How to Properly Create a Custom 404 Page
Visitors usually see a 404 page after clicking on a non-existing URL. It informs users that the page they have been searching for is missing.
It may seem plain and simple, but in fact, plenty of things can go wrong when it comes to crafting a proper 404 page. Let’s find out what mistakes webmasters and developers make when setting up a 404 page.
Get a free copy of our research findings for exclusive insights!
Click the confirmation link we sent to your you email
Why users see a 404 page
A 404 page is the HTTP standard response code that indicates that a user reached a non-existent page because of clicking on a broken link, mistyping a URL, or because the page has been deleted.
In such cases, a user usually sees one of the standard messages:
- 404 Not Found
- 404 Error
- HTTP 404 Not Found
- The page cannot be found
- The requested URL was not found on this server

Yet, there is another option. Instead of the standard messages, a user may see a well-designed page with customized navigation elements. This scenario is much better, and later we’ll explain why. In the meantime, let’s figure out why a user sees a 404 page:
- Broken inbound links. Let’s say that you have a page with subscription plans that looks like this https://seranking.com/subscription.html. If we add one letter “s” to the word “subscription”, the link will lead to a non-existing page https://seranking.com/subscriptions.html.
- Incorrect internal links on your website. For example, a webmaster or a content manager forgot to add “.html” to the URL https://seranking.com/subscription.html. If users follow the link https://seranking.com/subscription, they will see a 404 page.
- User mistakes. A user can type an incorrect URL in the address bar.
- Hidden content. When users try to access hidden pieces of content on a website, they will be redirected to a 404 page as well.
- Deleted pages. Finally, you could have deleted a page from your site and someone would try to access it from saved bookmarks or by following a link on another website.
Although there is technically nothing wrong with having 404 pages on a website, webmasters should keep tabs on them to make sure all the pages that were removed were deleted on purpose. It’s essential to regularly do website audit to identify all the 404 pages and address any possible errors promptly.
Once you know the reason for 404 pages, here’s what you can do about it:
- Minimize the chance of displaying a 404 page to a visitor. Of course, you cannot make users enter a URL address correctly. Yet, you can fix the broken internal links as well as broken inbound links.
- If a user ends up seeing a 404 page, you have to make sure that it is well-thought-out. Thus, you can minimize reputational and usability damages.
How to fix 404 errors – tips for users
If you got a 404 error, here is what you can do:
- Try refreshing the page. Maybe some one-moment glitch occurred and this time the page will load smoothly.
- Check once again if there are any typos in the URL. Are all slashes in place? Has the “l” in “.html” not been occasionally deleted?
- Try loading the page from another device. If any error on the client side (device or browser) took place, the page would still be accessible from another one. If that worked, do not forget to clean the cache on the first device.
- Use the search. Google “site:[domain] [keyword]” of that page. It may happen that the page’s URL was changed without redirecting to the new address. If so, searching should help.
- Head over to the Web Archive. If none of the above solved the issue, there is still a chance to reach the content you need or at least one of its previous versions.
It also will be a plus if you report a problem to a website’s support so they solve it at the first convenience.
What makes a good or bad 404 page?
No matter how hard you try fixing all the errors, users will occasionally bump into your 404 page for one reason or another. That’s why your main goal is to provide a user with a rather pleasant experience.
First, let’s take a look at Google’s recommendations to create the right 404 pages:
- Notify users in a polite form that the requested page is not available.
- Design a 404 page in the same way as other pages of the website. Navigation elements should look the same too.
- Link your 404 page to the most popular articles or comment sections, as well as to the main page.
- Provide users with an opportunity to report broken links.
- Even if your 404 page is useful and looks great, you don’t want it to appear in Google search results. Make sure that the webserver returns an actual 404 HTTP status code when a missing page is requested. It is necessary to prevent such pages to be indexed by search engines.
Let’s take a look at each of these recommendations in more detail. The classic example is a server error page that doesn’t have any design and what’s worse—it doesn’t help visitors navigate to a valid page.
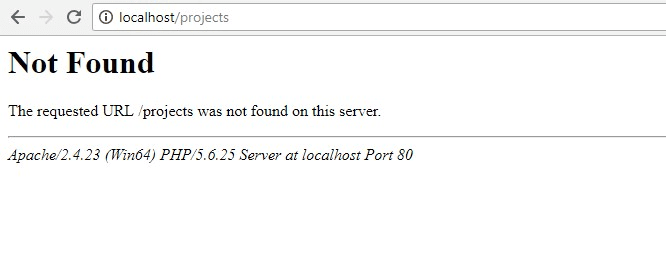
No one is happy to see such pages. For instance, if you’re trying to get information on a product and click a link that you expect will lead you to that information, landing on a 404 page can be frustrating. A 404 page indicates that the content you were looking for wasn’t found. Most users would be annoyed and just leave your website to look somewhere else. In other words, you’ll turn many potential customers off to your brand. Studies also show that plain 404 error pages are definitely not the best solution because users make decisions extremely quickly nowadays.
