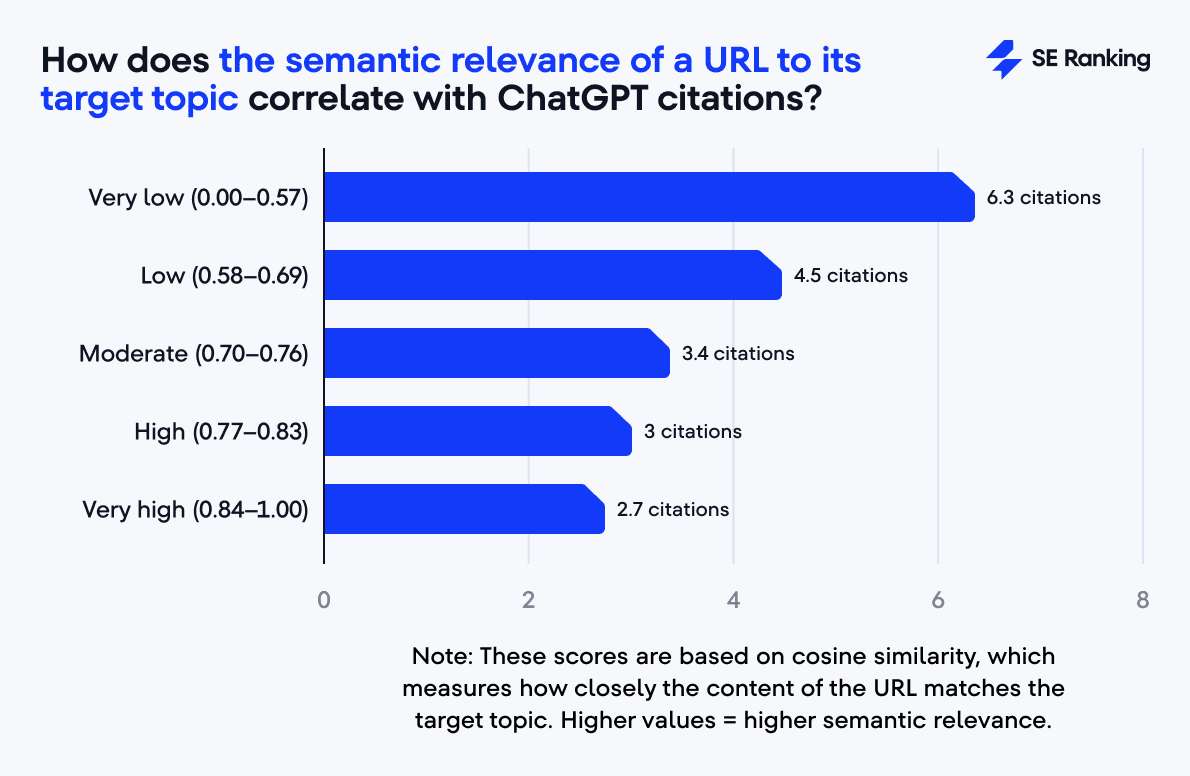
This shows that ChatGPT prefers URLs that clearly describe the overall topic rather than those strictly optimized for a single keyword.
When it comes to titles, the overall picture is pretty similar. Titles with low semantic relevance (0.00–0.59) average 5.9 citations, while those with the highest (0.84–1.00) get around 2.8. This is over two times the difference.
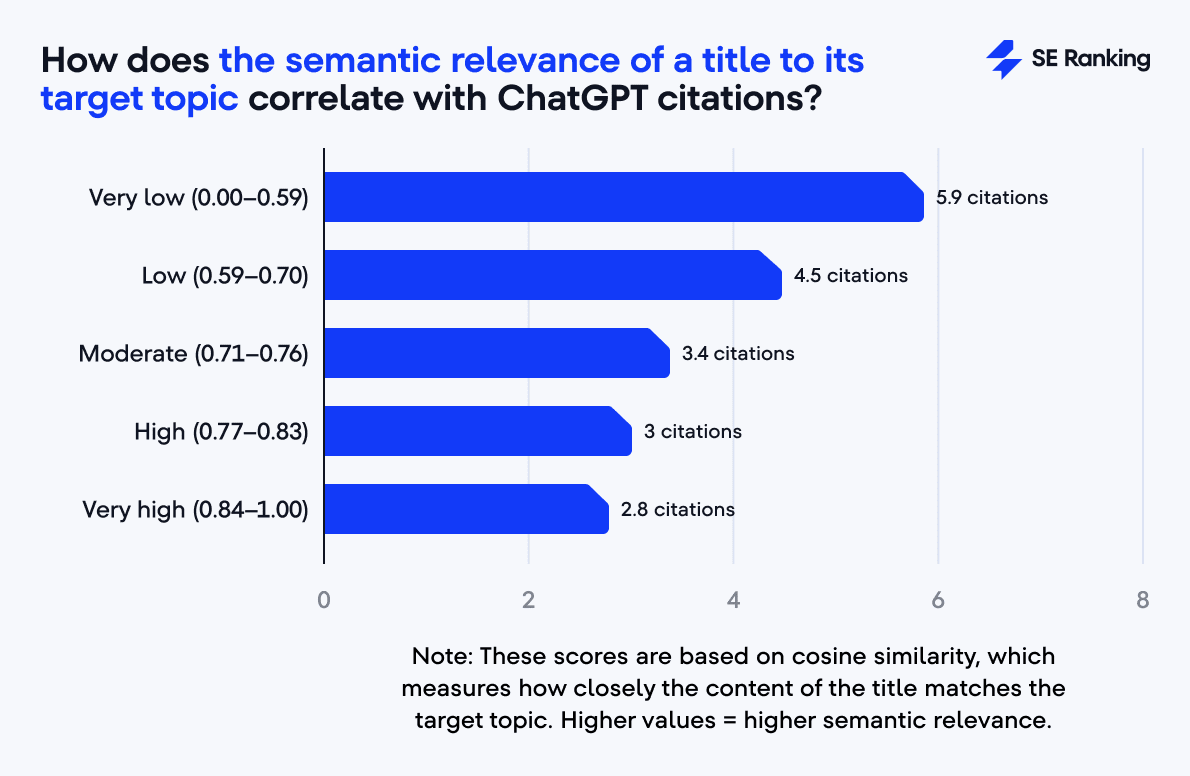
All in all, focusing on clarity and relevance (rather than cramming in keywords) makes your content easier for AI to understand and trust.
Optimize Core Web Vitals: INP, FCP, LCP, and Speed Index
Loading speed does matter, but it comes with some nuances.
Metrics like First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) show an inverse correlation with citations: the faster, the better, but only up to a point.
- The fastest sites (FCP under 0.4s) average 6.7 citations.
- The slowest (over 1.1s) drop to 2.1 citations.
- However, the mid-range (around 0.65–0.82s) remains stable at 4.2 citations.