Finally, this is the exact opposite of what Google recommends. After realizing that the needed page is not found, users are not encouraged to look further into your website. That’s why your main goal is to turn this error into something beautiful.
So, what is an amazing 404 page? Google describes it as follows:
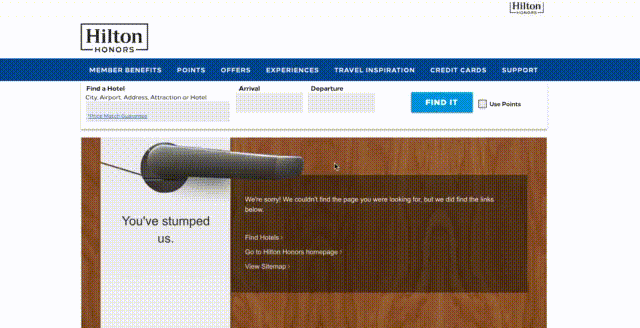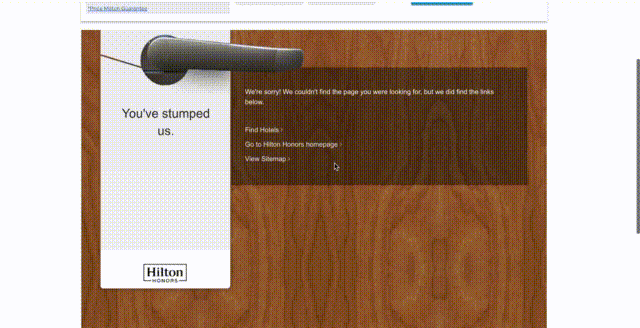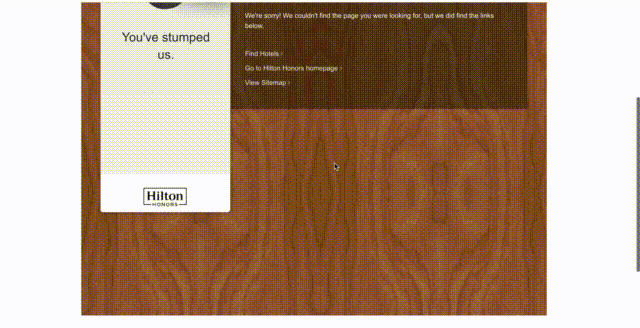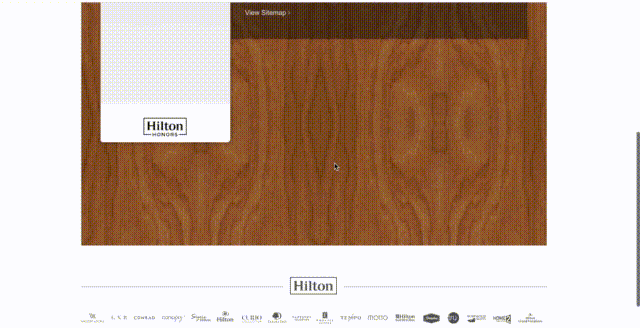
- A 404 page should be similar to other pages of the website, except for the textual content. And that makes sense because the main goal of this page is to inform users that even when the page is missing, they are still on the same website and everything’s going to be fine. Visitors should see the familiar colors, logo, menu, and navigation elements.
- Add a navigation block with links to your best-selling or the most popular categories to make a user stay on the website.

- Feature a search bar. There is a chance that visitors will use it, enter a more relevant request, and find exactly what they need.
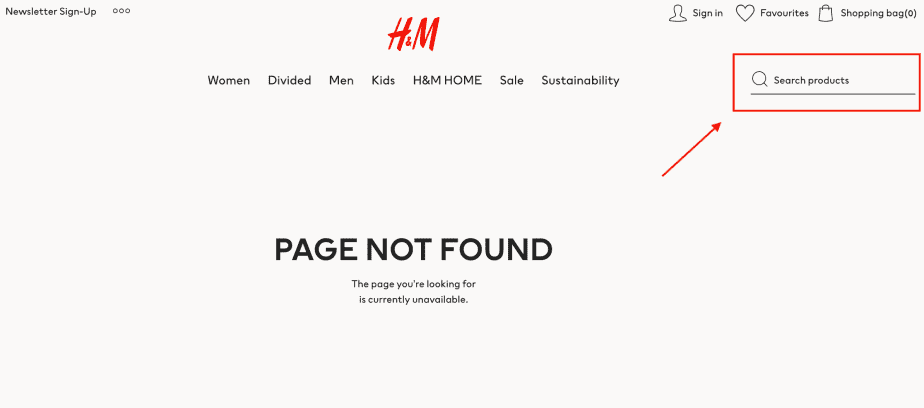
- Add a contact form to allow users to notify you about the problem and report a broken link. This way, you can effectively communicate with users, improve the quality of your website, and even find hidden errors.