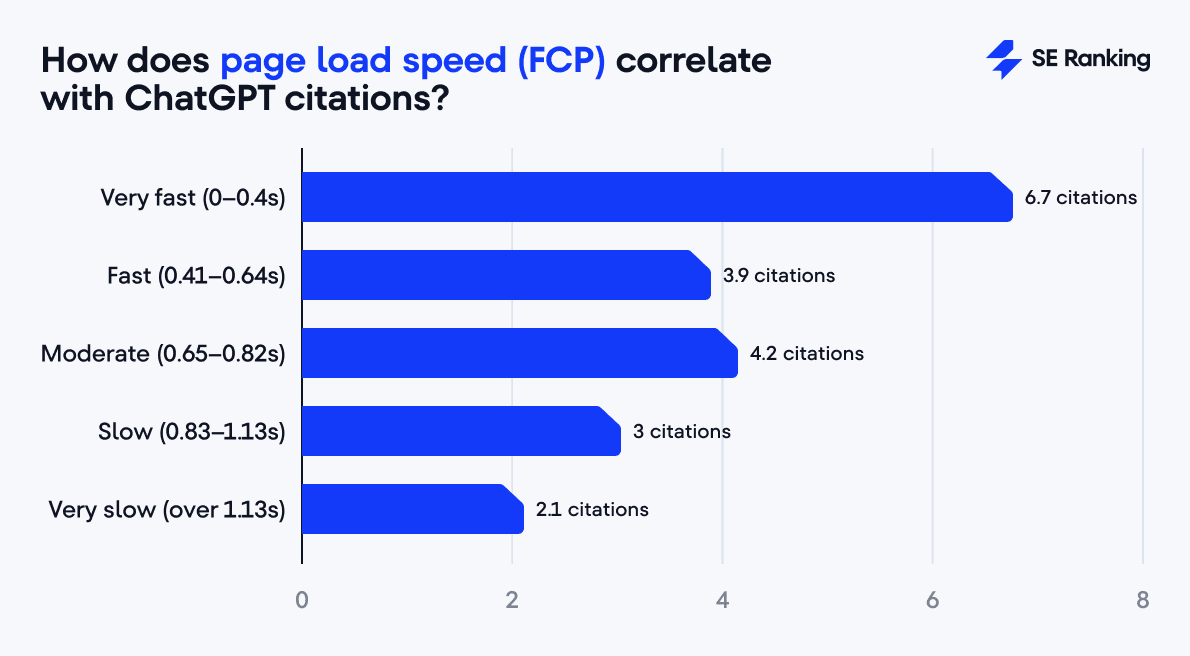
This tells us that you don’t need to chase extreme speed scores. You just need to avoid slowness that signals poor technical quality.
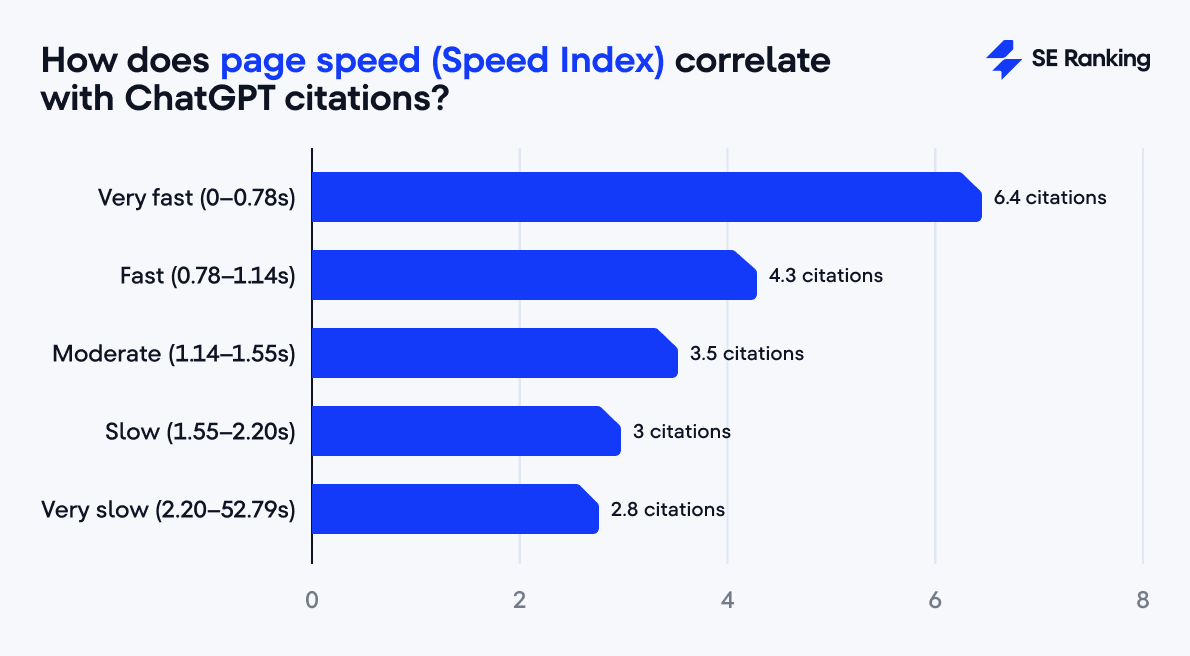
The Speed Index confirms this: sites with indices below 1.14s perform reliably well, but those above 2.2s experience a steep decline.