- Get rid of the scroll bar. It is important to fit the webpage exactly as the screen size without scrolling.
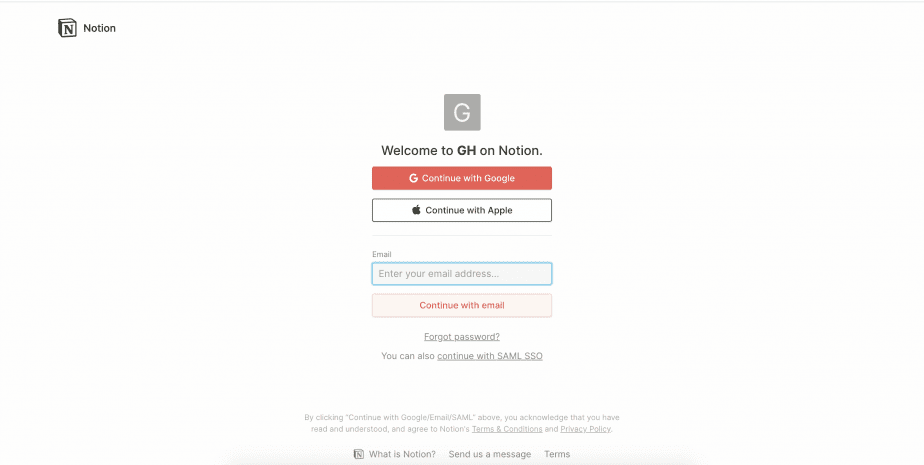
- If a 404 page shows up because of an authorization request, you should provide the login form on the page.
Yet, there is something more. By creating a brilliant 404 page, you can turn the situation to your advantage and become viral—people might share your masterpiece and forget about all negative emotions associated with non-existent pages. You can find examples of great themed pages here or just search for “best 404 pages.”
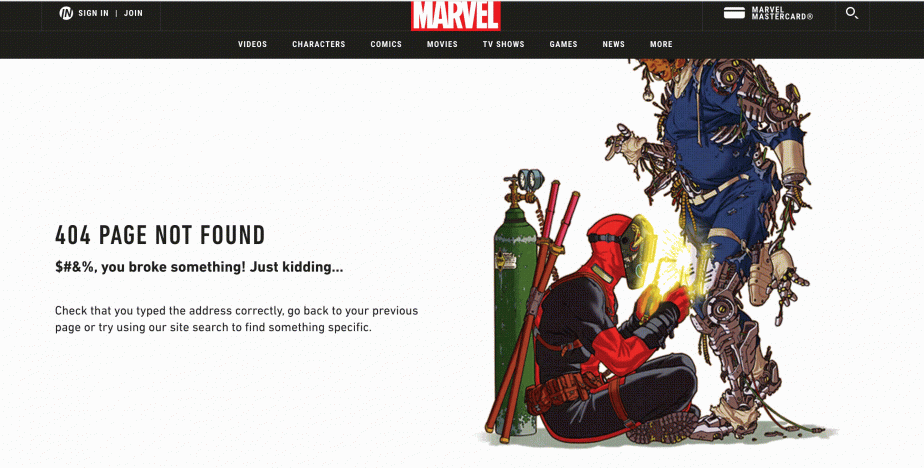
These guys really did a great job as this is something people want to share on social networks.
Don’ts for 404 pages
Poor information on 404 is not the only problem with error pages. There are a few other common mistakes to avoid.
Redirect to the main page
A 404 page is still a 404 page, so you should not set up a redirect from this page. Your only viable option is to paste links to the main page (and other relevant pages) so that users can click on them and continue their journey. The web crawler should understand that the page is not found (in case of 404 status code) or deleted (in case of 410 status code).
Thus, you shouldn’t redirect users to an irrelevant page, such as the homepage. John Mueller, the search advocate at Google, stated the same in one of his tweets:
You may still find WordPress plugins that redirect non-existent pages to the main page, but we strongly advise against using them.
There is only one situation in which these redirects are reasonable, which is when the redirects are to pages that meet the user’s similar search intent and solve the user’s similar problem.