Interestingly, pages with the best INP scores (under 0.4s) tend to get fewer citations (1.6 on average), while those with moderate INP scores (0.8–1.0s) receive more citations (4.5). This suggests that pages that are too simple or static (even if they perform perfectly) may not be seen by ChatGPT as authoritative or engaging sources.
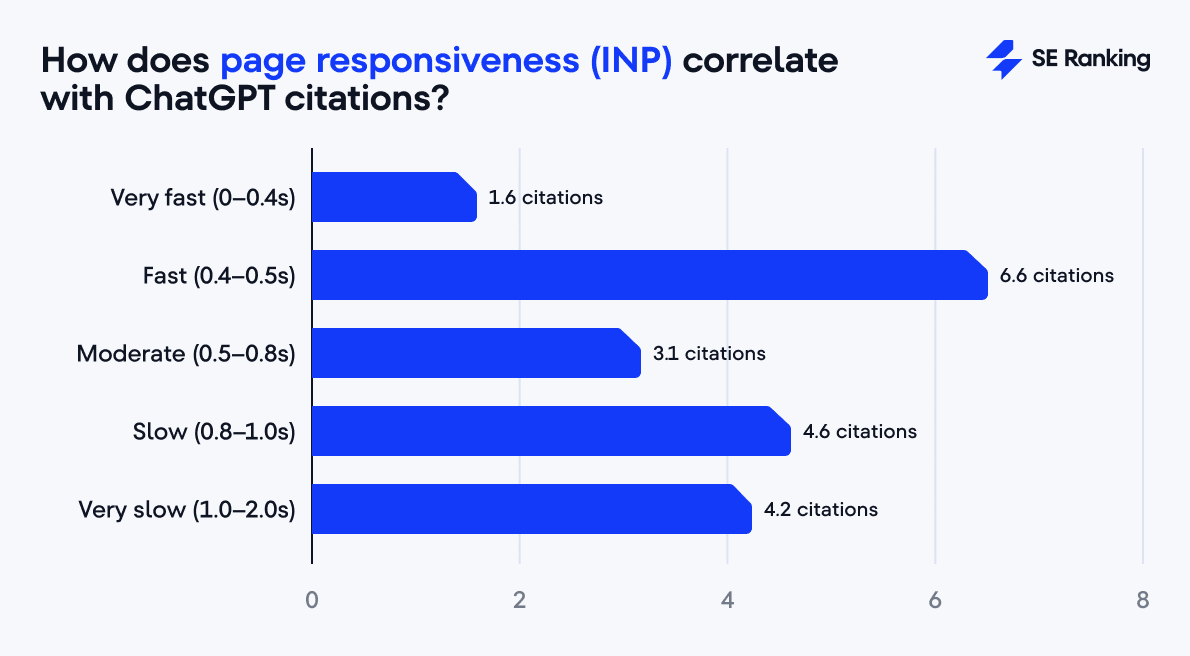
So, if you want to prioritize technical work, start with page responsiveness and load speed. These show much stronger correlations than visual stability.
Build brand visibility on Quora and Reddit
Today, mentions on discussion platforms act as digital word-of-mouth.
- Minimal Quora presence (up to 33 mentions) → 1.7 citations.
- Heavy Quora presence (6.6M mentions) → 7.0 citations.
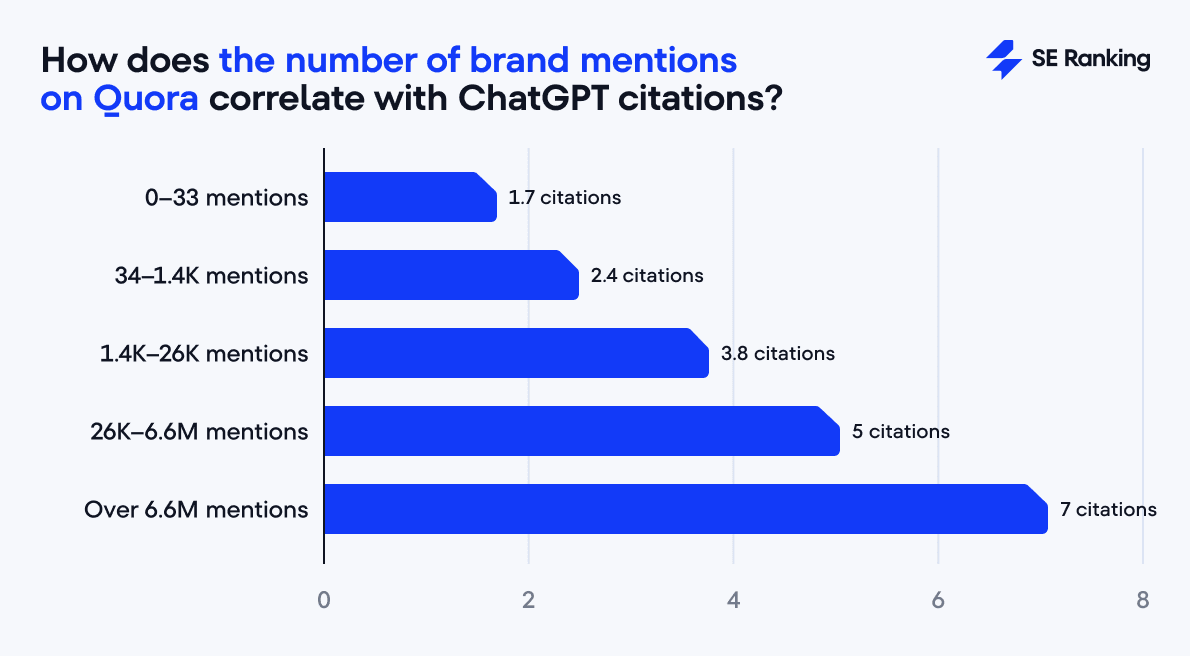
The same applies to Reddit: from 1.8 to 7 citations across the scale.

This is especially encouraging for smaller, less-established websites: engaging on Quora and Reddit gives them a chance to earn trust in the eyes of ChatGPT. In other words, it’s a way to build authority similar to what well-established domains achieve through diverse referring domains and high web traffic.
So, the main practical steps you need to take to optimize for ChatGPT are:
- Participating in relevant discussions, not just promotions.
- Encouraging organic brand mentions through helpful contributions.
- Using these platforms to demonstrate expertise and authority.
Establish a presence on review platforms
For this analysis, we took into account five major review platforms like Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, Sitejabber, and Yelp.
And the trend here is the same as with Reddit and Quora. Domains present on review platforms consistently outperform those without such visibility.
- Domains featured on multiple review platforms earn 4.6–6.3 citations,
- Versus 1.8 for those absent from such platforms.