Create a custom 404 page
We have figured out what the perfect error page should look like. Now, let’s see how to add a 404 page to website:
- Once your page is done, add it to the root directory of your website (or update to a new version if there was one). For example, it may be “404.html” or “404.php”.
- While in the root directory, open the .htaccess file (or create one if missing).
- In the .htaccess file, add the record ‘ErrorDocument 404 /404.html’.
This is the basic flow. However, some CMS (content management systems) may generate a 404 page automatically or provide a user-friendly way to edit it. Also, there are plenty of plugins (like the 404 page for WordPress) for popular CMSs that allow you easily create, manage and set redirects for 404 not found errors.
Other HTTP status codes for error pages
According to Google Search Central, there is only one HTTP response status code for a non-existent page, and this code is 404.
But among other 4xx errors, there are 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, 403 Forbidden, 408 Request Timeout and 410 Gone.
Another story is that very often, webmasters intentionally make a custom 404 page send a 200 status code when it should return 404.
In that case, 200 status code indicates that the request has succeeded, but there is no result. That’s why serving up a 200 status code on the not found page to crawlers is not a good idea and can eventually lead to negative consequences:
- 200 status code allows robots to scan and index the page if there are no other limitations;
- The page is not tagged as non-existent and thus is not blocked from crawling. This can cause soft-404 errors.
That’s why you need to monitor servers’ response codes. You can do it with the help of the SE Ranking tool for SEO website audit.
In the “Page Analysis” section, you can see how many 404 pages are on your website. In the “Crawled Pages” section, you can filter the needed pages by HTTP response status codes.
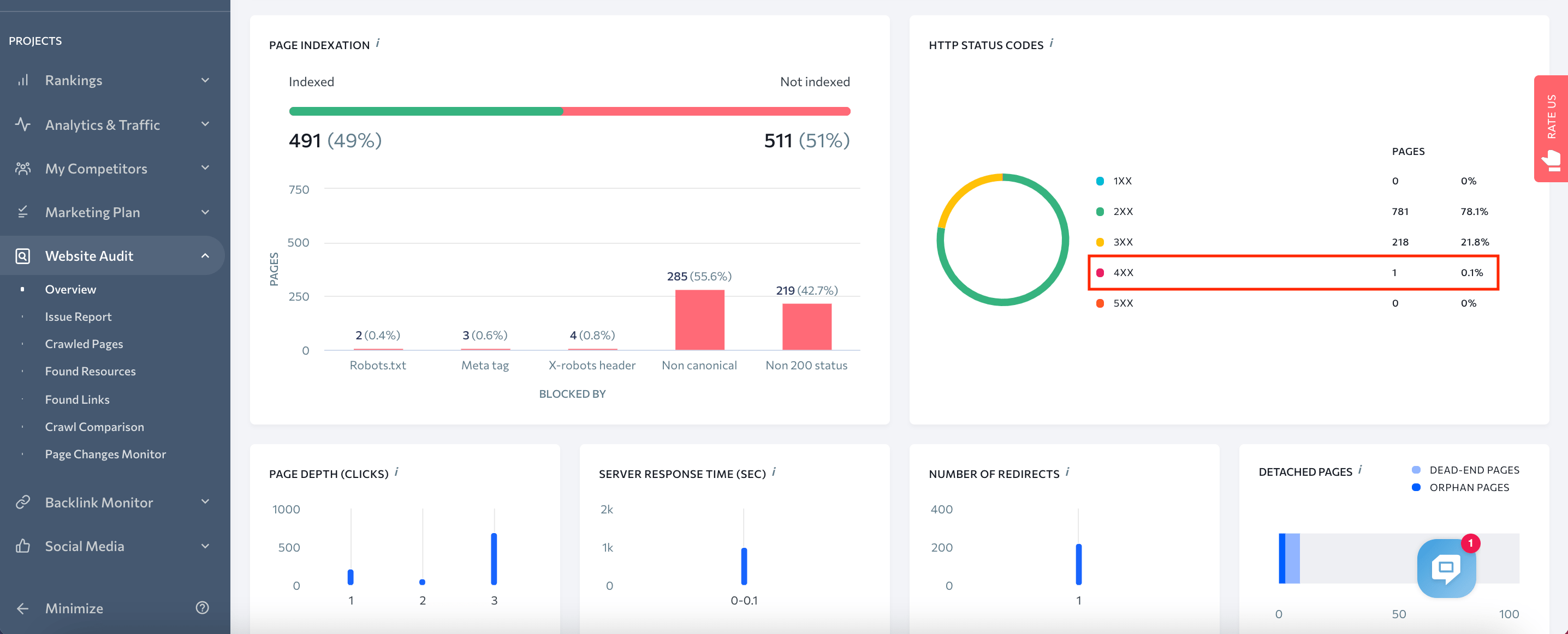
By properly handling error page status codes, you can help your website improve rankings. Check if your site positions improved with SE Ranking’s search rankings checker.