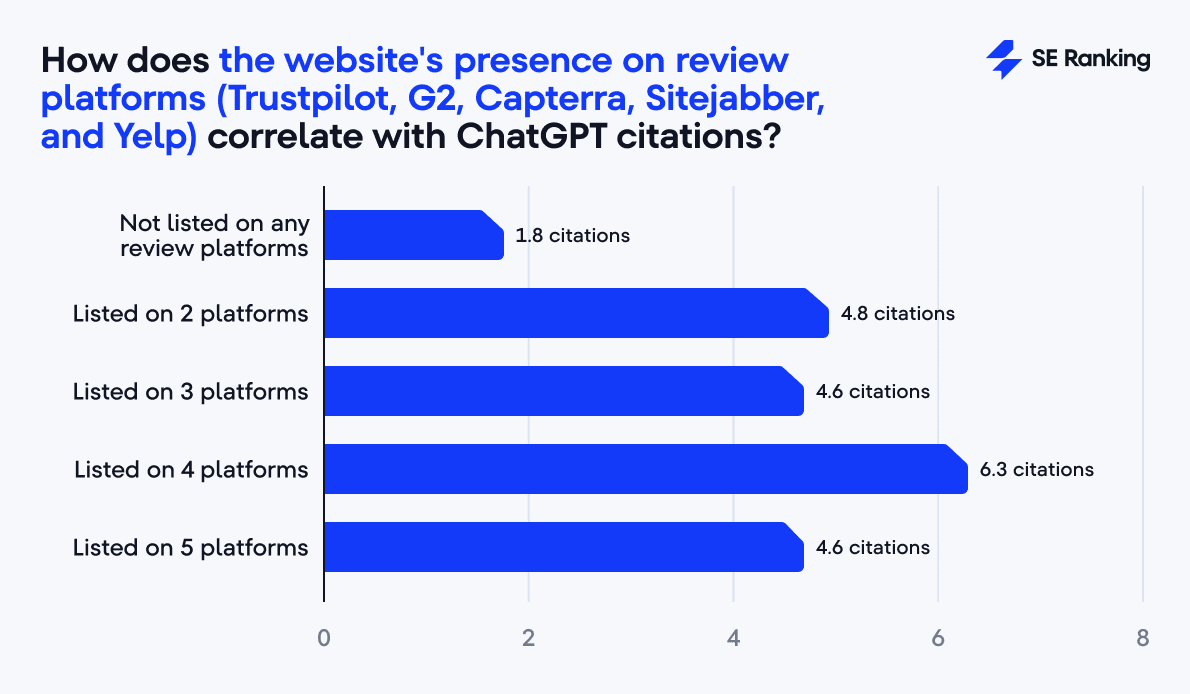
To sum it up, ChatGPT does notice social validation. Even if these platforms aren’t direct SEO factors, they function as trust multipliers.
To use this insight in practice:
- Claim and verify your profiles on major review sites.
- Encourage authentic reviews from real users.
- Monitor and respond to feedback to build trust signals.
Don’t rely solely on LLMs.txt or FAQ schema markup
Many so-called “AI optimization” strategies don’t deliver the expected results. One notable example is LLMs.txt, a proposed file format meant to help AI models understand and cite website content.
Contrary to its promise, its inclusion actually reduced model accuracy during analysis. Removing it improved predictive results, which suggests that ChatGPT currently doesn’t rely on it at all.
At the same time, the use of FAQ schema markup, often promoted as a must-have element for LLM optimization, has actually shown surprisingly weak results. In fact, pages with FAQ schema markup have 3.6 citations, compared to 4.2 without.
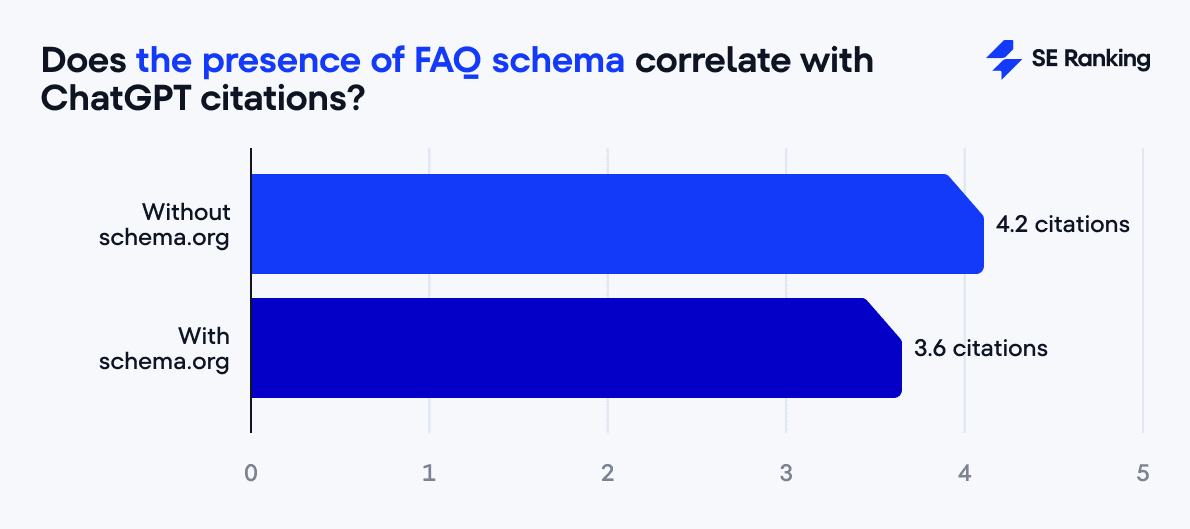
The main insight here is that structured data is a nice-to-have, not a game-changer. LLMs seem to care more about whether the information is structured (via headings) than whether it’s technically marked up.
So, focus on content organization first; schema markup is icing on the cake.
Research methodology
This research examines the factors that influence how LLMs, specifically ChatGPT, cite websites as sources when generating responses. To explore this, we analyzed a large dataset of 129,000 unique domains spanning 216,524 pages, covering 20 different niches to ensure a diverse and representative sample.
We collected data on a wide range of factors for each domain, including:
- Domain authority and trust: number of referring domains, Domain Trust, Page Trust, presence of trusted zones (e.g., .gov, .edu), keyword–domain match, media mentions, authoritativeness of external links.
- Brand visibility and social presence: brand mentions on Reddit and Quora, global and U.S. brand search volume, presence on review platforms and review scores.
- Content quality and semantic relevance: semantic relevance (first 100 characters, first paragraph, first three paragraphs, full content, meta title, meta description, H1, URL, fraggles), fraggles at the beginning, content type, content length, sentence and paragraph length (content and fraggles), section length, position of fraggles, readability (Flesch Reading Ease, Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level), content freshness (first publication and update), inclusion of statistics, quotes, tables, lists, definitions, quick summaries (e.g., Key Takeaways), FAQs/Q&A in content and structured data, question format in title or headings.
- Technical performance: Core Web Vitals (CLS, FCP, LCP, Speed Index, INP, TBT, TTFB, TTI), indexability checks (canonical, noindex), HTTP status codes, structured data, presence of LLMs.txt files.
- SEO visibility and traffic metrics: domain and URL traffic (global and USA), main page traffic (global), SERP positions (Google, Bing), Top-10 presence, average URL position in organic search.
To analyze the relationships between these factors and citation likelihood, we employed an XGBoost regression model. The target variable in our model was the number of citations a domain receives in ChatGPT responses, based on our parsed dataset of 100,000 prompts. This regression approach allowed us to identify which features most strongly predict citation frequency.
To interpret the model and understand how each factor influences the probability of being cited, we applied SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis, a method from game theory that quantifies each feature’s contribution to the model’s predictions. Our report focuses on the top 20 most impactful factors, ranked by their importance in the model.
Disclaimer: While we aim to present the most objective interpretations of the data, alternative perspectives and analyses may also be valid.
Conclusion
Our study shows that flashy “AI hacks” like LLMs.txt barely have any impact..
What really drives ChatGPT citations are the fundamentals: strong backlinks, high domain and page trust, solid web traffic, and content that’s deep, clear, and easy to read. Fast, responsive pages also help, and being active on Quora, Reddit, and major review sites gives your visibility a noticeable lift. Apart from that, updating your content regularly keeps ChatGPT coming back for more.
So, focus on building real authority and delivering value. Small sites can punch above their weight with thorough, well-structured content and social presence, while big sites can maintain their lead by doubling down on trust, backlinks, and consistent content quality.