HTTP status codes key takeaways:
- After finding a 404 error, a web crawler will continue visiting the page for a while. It assumes that the error response has been accidentally displayed and the page will be back. Eventually, a bot will understand that the page does not exist and remove it from the index.
- Pages can be deleted faster if a 410 (Gone) status code is used. However, this is usually not a big deal for webmasters, so they tend to use a 404 code.
- The 200 status code shows that the request has succeeded and the page exists.
- When a browser displays a 200 message when technically the page doesn’t exist, the page can be flagged as a Soft 404. You can read more about Soft 404 on Google Search Central. Here, John Mueller also explains why pages may become Soft 404s.
- The 301 (Moved Permanently) code shows that the non-existing URL has been redirected to a new permanent URL.
So, let’s sum it up. What should you do to avoid problems with 404 pages? Just create an amazing 404 page that will deliver the 404 response code and provide users with all necessary options to keep them on-site.
404 page FAQ
In this FAQ section, we’ve collected and answered some of the most commonly asked questions about 404 error pages. If you still have unanswered questions after reading this article, you will find further explanations and solutions here.
Why should I create a custom 404 page?
There are several reasons why creating a custom 404 page can benefit your website. It is a great way to:
- Improve the UX. It provides helpful information to visitors who may have landed on an error page. This includes links to other pages on your site, a search bar, or a message explaining what may have gone wrong and how visitors can find what they’re looking for.
- Build brand identity. Creating a 404 page that showcases your unique style and personality helps set your site apart from others and creates a memorable experience for visitors.
- Reduce bounce rates. Visitors may be more likely to stay on your site and explore other pages if they find the error page engaging and informative.
Are 404 pages on my site bad for SEO?
Having 404 error pages on your site isn’t inherently bad for its SEO. Google Search Console Help notes that 404 errors won’t affect your website’s search performance, so you can safely live with them as long as you’re sure that all URLs returning 404 responses don’t exist.
But if this isn’t the case or you aren’t handling them properly, 404 pages can certainly do harm to your website. You want to be 100% certain that the page with a 404 code isn’t an important page on your site, (i.e., one that drives traffic to your website, converts visitors, or describes your brand). In addition, if many pages on your site return a 404 error, search engines might also think that your site is unreliable or poorly maintained, ultimately harming your search rankings.
How to find 404 pages
You can use different methods to find 404 pages on your website. You can use Google Search Console if your website is connected to it. If you haven’t connected your website to GSC, consider checking out our guide on how to set up GSC. Once you’ve connected your site, go to the Indexing tab and choose the Pages report. In the table, click Not found (404) as the reason why your pages aren’t indexed, and a list of 404 pages on your website will appear.
You can also use site crawlers like SE Ranking’s Website Audit to identify 404 pages. Once you create a project and run an audit, the Issue Report will display problems related to the HTTP status codes on your website. The Crawled Pages report under the Website Audit tool allows you to filter out all 404 pages for further analysis.
Can soft 404 pages harm my website’s SEO?
Yes, soft 404 pages can potentially harm your website’s SEO because they are confusing to both search engine bots and users. Search engine bots will mistakenly assume that the page is valuable and relevant and crawl the page because soft 404s always return a “200 OK” status code. Since the page doesn’t actually exist or doesn’t have any content, it doesn’t provide any relevance to the user.
Returning a “200 OK” status code for a missing or empty page is considered bad practice and offers poor user experience, resulting in lower rankings.
How to create custom 404 pages that benefit UX
Crafting a well-designed 404 page contributes to providing visitors with a better site experience. Do it right by following these tips:
- Explain to the user what happened and what they can do next.
- Make a 404-page design consistent with the rest of your website.
- Include links to popular pages, categories, or recent posts to help the user find what they’re looking for.
- Add humor, images, or other engaging elements to the 404 page to make it more interesting and memorable.
- Test your 404 page to ensure it’s working as intended. Use analytics to monitor how users interact with it.
What’s next?
There are lots of other page types that commonly get dismissed but affect your website’s UX and SEO. Here are some more resources to get you started so you can make sure every page on your website delights your users:
- The most common HTTP status codes manual and how to handle them
- The complete SEO guide to redirects
- 5 essential tips for creating a high-converting landing page
Have a good and helpful read!

